Algorytm Petersona dla wzajemnego wykluczania | Zestaw 2 (cykle procesora i zabezpieczenie pamięci)
Problem: Biorąc pod uwagę 2 procesy i oraz j, musisz napisać program, który zagwarantuje wzajemne wykluczenie między nimi bez dodatkowego wsparcia sprzętowego.
Marnowanie cykli zegara procesora
Mówiąc laikiem, gdy wątek czekał na swoją kolej, kończył się długą pętlą while, która testowała warunek miliony razy na sekundę, wykonując w ten sposób niepotrzebne obliczenia. Istnieje lepszy sposób na czekanie i jest on znany jako 'dawać' .
Aby zrozumieć, co to robi, musimy głęboko przyjrzeć się działaniu harmonogramu procesów w systemie Linux. Wspomniany tutaj pomysł to uproszczona wersja harmonogramu, a faktyczna implementacja wiąże się z wieloma komplikacjami.
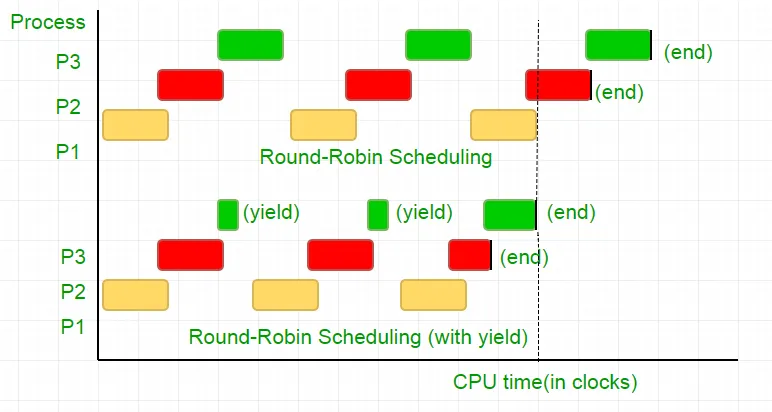
Rozważ następujący przykład
Istnieją trzy procesy P1 P2 i P3. Proces P3 jest taki, że ma pętlę while podobną do tej w naszym kodzie, wykonującą niezbyt przydatne obliczenia i wychodzi z pętli dopiero wtedy, gdy P2 zakończy wykonywanie. Osoba planująca umieszcza je wszystkie w kolejce okrężnej. Powiedzmy teraz, że prędkość zegara procesora wynosi 1000000/s i przydziela on 100 zegarów każdemu procesowi w każdej iteracji. Następnie najpierw zostanie uruchomiony P1 na 100 zegarów (0,0001 sekundy), następnie P2 (0,0001 sekundy), a następnie P3 (0,0001 sekundy), ponieważ nie ma już więcej procesów, cykl ten powtarza się aż do zakończenia P2, a następnie wykonanie P3 i ostatecznie jego zakończenie.
Jest to całkowita strata 100 cykli zegara procesora. Aby tego uniknąć, wspólnie rezygnujemy z wycinka czasu procesora, tj. wydajności, która zasadniczo kończy ten wycinek czasu, a program planujący wybiera następny proces do uruchomienia. Teraz raz testujemy nasz stan i rezygnujemy z procesora. Biorąc pod uwagę, że nasz test zajmuje 25 cykli zegara, oszczędzamy 75% naszych obliczeń w wycinku czasu. Ujmując to graficznie

Biorąc pod uwagę częstotliwość taktowania procesora wynoszącą 1 MHz, jest to duża oszczędność!.
Różne dystrybucje zapewniają różne funkcje umożliwiające osiągnięcie tej funkcjonalności. Linux zapewnia sched_yield() .
void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] = 1 ; turn = 1 - self ; while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Only change is the addition of // sched_yield() call sched_yield (); }
Ogrodzenie pamięci.
Kod z wcześniejszego samouczka mógł działać na większości systemów, ale nie był w 100% poprawny. Logika była doskonała, ale większość nowoczesnych procesorów wykorzystuje optymalizację wydajności, która może skutkować wykonaniem poza kolejnością. Ta zmiana kolejności operacji pamięciowych (ładowania i przechowywania) zwykle pozostaje niezauważona w ramach pojedynczego wątku wykonania, ale może powodować nieprzewidywalne zachowanie w programach współbieżnych.
Rozważmy ten przykład
while ( f == 0 ); // Memory fence required here print x ;
W powyższym przykładzie kompilator uważa te 2 instrukcje za niezależne od siebie i w ten sposób próbuje zwiększyć wydajność kodu poprzez zmianę ich kolejności, co może prowadzić do problemów w przypadku programów współbieżnych. Aby tego uniknąć, umieszczamy barierę pamięci, aby dać kompilatorowi wskazówkę dotyczącą możliwych relacji między instrukcjami przekraczającymi barierę.
A więc kolejność wypowiedzi
flaga[samodzielność] = 1;
tura = 1-ja;
while (sprawdzanie warunku włączenia)
dawać();
musi być dokładnie taki sam, aby zamek działał, w przeciwnym razie nastąpi zakleszczenie.
Aby mieć pewność, że kompilatory dostarczają instrukcje uniemożliwiające porządkowanie instrukcji przez tę barierę. W przypadku gcc jest to __sync_synchronize() .
Zatem zmodyfikowany kod staje się
Pełna implementacja w C:
// Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp // Use below command to compile: // g++ -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include std :: atomic < int > flag [ 2 ]; std :: atomic < int > turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. std :: atomic_thread_fence ( std :: memory_order_seq_cst ); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. std :: this_thread :: yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; std :: cout < < 'Thread Entered: ' < < self < < std :: endl ; lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) std :: thread t1 ( func 0 ); std :: thread t2 ( func 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); std :: cout < < 'Actual Count: ' < < ans < < ' | Expected Count: ' < < MAX * 2 < < std :: endl ; return 0 ; }
C // Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c // Use below command to compile: // gcc -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include 'mythreads.h' int flag [ 2 ]; int turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. __sync_synchronize (); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. sched_yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void * func ( void * s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = ( int * ) s ; printf ( 'Thread Entered: %d n ' self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { pthread_t p1 p2 ; // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) Pthread_create ( & p1 NULL func ( void * ) 0 ); Pthread_create ( & p2 NULL func ( void * ) 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. Pthread_join ( p1 NULL ); Pthread_join ( p2 NULL ); printf ( 'Actual Count: %d | Expected Count:' ' %d n ' ans MAX * 2 ); return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger ; public class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static AtomicInteger [] flag = new AtomicInteger [ 2 ] ; static AtomicInteger turn = new AtomicInteger (); static final int MAX = 1000000000 ; static int ans = 0 ; static void lockInit () { flag [ 0 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 1 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 0 ] . set ( 0 ); flag [ 1 ] . set ( 0 ); turn . set ( 0 ); } static void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 1 ); turn . set ( 1 - self ); // Memory fence to prevent the reordering of instructions beyond this barrier. // In Java volatile variables provide this guarantee implicitly. // No direct equivalent to atomic_thread_fence is needed. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] . get () == 1 && turn . get () == 1 - self ) Thread . yield (); } static void unlock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 0 ); } static void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; System . out . println ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Initialize the lock lockInit (); // Create two threads (both run func) Thread t1 = new Thread (() -> func ( 0 )); Thread t2 = new Thread (() -> func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); try { // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } System . out . println ( 'Actual Count: ' + ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + MAX * 2 ); } }
Python import threading flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 MAX = 10 ** 9 ans = 0 def lock_init (): # This function initializes the lock by resetting the flags and turn. global flag turn flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 def lock ( self ): # This function is executed before entering the critical section. It sets the flag for the current thread and gives the turn to the other thread. global flag turn flag [ self ] = 1 turn = 1 - self while flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 and turn == 1 - self : pass def unlock ( self ): # This function is executed after leaving the critical section. It resets the flag for the current thread. global flag flag [ self ] = 0 def func ( s ): # This function is executed by each thread. It locks the critical section increments the shared variable and then unlocks the critical section. global ans self = s print ( f 'Thread Entered: { self } ' ) lock ( self ) for _ in range ( MAX ): ans += 1 unlock ( self ) def main (): # This is the main function where the threads are created and started. lock_init () t1 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 0 )) t2 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 1 )) t1 . start () t2 . start () t1 . join () t2 . join () print ( f 'Actual Count: { ans } | Expected Count: { MAX * 2 } ' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static flag = [ 0 0 ]; static turn = 0 ; static MAX = 1000000000 ; static ans = 0 ; // Function to acquire the lock static async lock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 1 ; PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn = 1 - self ; // Asynchronous loop with a small delay to yield while ( PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn == 1 - self ) { await new Promise ( resolve => setTimeout ( resolve 0 )); } } // Function to release the lock static unlock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // Function representing the critical section static func ( s ) { let i = 0 ; let self = s ; console . log ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); // Lock the critical section PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . lock ( self ). then (() => { // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX ; i ++ ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans ++ ; } // Release the lock PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . unlock ( self ); }); } // Main function static main () { // Create two threads (both run func) const t1 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 0 )); const t2 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); // Wait for the threads to end. setTimeout (() => { console . log ( 'Actual Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX * 2 ); } 1000 ); // Delay for a while to ensure threads finish } } // Define a simple Thread class for simulation class Thread { constructor ( func ) { this . func = func ; } start () { this . func (); } } // Run the main function PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . main ();
C++ // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include // Function to lock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was locked successfully } // Function to unlock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was unlocked successfully } // Function to create a pthread void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was created successfully } // Function to join a pthread void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was joined successfully } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
C // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert // statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
Python import threading import ctypes # Function to lock a thread lock def Thread_lock ( lock ): lock . acquire () # Acquire the lock # No need for assert in Python acquire will raise an exception if it fails # Function to unlock a thread lock def Thread_unlock ( lock ): lock . release () # Release the lock # No need for assert in Python release will raise an exception if it fails # Function to create a thread def Thread_create ( target args = ()): thread = threading . Thread ( target = target args = args ) thread . start () # Start the thread # No need for assert in Python thread.start() will raise an exception if it fails # Function to join a thread def Thread_join ( thread ): thread . join () # Wait for the thread to finish # No need for assert in Python thread.join() will raise an exception if it fails
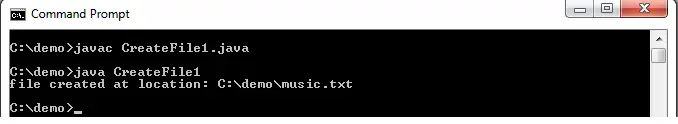
Wyjście:
Thread Entered: 1
Thread Entered: 0
Actual Count: 2000000000 | Expected Count: 2000000000