표현식 트리 평가
간단히 말하면 표현 트리 + - * 및 /와 같은 기본 이진 연산자와 일부 정수로 구성되어 표현식 트리를 평가합니다.
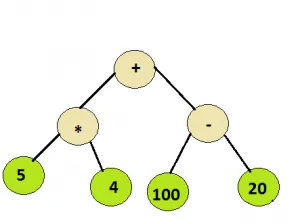
예:
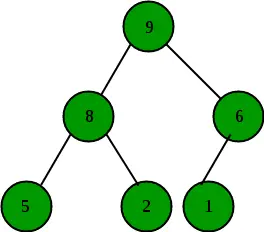
권장 실습 표현식 트리 시도해 보세요!입력: 아래 트리의 루트 노드

산출: 100
입력: 아래 트리의 루트 노드
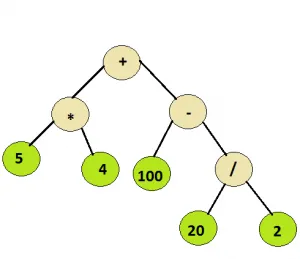
산출: 110
접근하다: 이 문제를 해결하기 위한 접근 방식은 다음 관찰을 기반으로 합니다.
트리의 모든 연산자는 이진이므로 각 노드에는 0개 또는 2개의 자식이 있습니다. 위의 예에서 추론할 수 있듯이 모든 정수 값은 리프 노드에 나타나고 내부 노드는 연산자를 나타냅니다.
그러므로 우리는 할 수 있습니다 이진 트리의 중위순회 계속 진행하면서 표현식을 평가합니다.
구문 트리를 평가하려면 재귀적 접근 방식을 따를 수 있습니다.
연산:
- t를 구문 트리라고 하자
- t가 null이 아닌 경우
- t.info가 피연산자이면
- t.info 반환
- 또 다른
- A = 풀기(t.left)
- B = 풀기(t.right)
- A 연산자 B를 반환합니다. 여기서 연산자는 t에 포함된 정보입니다.
다음은 위의 접근 방식을 구현한 것입니다.
C++ // C++ program to evaluate an expression tree #include using namespace std ; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class node { public : string info ; node * left = NULL * right = NULL ; node ( string x ) { info = x ; } }; // Utility function to return the integer value // of a given string int toInt ( string s ) { int num = 0 ; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate the number // normally if ( s [ 0 ] != '-' ) for ( int i = 0 ; i < s . length (); i ++ ) num = num * 10 + ( int ( s [ i ]) -48 ); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for ( int i = 1 ; i < s . length (); i ++ ) num = num * 10 + ( int ( s [ i ]) -48 ); num = num * -1 ; } return num ; } // This function receives a node of the syntax tree // and recursively evaluates it int eval ( node * root ) { // empty tree if ( ! root ) return 0 ; // leaf node i.e an integer if ( ! root -> left && ! root -> right ) return toInt ( root -> info ); // Evaluate left subtree int l_val = eval ( root -> left ); // Evaluate right subtree int r_val = eval ( root -> right ); // Check which operator to apply if ( root -> info == '+' ) return l_val + r_val ; if ( root -> info == '-' ) return l_val - r_val ; if ( root -> info == '*' ) return l_val * r_val ; return l_val / r_val ; } //driver function to check the above program int main () { // create a syntax tree node * root = new node ( '+' ); root -> left = new node ( '*' ); root -> left -> left = new node ( '5' ); root -> left -> right = new node ( '-4' ); root -> right = new node ( '-' ); root -> right -> left = new node ( '100' ); root -> right -> right = new node ( '20' ); cout < < eval ( root ) < < endl ; delete ( root ); root = new node ( '+' ); root -> left = new node ( '*' ); root -> left -> left = new node ( '5' ); root -> left -> right = new node ( '4' ); root -> right = new node ( '-' ); root -> right -> left = new node ( '100' ); root -> right -> right = new node ( '/' ); root -> right -> right -> left = new node ( '20' ); root -> right -> right -> right = new node ( '2' ); cout < < eval ( root ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to evaluate expression tree import java.lang.* ; class GFG { Node root ; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public static class Node { String data ; Node left right ; Node ( String d ) { data = d ; left = null ; right = null ; } } private static int toInt ( String s ) { int num = 0 ; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if ( s . charAt ( 0 ) != '-' ) for ( int i = 0 ; i < s . length (); i ++ ) num = num * 10 + (( int ) s . charAt ( i ) - 48 ); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for ( int i = 1 ; i < s . length (); i ++ ) num = num * 10 + (( int )( s . charAt ( i )) - 48 ); num = num * - 1 ; } return num ; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree ( Node root ) { // Empty tree if ( root == null ) return 0 ; // Leaf node i.e an integer if ( root . left == null && root . right == null ) return toInt ( root . data ); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree ( root . left ); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree ( root . right ); // Check which operator to apply if ( root . data . equals ( '+' )) return leftEval + rightEval ; if ( root . data . equals ( '-' )) return leftEval - rightEval ; if ( root . data . equals ( '*' )) return leftEval * rightEval ; return leftEval / rightEval ; } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node ( '+' ); root . left = new Node ( '*' ); root . left . left = new Node ( '5' ); root . left . right = new Node ( '-4' ); root . right = new Node ( '-' ); root . right . left = new Node ( '100' ); root . right . right = new Node ( '20' ); System . out . println ( evalTree ( root )); root = null ; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node ( '+' ); root . left = new Node ( '*' ); root . left . left = new Node ( '5' ); root . left . right = new Node ( '4' ); root . right = new Node ( '-' ); root . right . left = new Node ( '100' ); root . right . right = new Node ( '/' ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( '20' ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( '2' ); System . out . println ( evalTree ( root )); } } // This code is contributed by Ankit Gupta
Python3 # Python program to evaluate expression tree # Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class node : def __init__ ( self value ): self . left = None self . data = value self . right = None # This function receives a node of the syntax tree # and recursively evaluate it def evaluateExpressionTree ( root ): # empty tree if root is None : return 0 # leaf node if root . left is None and root . right is None : return int ( root . data ) # evaluate left tree left_sum = evaluateExpressionTree ( root . left ) # evaluate right tree right_sum = evaluateExpressionTree ( root . right ) # check which operation to apply if root . data == '+' : return left_sum + right_sum elif root . data == '-' : return left_sum - right_sum elif root . data == '*' : return left_sum * right_sum else : return left_sum // right_sum # Driver function to test above problem if __name__ == '__main__' : # creating a sample tree root = node ( '+' ) root . left = node ( '*' ) root . left . left = node ( '5' ) root . left . right = node ( '-4' ) root . right = node ( '-' ) root . right . left = node ( '100' ) root . right . right = node ( '20' ) print ( evaluateExpressionTree ( root )) root = None # creating a sample tree root = node ( '+' ) root . left = node ( '*' ) root . left . left = node ( '5' ) root . left . right = node ( '4' ) root . right = node ( '-' ) root . right . left = node ( '100' ) root . right . right = node ( '/' ) root . right . right . left = node ( '20' ) root . right . right . right = node ( '2' ) print ( evaluateExpressionTree ( root )) # This code is contributed by Harshit Sidhwa
C# // C# program to evaluate expression tree using System ; public class GFG { // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public class Node { public String data ; public Node left right ; public Node ( String d ) { data = d ; left = null ; right = null ; } } private static int toInt ( String s ) { int num = 0 ; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if ( s [ 0 ] != '-' ) for ( int i = 0 ; i < s . Length ; i ++ ) num = num * 10 + (( int ) s [ i ] - 48 ); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for ( int i = 1 ; i < s . Length ; i ++ ) num = num * 10 + (( int ) ( s [ i ]) - 48 ); num = num * - 1 ; } return num ; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree ( Node root ) { // Empty tree if ( root == null ) return 0 ; // Leaf node i.e an integer if ( root . left == null && root . right == null ) return toInt ( root . data ); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree ( root . left ); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree ( root . right ); // Check which operator to apply if ( root . data . Equals ( '+' )) return leftEval + rightEval ; if ( root . data . Equals ( '-' )) return leftEval - rightEval ; if ( root . data . Equals ( '*' )) return leftEval * rightEval ; return leftEval / rightEval ; } // Driver code public static void Main ( String [] args ) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node ( '+' ); root . left = new Node ( '*' ); root . left . left = new Node ( '5' ); root . left . right = new Node ( '-4' ); root . right = new Node ( '-' ); root . right . left = new Node ( '100' ); root . right . right = new Node ( '20' ); Console . WriteLine ( evalTree ( root )); root = null ; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node ( '+' ); root . left = new Node ( '*' ); root . left . left = new Node ( '5' ); root . left . right = new Node ( '4' ); root . right = new Node ( '-' ); root . right . left = new Node ( '100' ); root . right . right = new Node ( '/' ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( '20' ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( '2' ); Console . WriteLine ( evalTree ( root )); } } // This code is contributed by umadevi9616
JavaScript < script > // javascript program to evaluate expression tree var root ; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class Node { constructor ( val ) { this . data = val ; this . left = null ; this . right = null ; } } function toInt ( s ) { var num = 0 ; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if ( s . charAt ( 0 ) != '-' ) for ( i = 0 ; i < s . length ; i ++ ) num = num * 10 + ( s . charCodeAt ( i ) - 48 ); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for ( i = 1 ; i < s . length ; i ++ ) num = num * 10 + ( s . charCodeAt ( i ) - 48 ); num = num * - 1 ; } return num ; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it function evalTree ( root ) { // Empty tree if ( root == null ) return 0 ; // Leaf node i.e an integer if ( root . left == null && root . right == null ) return toInt ( root . data ); // Evaluate left subtree var leftEval = evalTree ( root . left ); // Evaluate right subtree var rightEval = evalTree ( root . right ); // Check which operator to apply if ( root . data === ( '+' )) return leftEval + rightEval ; if ( root . data === ( '-' )) return leftEval - rightEval ; if ( root . data === ( '*' )) return leftEval * rightEval ; return leftEval / rightEval ; } // Driver code // Creating a sample tree var root = new Node ( '+' ); root . left = new Node ( '*' ); root . left . left = new Node ( '5' ); root . left . right = new Node ( '-4' ); root . right = new Node ( '-' ); root . right . left = new Node ( '100' ); root . right . right = new Node ( '20' ); document . write ( evalTree ( root )); root = null ; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node ( '+' ); root . left = new Node ( '*' ); root . left . left = new Node ( '5' ); root . left . right = new Node ( '4' ); root . right = new Node ( '-' ); root . right . left = new Node ( '100' ); root . right . right = new Node ( '/' ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( '20' ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( '2' ); document . write ( '
' + evalTree ( root )); // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 < /script>
산출
60 110
시간 복잡도: O(n) 각 노드를 한 번 방문합니다.
보조 공간: 에)