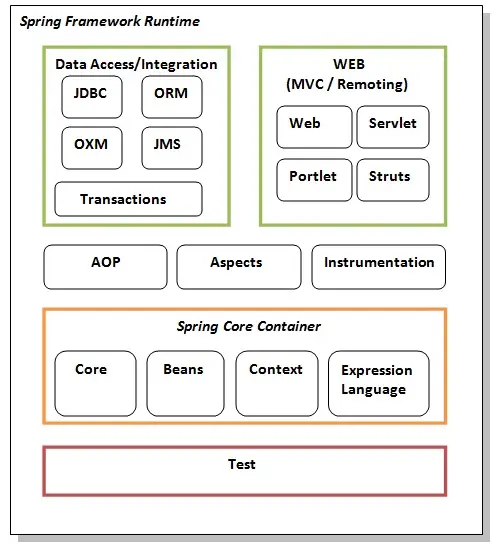
C 논리 연산자
C의 논리 연산자는 여러 조건/제약 조건을 결합하는 데 사용됩니다. 논리 연산자는 0 또는 1을 반환하며, 이는 표현식 결과가 참인지 거짓인지에 따라 달라집니다. 의사결정을 위한 C 프로그래밍에서는 논리 연산자를 사용합니다.
C 언어에는 3개의 논리 연산자가 있습니다.
- 논리 AND( && ) 논리 OR( || ) 논리 NOT( ! )
논리 연산자의 유형
1. 논리 AND 연산자( && )
두 피연산자가 모두 0이 아니면 조건은 참이 됩니다. 그렇지 않으면 결과 값은 0입니다. 결과의 반환 유형은 int입니다. 다음은 논리 AND 연산자에 대한 진리표입니다.
| 엑스 | 그리고 | X && Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
통사론
(operand_1 && operand_2)
예
씨
// C program for Logical> // AND Operator> #include> // Driver code> int> main()> {> > int> a = 10, b = 20;> > if> (a>0 && b> 0) {> > printf> (> 'Both values are greater than 0
'> );> > }> > else> {> > printf> (> 'Both values are less than 0
'> );> > }> > return> 0;> }> |
산출
Both values are greater than 0
2. 논리 OR 연산자( || )
둘 중 하나라도 0이 아니면 조건이 참이 됩니다. 그렇지 않으면 false, 즉 0을 값으로 반환합니다. 아래는 논리 OR 연산자에 대한 진리표입니다.
| 엑스 | 그리고 | 엑스 || 그리고 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
통사론
(operand_1 || operand_2)
예
씨
// C program for Logical> // OR Operator> #include> // Driver code> int> main()> {> > int> a = -1, b = 20;> > if> (a>0 || b> 0) {> > printf> (> 'Any one of the given value is '> > 'greater than 0
'> );> > }> > else> {> > printf> (> 'Both values are less than 0
'> );> > }> > return> 0;> }> |
산출
Any one of the given value is greater than 0
3. 논리 NOT 연산자( ! )
조건이 참이면 논리 NOT 연산자는 조건을 거짓으로 만들고 그 반대의 경우도 마찬가지입니다. 아래는 논리 NOT 연산자의 진리표입니다.
| 엑스 | !엑스 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
통사론
! (operand_1 && operand_2)
예
씨
// C program for Logical> // NOT Operator> #include> // Driver code> int> main()> {> > int> a = 10, b = 20;> > if> (!(a>0 && b> 0)) {> > // condition returned true but> > // logical NOT operator changed> > // it to false> > printf> (> 'Both values are greater than 0
'> );> > }> > else> {> > printf> (> 'Both values are less than 0
'> );> > }> > return> 0;> }> |
단락 논리 연산자
추가 피연산자를 평가하지 않고 앞의 논리식을 평가하여 결과를 확인할 수 있는 경우를 단락이라고 합니다.
단락은 둘 이상의 논리 연산자가 있는 방정식에서 볼 수 있습니다. AND, OR 또는 둘 다 가능합니다.
1. 논리 AND 연산자의 단락
논리 AND 연산자는 모든 피연산자가 true로 평가되는 경우에만 true를 반환합니다. 첫 번째 피연산자가 거짓이면 다음 피연산자는 평가되지 않습니다. 이는 추가 피연산자가 true로 평가되더라도 전체 조건이 여전히 false를 반환하기 때문입니다.
예
C++
// C++ Program to illustrate short circuiting in Logical AND> #include> using> namespace> std;> // utility function to check positive> bool> is_positive(> int> number)> {> > if> (number>0)> > return> true> ;> > else> > return> false> ;> }> // utility function to check if the number is even> bool> is_even(> int> number)> {> > if> (number % 2 == 0)> > return> true> ;> > else> > return> false> ;> }> // driver code> int> main()> {> > int> x = 10;> > // Both conditions are evaluated> > if> (is_positive(x) && is_even(x)) {> > cout < <> 'Both conditions are satisfied.'> < < endl;> > }> > else> {> > cout < <> 'Conditions not satisfied.'> < < endl;> > }> > int> y = -5;> > // The first condition is evaluated and found to be> > // false, so the second condition is not evaluated> > if> (is_positive(y) && is_even(y)) {> > cout < <> 'Both conditions are satisfied.'> < < endl;> > }> > else> {> > cout < <> 'Conditions not satisfied.'> < < endl;> > }> > return> 0;> }> |
산출
Both conditions are satisfied. Conditions not satisfied.
2. 논리 OR 연산자의 단락
OR 연산자는 하나 이상의 피연산자가 true로 평가되면 true를 반환합니다. 첫 번째 피연산자가 true이면 다음 피연산자는 평가되지 않습니다. 이는 추가 피연산자가 false로 평가되더라도 전체 조건이 여전히 true를 반환하기 때문입니다.
예
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the short circuiting in Logical> // OR> #include> using> namespace> std;> // utility function to check positive number> bool> is_positive(> int> number)> {> > if> (number>0)> > return> true> ;> > else> > return> false> ;> }> // utility function to check if the number is even> bool> is_even(> int> number)> {> > if> (number % 2 == 0)> > return> true> ;> > else> > return> false> ;> }> // driver code> int> main()> {> > int> x = 8;> > // The first condition is evaluated and found to be> > // true, so the second condition is not evaluated> > if> (is_positive(x) || is_even(x)) {> > cout < <> 'At least one condition is satisfied.'> > < < endl;> > }> > else> {> > cout < <> 'Conditions not satisfied.'> < < endl;> > }> > int> y = -5;> > // The first condition is evaluated and found to be> > // false, so the second condition is evaluated> > if> (is_positive(y) || is_even(y)) {> > cout < <> 'At least one condition is satisfied.'> > < < endl;> > }> > else> {> > cout < <> 'Conditions not satisfied.'> < < endl;> > }> > return> 0;> }> |
산출
At least one condition is satisfied. Conditions not satisfied.
논리 연산자에 대한 FAQ
Q1. 프로그래밍에서 논리 연산자의 우선 순위는 무엇입니까?
답변:
논리 연산자의 우선순위는 NOT, AND, OR입니다. 그러나 평가 순서를 명확하게 하고 혼동을 피하기 위해 항상 괄호를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
Q2. 논리 연산자를 서로 연결할 수 있나요?
답변:
예, 논리 연산자를 서로 연결하여 복잡한 조건을 만들 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 여러 논리 AND(&&) 또는 논리 OR(||) 연산자를 단일 표현식에 결합하여 여러 조건을 동시에 평가할 수 있습니다.
Q3. 다음 코드의 출력은 무엇입니까?
씨
#include> void> main()> > > int> a = 1, b = 0, c = 5;> > int> d = a && b> |
답변:
6
Q4. 다음 코드의 출력은 무엇입니까?
씨
#include> int> main()> {> > int> i = 1;> > if> (i++ && (i == 1))> > printf> (> 'techcodeview.com
'> );> > else> > printf> (> 'Coding
'> );> }> |
답변:
Coding