Java PipedWriter klase
The PipedWriter klase Java valodā ļauj diviem pavedieniem sazināties vienam ar otru, nododot datus caur cauruli. Šī klase ir noderīga, ja vēlamies, lai viena programmas daļa nosūtītu datus citai daļai, nesaglabājot tos atmiņā.
PipedWriter klases iezīmes:
- Tas ļauj ierakstīt datus caurulē.
- Tas izmanto buferi, lai īslaicīgi uzglabātu datus pirms to nosūtīšanas uz PipedReader.
- Tas darbojas ar PipedReader, lai nodrošinātu drošu datu pārsūtīšanu starp pavedieniem.
- Ja caurule saplīst, tiek parādīta kļūda.
PipedWriter deklarācija Java valodā
PipedWriter klases deklarācija ir:
publiskā klase PipedWriter paplašina Writer
Visas ieviestās saskarnes:
- Aizverams: Šo saskarni izmanto klases, kas apstrādā resursus.
- Izskalojams: Šī saskarne tiek izmantota, lai izskalotu datus līdz galamērķim.
- Pievienojams: Šī saskarne tiek izmantota, lai pievienotu datus esošai straumei.
- Automātiski aizverams: Šī saskarne ļauj automātiski aizvērt resursus.
Konstruktori PipedWriter klasē
Šī klase sastāv no diviem konstruktoriem, ar kuru palīdzību mēs varam dažādos veidos izveidot šīs klases objektus. Šajā klasē ir pieejami šādi konstruktori:
1. PipedWriter(): Šis konstruktors tiek izmantots, lai izveidotu PipedWriter, kas vēl nav savienots ar neko.
Sintakse:
PipedWriter()
Piemērs:
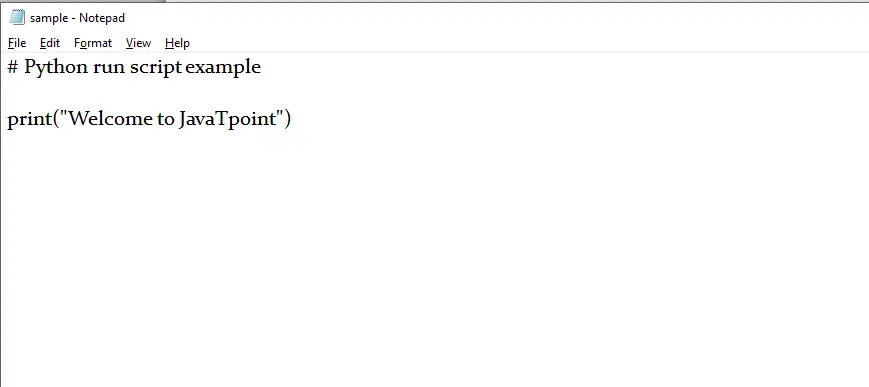
Java // Demonstrating the working // of PipedWriter() import java.io.* ; class Geeks { public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create PipedWriter and PipedReader PipedWriter w = new PipedWriter (); PipedReader r = new PipedReader (); try { // Connect the PipedWriter to the PipedReader w . connect ( r ); // Create a thread to write data into the pipe Thread writerThread = new Thread ( new Runnable () { public void run () { try { w . write ( 'Hello from PipedWriter!' ); w . close (); } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } } }); // Create a thread to read data from the pipe Thread readerThread = new Thread ( new Runnable () { public void run () { try { int data ; while (( data = r . read ()) != - 1 ) { System . out . print (( char ) data ); } r . close (); } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } } }); // Start both threads writerThread . start (); readerThread . start (); // Wait for both threads to finish writerThread . join (); readerThread . join (); } catch ( IOException | InterruptedException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } } }
Izvade
Hello from PipedWriter!
2. PipedWriter (PipedReader inStream): Šis konstruktors, ko mēs izmantojām, izveido PipedWriter un savieno to ar PipedReader.
Sintakse:
PipedWriter (PipedReader snk)
Piemērs:
Java // Demonstrating the working // PipedWriter(PipedReader snk) import java.io.* ; public class Geeks { public static void main ( String [] args ) { try { // Create a PipedReader and a PipedWriter PipedReader r = new PipedReader (); PipedWriter w = new PipedWriter ( r ); // Create a thread to write data to the PipedWriter Thread writerThread = new Thread (() -> { try { w . write ( 'Hello PipedWriter' ); w . close (); } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } }); // Create a thread to read data from the PipedReader Thread readerThread = new Thread (() -> { try { int data ; while (( data = r . read ()) != - 1 ) { System . out . print (( char ) data ); } } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } }); // Start both threads writerThread . start (); readerThread . start (); // Wait for both threads to finish writerThread . join (); readerThread . join (); } catch ( IOException | InterruptedException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } } }
Izvade
Hello PipedWriter
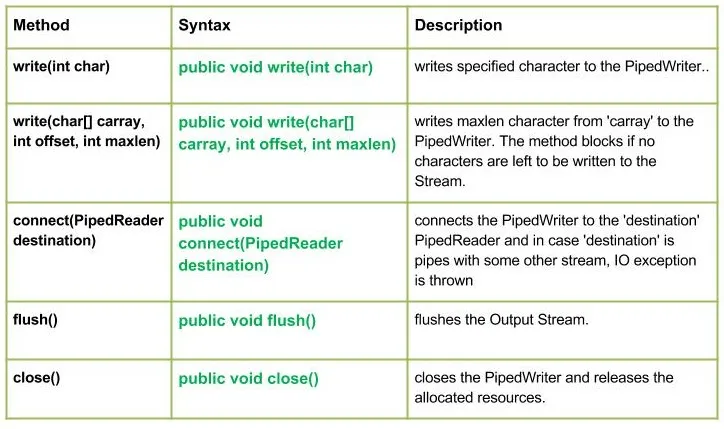
Java PipedWriter metodes
Zemāk esošajā attēlā ir parādītas PipedWriter klases metodes.

Tagad mēs detalizēti apspriedīsim katru metodi pa vienam:
1. rakstiet (int char): Šo metodi izmanto, lai caurulē ierakstītu vienu rakstzīmi.
Sintakse:
publisks nederīgs rakstīšana (int char)
- Parametrs: Šī metode ņem vienu parametru, kas apzīmē rakstāmo rakstzīmi.
- Izņēmums: Šī metode atgriež IOException, ja rodas problēma ar I/O darbību.
2. write(char[] carray int offset int maxlen): Šo metodi izmanto, lai rakstītu rakstzīmes no masīva uz cauruli.
Sintakse:
public void write(char[] carray int offset int maxlen)
- Parametrs: Šī metode ietver trīs tālāk norādītos parametrus:
- carray: Tas ir rakstzīmju masīvs, kas satur datus
- nobīde: Tā ir pozīcija masīvā, kur sākt rakstīt veidlapu
- Maxlen: Tas ir maksimālais rakstāmo rakstzīmju skaits.
- Izņēmums: Šī metode atgriež IOException, ja rodas problēma ar I/O darbību.
3. savienojums (PipedReader galamērķis): Šo metodi izmanto, lai savienotu PipedWriter ar PipedReader.
Sintakse:
publiskais savienojums (PipedReader galamērķis)
- Parametrs: Šī metode izmanto vienu parametru galamērķi, tas ir PipedReader, ar kuru PipedWriter savienosies datu pārsūtīšanai.
- Izņēmums: Šī metode rada IOException, ja savienojuma laikā rodas kļūda.
4. flush(): Šo metodi izmanto, lai izskalotu datus caurulē.
Sintakse:
public void flush()
- Parametrs: Šī metode neņem nekādus parametrus.
- Izņēmums: Šī metode rada IOException, ja datu skalošanas laikā rodas kļūda.
5. aizvērt(): Šo metodi izmanto, lai aizvērtu PipedWriter.
Sinatss:
publisks tukšums aizvērt ()
- Parametrs: Šī metode neņem nekādus parametrus.
- Izņēmums: Šī metode rada IOException, ja rodas problēma ar rakstītāja aizvēršanu.
Tagad mēs apspriedīsim, kā mēs varam izmantot PipedWriter klasi, lai rakstītu datus un lasītu tos, izmantojot pievienoto PipedReader.
Piemērs:
Java // Demonstrating how to use PipedReader // and PipedWriter to transferr an array // of characters between two threads import java.io.* ; public class Geeks { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { PipedReader r = new PipedReader (); PipedWriter w = new PipedWriter (); r . connect ( w ); // Must connect before use // Writing a char array char [] c = { 'J' 'A' 'V' 'A' }; w . write ( c 0 4 ); // Reading blocks if no data is written yet System . out . print ( 'Output from the pipe:' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i ++ ) { System . out . print ( ' ' + ( char ) r . read ()); } w . close (); r . close (); } }
Izvade
Output from the pipe: J A V A
Java programma, kas ilustrē PipedWriter klases metožu darbību
Tagad mēs rakstīsim dažas rakstzīmes, izskalosim izvadi un aizvērsim rakstītāju.
Piemērs:
Java // Java program illustrating the working of PipedWriter // write() connect // close() flush() import java.io.* ; public class Geeks { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { PipedReader r = new PipedReader (); PipedWriter w = new PipedWriter (); try { // Use of connect(): Connecting the writer to the reader r . connect ( w ); // Use of write(int byte): Writing characters to the pipe w . write ( 71 ); w . write ( 69 ); w . write ( 69 ); w . write ( 75 ); w . write ( 83 ); // Use of flush() method: Flushing the output to // make sure all data is written w . flush (); System . out . println ( 'Output after flush():' ); // Reading from the pipe for ( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++ ) { System . out . print ( ' ' + ( char ) r . read ()); } // Use of close() method: Closing the writer System . out . println ( 'nClosing the Writer stream' ); w . close (); } catch ( IOException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } } }
Izvade
Output after flush(): G E E K S Closing the Writer streamIzveidojiet viktorīnu