Algorithme de suppression inversée pour l'arbre couvrant minimum
 #practiceLinkDiv { display : aucun !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display : aucun !important; } L'algorithme de suppression inversée est étroitement lié à L'algorithme de Kruskal . Dans l'algorithme de Kruskal, ce que nous faisons est de : Trier les arêtes par ordre croissant de leurs poids. Après le tri, nous sélectionnons les bords un par un par ordre croissant. Nous incluons l'arête actuelle sélectionnée si, en l'incluant dans l'arbre couvrant, nous ne formons aucun cycle jusqu'à ce qu'il y ait des arêtes V-1 dans l'arbre couvrant où V = nombre de sommets.
Dans l'algorithme Reverse Supprimer, nous trions toutes les arêtes dans décroissant ordre de leurs poids. Après le tri, nous sélectionnons les bords un par un par ordre décroissant. Nous inclure le bord sélectionné actuel si l'exclusion du bord actuel entraîne une déconnexion dans le graphique actuel . L'idée principale est de supprimer le bord si sa suppression n'entraîne pas la déconnexion du graphique.
L'algorithme :
- Triez toutes les arêtes du graphique par ordre non croissant de poids des arêtes.
- Initialisez MST en tant que graphique d'origine et supprimez les arêtes supplémentaires à l'aide de l'étape 3.
- Choisissez le bord le plus lourd parmi les bords restants et vérifiez si la suppression du bord déconnecte le graphique ou non .
En cas de déconnexion, nous ne supprimons pas le bord.
Sinon, nous supprimons le bord et continuons.
Illustration:
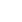
Comprenons avec l'exemple suivant :
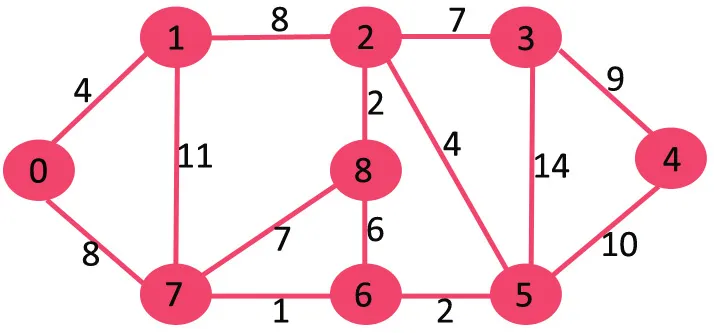
Si nous supprimons le bord de poids le plus élevé du poids 14, le graphique ne se déconnecte pas, nous le supprimons donc.
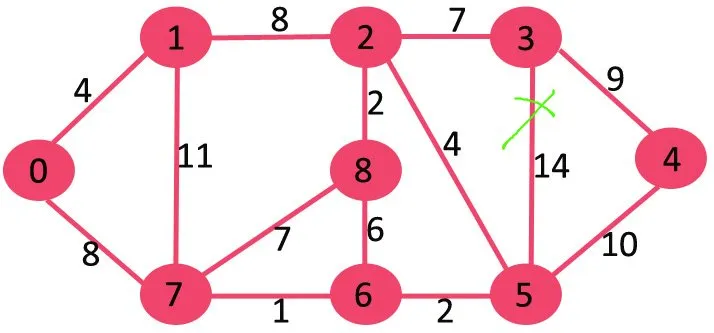
Ensuite, nous supprimons 11 car sa suppression ne déconnecte pas le graphique.
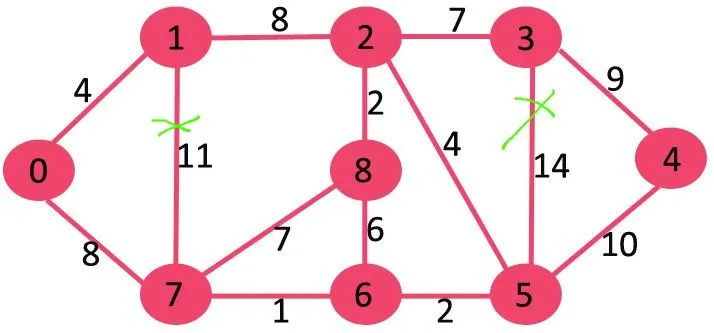
Ensuite, nous supprimons 10 car sa suppression ne déconnecte pas le graphique.

Vient ensuite 9. Nous ne pouvons pas supprimer 9 car sa suppression entraîne une déconnexion.

Nous continuons ainsi et les arêtes suivantes restent dans le MST final.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
Note : Dans le cas d’arêtes de même poids, nous pouvons choisir n’importe quelle arête de même poids.
Pratique recommandée Algorithme de suppression inversée pour l'arbre couvrant minimum Essayez-le !Mise en œuvre:
C++Java// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #includeusing namespace std ; // Creating shortcut for an integer pair typedef pair < int int > iPair ; // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { int V ; // No. of vertices list < int > * adj ; vector < pair < int iPair > > edges ; void DFS ( int v bool visited []); public : Graph ( int V ); // Constructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge ( int u int v int w ); // Returns true if graph is connected bool isConnected (); void reverseDeleteMST (); }; Graph :: Graph ( int V ) { this -> V = V ; adj = new list < int > [ V ]; } void Graph :: addEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ]. push_back ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ]. push_back ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . push_back ({ w { u v }}); } void Graph :: DFS ( int v bool visited []) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex list < int >:: iterator i ; for ( i = adj [ v ]. begin (); i != adj [ v ]. end (); ++ i ) if ( ! visited [ * i ]) DFS ( * i visited ); } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false bool Graph :: isConnected () { bool visited [ V ]; memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not void Graph :: reverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost sort ( edges . begin () edges . end ()); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST cout < < 'Edges in MST n ' ; // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . size () -1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges [ i ]. second . first ; int v = edges [ i ]. second . second ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ]. remove ( v ); adj [ v ]. remove ( u ); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( isConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ]. push_back ( v ); adj [ v ]. push_back ( u ); // This edge is part of MST cout < < '(' < < u < < ' ' < < v < < ') n ' ; mst_wt += edges [ i ]. first ; } } cout < < 'Total weight of MST is ' < < mst_wt ; } // Driver code int main () { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; Graph g ( V ); // making above shown graph g . addEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . addEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . addEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . addEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . addEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . addEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . addEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . addEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . addEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . addEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . addEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . addEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . addEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . addEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . reverseDeleteMST (); return 0 ; } Python3// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.* ; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable < Edge > { int u v w ; Edge ( int u int v int w ) { this . u = u ; this . w = w ; this . v = v ; } public int compareTo ( Edge other ) { return ( this . w - other . w ); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V ; // No. of vertices private List < Integer >[] adj ; private List < Edge > edges ; @SuppressWarnings ({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG ( int v ) // Constructor { V = v ; adj = new ArrayList [ v ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < v ; i ++ ) adj [ i ] = new ArrayList < Integer > (); edges = new ArrayList < Edge > (); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ] . add ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ] . add ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . add ( new Edge ( u v w )); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS ( int v boolean [] visited ) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for ( int i : adj [ v ] ) { if ( ! visited [ i ] ) DFS ( i visited ); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected () { boolean [] visited = new boolean [ V ] ; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) { if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; } return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections . sort ( edges ); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST System . out . println ( 'Edges in MST' ); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . size () - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges . get ( i ). u ; int v = edges . get ( i ). v ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ] . remove ( adj [ u ] . indexOf ( v )); adj [ v ] . remove ( adj [ v ] . indexOf ( u )); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( IsConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ] . add ( v ); adj [ v ] . add ( u ); // This edge is part of MST System . out . println ( '(' + u + ' ' + v + ')' ); mst_wt += edges . get ( i ). w ; } } System . out . println ( 'Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; GFG g = new GFG ( V ); // making above shown graph g . AddEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . AddEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . AddEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . AddEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . ReverseDeleteMST (); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_DeyC## Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph : def __init__ ( self v ): # No. of vertices self . v = v self . adj = [ 0 ] * v self . edges = [] for i in range ( v ): self . adj [ i ] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge ( self u : int v : int w : int ): self . adj [ u ] . append ( v ) # Add w to v’s list. self . adj [ v ] . append ( u ) # Add w to v’s list. self . edges . append (( w ( u v ))) def dfs ( self v : int visited : list ): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self . adj [ v ]: if not visited [ i ]: self . dfs ( i visited ) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected ( self ): visited = [ False ] * self . v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self . dfs ( 0 visited ) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range ( 1 self . v ): if not visited [ i ]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST ( self ): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self . edges . sort ( key = lambda a : a [ 0 ]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print ( 'Edges in MST' ) # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range ( len ( self . edges ) - 1 - 1 - 1 ): u = self . edges [ i ][ 1 ][ 0 ] v = self . edges [ i ][ 1 ][ 1 ] # Remove edge from undirected graph self . adj [ u ] . remove ( v ) self . adj [ v ] . remove ( u ) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self . connected () == False : self . adj [ u ] . append ( v ) self . adj [ v ] . append ( u ) # This edge is part of MST print ( '( %d %d )' % ( u v )) mst_wt += self . edges [ i ][ 0 ] print ( 'Total weight of MST is' mst_wt ) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph ( V ) # making above shown graph g . addEdge ( 0 1 4 ) g . addEdge ( 0 7 8 ) g . addEdge ( 1 2 8 ) g . addEdge ( 1 7 11 ) g . addEdge ( 2 3 7 ) g . addEdge ( 2 8 2 ) g . addEdge ( 2 5 4 ) g . addEdge ( 3 4 9 ) g . addEdge ( 3 5 14 ) g . addEdge ( 4 5 10 ) g . addEdge ( 5 6 2 ) g . addEdge ( 6 7 1 ) g . addEdge ( 6 8 6 ) g . addEdge ( 7 8 7 ) g . reverseDeleteMST () # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552JavaScript// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable < Edge > { public int u v w ; public Edge ( int u int v int w ) { this . u = u ; this . v = v ; this . w = w ; } public int CompareTo ( Edge other ) { return this . w . CompareTo ( other . w ); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V ; // No. of vertices private List < int > [] adj ; private List < Edge > edges ; public Graph ( int v ) // Constructor { V = v ; adj = new List < int > [ v ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < v ; i ++ ) adj [ i ] = new List < int > (); edges = new List < Edge > (); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ]. Add ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ]. Add ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . Add ( new Edge ( u v w )); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS ( int v bool [] visited ) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach ( int i in adj [ v ]) { if ( ! visited [ i ]) DFS ( i visited ); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected () { bool [] visited = new bool [ V ]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) { if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; } return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges . Sort (); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST Console . WriteLine ( 'Edges in MST' ); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . Count - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges [ i ]. u ; int v = edges [ i ]. v ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ]. Remove ( v ); adj [ v ]. Remove ( u ); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( IsConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ]. Add ( v ); adj [ v ]. Add ( u ); // This edge is part of MST Console . WriteLine ( '({0} {1})' u v ); mst_wt += edges [ i ]. w ; } } Console . WriteLine ( 'Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt ); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main ( string [] args ) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; Graph g = new Graph ( V ); // making above shown graph g . AddEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . AddEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . AddEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . AddEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . ReverseDeleteMST (); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
SortirEdges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37Complexité temporelle : O((E*(V+E)) + E log E) où E est le nombre d’arêtes.
Complexité spatiale : O(V+E) où V est le nombre de sommets et E est le nombre d’arêtes. Nous utilisons une liste de contiguïté pour stocker le graphique, nous avons donc besoin d'un espace proportionnel à O(V+E).
Remarques :
- L'implémentation ci-dessus est une implémentation simple/naïve de l'algorithme Reverse Delete et peut être optimisée pour O(E log V (log log V) 3 ) [Source : Une semaine ]. Mais cette complexité temporelle optimisée est encore inférieure à Prim et Kruskal Algorithmes pour MST.
- L'implémentation ci-dessus modifie le graphique d'origine. Nous pouvons créer une copie du graphique si le graphique original doit être conservé.
Créer un quiz