Python의 최대 힙
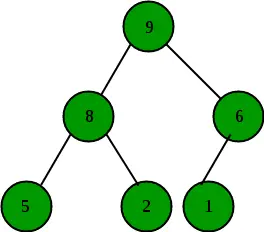
ㅏ 최대 힙 각 내부 노드의 값이 해당 노드의 하위 노드 값보다 크거나 같은 완전한 이진 트리입니다. 힙의 요소를 배열로 매핑하는 것은 간단합니다. 노드가 인덱스 k에 저장되면 왼쪽 자식은 인덱스에 저장됩니다. 2k+1 그리고 인덱스의 오른쪽 자식 2k+2 .
최대 힙의 예:

최대 힙은 어떻게 표현되나요?
최대 힙은 완전한 이진 트리입니다. 최대 힙은 일반적으로 배열로 표시됩니다. 루트 요소는 Arr[0]에 있습니다. 아래 표는 i번째 노드에 대한 다른 노드의 인덱스, 즉 Arr[i]를 보여줍니다.
- Arr[(i-1)/2] 상위 노드를 반환합니다.
- Arr[(2*i)+1] 왼쪽 자식 노드를 반환합니다.
- Arr[(2*i)+2] 오른쪽 자식 노드를 반환합니다.
최대 힙에 대한 작업:
- getMax() : Max Heap의 루트 요소를 반환합니다. 이 작업의 시간 복잡도는 오(1) .
- 추출최대() : MaxHeap에서 최대 요소를 제거합니다. 이 작업의 시간 복잡도는 O(로그 n) 이 작업은 루트를 제거한 후 (heapify()를 호출하여) 힙 속성을 유지해야 하기 때문입니다.
- 끼워 넣다() : 새 키를 삽입하려면 다음이 필요합니다. O(로그 n) 시간. 트리 끝에 새 키를 추가합니다. 새 키가 상위 키보다 작으면 아무 작업도 수행할 필요가 없습니다. 그렇지 않으면 위반된 힙 속성을 수정하기 위해 위로 순회해야 합니다.
메모: 아래 구현에서는 구현을 단순화하기 위해 인덱스 1에서 인덱싱을 수행합니다.
파이썬
# Python3 implementation of Max Heap> import> sys> class> MaxHeap:> > def> __init__(> self> , maxsize):> > > self> .maxsize> => maxsize> > self> .size> => 0> > self> .Heap> => [> 0> ]> *> (> self> .maxsize> +> 1> )> > self> .Heap[> 0> ]> => sys.maxsize> > self> .FRONT> => 1> > # Function to return the position of> > # parent for the node currently> > # at pos> > def> parent(> self> , pos):> > > return> pos> /> /> 2> > # Function to return the position of> > # the left child for the node currently> > # at pos> > def> leftChild(> self> , pos):> > > return> 2> *> pos> > # Function to return the position of> > # the right child for the node currently> > # at pos> > def> rightChild(> self> , pos):> > > return> (> 2> *> pos)> +> 1> > # Function that returns true if the passed> > # node is a leaf node> > def> isLeaf(> self> , pos):> > > if> pos>> => (> self> .size> /> /> 2> )> and> pos <> => self> .size:> > return> True> > return> False> > # Function to swap two nodes of the heap> > def> swap(> self> , fpos, spos):> > > self> .Heap[fpos],> self> .Heap[spos]> => (> self> .Heap[spos],> > self> .Heap[fpos])> > # Function to heapify the node at pos> > def> maxHeapify(> self> , pos):> > # If the node is a non-leaf node and smaller> > # than any of its child> > if> not> self> .isLeaf(pos):> > if> (> self> .Heap[pos] <> self> .Heap[> self> .leftChild(pos)]> or> > self> .Heap[pos] <> self> .Heap[> self> .rightChild(pos)]):> > # Swap with the left child and heapify> > # the left child> > if> (> self> .Heap[> self> .leftChild(pos)]>> > self> .Heap[> self> .rightChild(pos)]):> > self> .swap(pos,> self> .leftChild(pos))> > self> .maxHeapify(> self> .leftChild(pos))> > # Swap with the right child and heapify> > # the right child> > else> :> > self> .swap(pos,> self> .rightChild(pos))> > self> .maxHeapify(> self> .rightChild(pos))> > # Function to insert a node into the heap> > def> insert(> self> , element):> > > if> self> .size>> => self> .maxsize:> > return> > self> .size> +> => 1> > self> .Heap[> self> .size]> => element> > current> => self> .size> > while> (> self> .Heap[current]>> > self> .Heap[> self> .parent(current)]):> > self> .swap(current,> self> .parent(current))> > current> => self> .parent(current)> > # Function to print the contents of the heap> > def> Print> (> self> ):> > > for> i> in> range> (> 1> , (> self> .size> /> /> 2> )> +> 1> ):> > print> (> 'PARENT : '> +> str> (> self> .Heap[i])> +> > 'LEFT CHILD : '> +> str> (> self> .Heap[> 2> *> i])> +> > 'RIGHT CHILD : '> +> str> (> self> .Heap[> 2> *> i> +> 1> ]))> > # Function to remove and return the maximum> > # element from the heap> > def> extractMax(> self> ):> > popped> => self> .Heap[> self> .FRONT]> > self> .Heap[> self> .FRONT]> => self> .Heap[> self> .size]> > self> .size> -> => 1> > self> .maxHeapify(> self> .FRONT)> > > return> popped> # Driver Code> if> __name__> => => '__main__'> :> > > print> (> 'The maxHeap is '> )> > > maxHeap> => MaxHeap(> 15> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 5> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 3> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 17> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 10> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 84> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 19> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 6> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 22> )> > maxHeap.insert(> 9> )> > maxHeap.> Print> ()> > > print> (> 'The Max val is '> +> str> (maxHeap.extractMax()))> |
산출
The maxHeap is PARENT : 84LEFT CHILD : 22RIGHT CHILD : 19 PARENT : 22LEFT CHILD : 17RIGHT CHILD : 10 PARENT : 19LEFT CHILD : 5RIGHT CHILD : 6 PARENT : 17LEFT CHILD : 3RIGHT CHILD : 9 The Max val is 84
라이브러리 기능 사용:
우리는 사용 힙 Python에서 Heap을 구현하는 클래스입니다. 기본적으로 최소 힙은 이 클래스에 의해 구현됩니다. 하지만 MaxHeap으로 사용할 수 있도록 각 값에 -1을 곱합니다.
파이썬3
# Python3 program to demonstrate working of heapq> from> heapq> import> heappop, heappush, heapify> # Creating empty heap> heap> => []> heapify(heap)> # Adding items to the heap using heappush> # function by multiplying them with -1> heappush(heap,> -> 1> *> 10> )> heappush(heap,> -> 1> *> 30> )> heappush(heap,> -> 1> *> 20> )> heappush(heap,> -> 1> *> 400> )> # printing the value of maximum element> print> (> 'Head value of heap : '> +> str> (> -> 1> *> heap[> 0> ]))> # printing the elements of the heap> print> (> 'The heap elements : '> )> for> i> in> heap:> > print> ((> -> 1> *> i), end> => ' '> )> print> (> '
'> )> element> => heappop(heap)> # printing the elements of the heap> print> (> 'The heap elements : '> )> for> i> in> heap:> > print> (> -> 1> *> i, end> => ' '> )> |
산출
Head value of heap : 400 The heap elements : 400 30 20 10 The heap elements : 30 10 20
숫자, 문자열, 튜플, 객체 등에 대한 dunder 메소드와 함께 라이브러리 함수 사용
우리는 사용 힙 Python에서 Heap을 구현하는 클래스입니다. 기본적으로 최소 힙은 이 클래스에 의해 구현됩니다.
숫자뿐만 아니라 모든 유형의 객체(문자열, 튜플, 객체 등)에 제한되지 않는 MaxHeap을 구현하려면 다음을 수행해야 합니다.
- 목록의 항목에 대한 Wrapper 클래스를 만듭니다.
- 재정의 __lt__ 반대 결과를 제공하는 Dunder 방법.
다음은 여기에 언급된 방법의 구현입니다.
파이썬3
'''> Python3 program to implement MaxHeap Operation> with built-in module heapq> for String, Numbers, Objects> '''> from> functools> import> total_ordering> import> heapq> |_+_| |