Més gran o "+" format per tots en una matriu quadrada binària
Donat un n × n matriu binària juntament amb consistent en 0s i 1s . La teva tasca és trobar la mida del més gran '+' forma que només es pot formar utilitzant 1s .

A '+' La forma consisteix en una cel·la central amb quatre braços que s'estenen en les quatre direccions ( amunt avall esquerra i dreta ) tot romanent dins dels límits de la matriu. La mida d'a '+' es defineix com el nombre total de cèl·lules formant-lo incloent el centre i tots els braços.
La tasca és tornar el mida màxima de qualsevol vàlid '+' en juntament amb . Si no '+' es pot formar retorn .
Exemples:
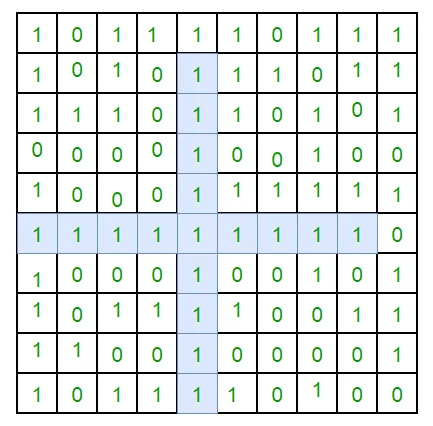
Entrada: amb = [ [0 1 1 0 1] [0 0 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 0 1] [0 1 1 1 0] ]
Sortida: 9
Explicació: Es pot formar un "+" amb una longitud de braç de 2 (2 cel·les en cada direcció + 1 centre) al centre de la catifa.
0 1 1 0 1
0 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 1
0 1 1 10
Mida total = (2 × 4) + 1 = 9Entrada: amb = [ [0 1 1] [0 0 1] [1 1 1] ]
Sortida: 1
Explicació: Un "+" amb una longitud de braç de 0 (0 cel·les en cada direcció + 1 centre) es pot formar amb qualsevol dels 1.Entrada: amb = [ [0] ]
Sortida:
Explicació: No Es pot formar el signe ‘+’.
[Enfocament ingenu] - Considereu cada punt com a centre - O(n^4) Temps i O(n^4) Espai
Travessa les cel·les de la matriu una per una. Considereu cada punt travessat com el centre d'un plus i trobeu la mida del +. Per a cada element travessem esquerra dreta avall i amunt. El pitjor cas d'aquesta solució passa quan tenim tots els 1.
[Enfocament esperat] - Precàlcul de 4 matrius - O(n^2) Temps i O (n^2) Espai
El idea és mantenir quatre matrius auxiliars esquerra[][] dreta[][] superior[][] inferior[][] per emmagatzemar 1 consecutius en totes direccions. Per a cada cèl·lula (i j) a la matriu d'entrada emmagatzemem informació a continuació en aquests quatre matrius -
- esquerra (i j) emmagatzema el nombre màxim d'1 consecutius a esquerra de la cel·la (i j) inclosa la cel·la (i j).
- dret (i j) emmagatzema el nombre màxim d'1 consecutius a dret de la cel·la (i j) inclosa la cel·la (i j).
- superior (i j) emmagatzema el nombre màxim d'1 consecutius a superior de la cel·la (i j) inclosa la cel·la (i j).
- inferior (i j) emmagatzema el nombre màxim d'1 consecutius a inferior de la cel·la (i j) inclosa la cel·la (i j).
Després de calcular el valor de cada cel·la de les matrius anteriors, el més gran'+' estaria formada per una cel·la de matriu d'entrada que tingui un valor màxim considerant el mínim de ( esquerra (i j) dreta (i j) superior (i j) inferior (i j) )
Podem utilitzar Programació dinàmica per calcular la quantitat total d'1 consecutius en totes les direccions:
si mat(i j) == 1
esquerra (i j) = esquerra (i j - 1) + 1altrament a l'esquerra (i j) = 0
si mat(i j) == 1
top(i j) = top(i - 1 j) + 1;else top(i j) = 0;
si mat(i j) == 1
fons (i j) = fons (i + 1 j) + 1;else bottom(i j) = 0;
si mat(i j) == 1
dreta(i j) = dreta(i j + 1) + 1;sinó dreta(i j) = 0;
A continuació es mostra la implementació de l'enfocament anterior:
C++ // C++ program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming #include using namespace std ; int findLargestPlus ( vector < vector < int >> & mat ) { int n = mat . size (); vector < vector < int >> left ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); vector < vector < int >> right ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); vector < vector < int >> top ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); vector < vector < int >> bottom ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); // Fill left and top matrices for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { left [ i ][ j ] = ( j == 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i ][ j ] = ( i == 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { right [ i ][ j ] = ( j == n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i ][ j ] = ( i == n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } int maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { int armLength = min ({ left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ]}); maxPlusSize = max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } int main () { // Hardcoded input matrix vector < vector < int >> mat = { { 0 1 1 0 1 } { 0 0 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 0 1 } { 0 1 1 1 0 } }; cout < < findLargestPlus ( mat ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming class GfG { static int findLargestPlus ( int [][] mat ) { int n = mat . length ; int [][] left = new int [ n ][ n ] ; int [][] right = new int [ n ][ n ] ; int [][] top = new int [ n ][ n ] ; int [][] bottom = new int [ n ][ n ] ; // Fill left and top matrices for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { left [ i ][ j ] = ( j == 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i ][ j ] = ( i == 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { right [ i ][ j ] = ( j == n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i ][ j ] = ( i == n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } int maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { int armLength = Math . min ( Math . min ( left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] ) Math . min ( top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ] )); maxPlusSize = Math . max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Hardcoded input matrix int [][] mat = { { 0 1 1 0 1 } { 0 0 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 0 1 } { 0 1 1 1 0 } }; System . out . println ( findLargestPlus ( mat )); } }
Python # Python program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix # using Dynamic Programming def findLargestPlus ( mat ): n = len ( mat ) left = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] right = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] top = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] bottom = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] # Fill left and top matrices for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( n ): if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 : left [ i ][ j ] = 1 if j == 0 else left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 top [ i ][ j ] = 1 if i == 0 else top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 # Fill right and bottom matrices for i in range ( n - 1 - 1 - 1 ): for j in range ( n - 1 - 1 - 1 ): if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 : right [ i ][ j ] = 1 if j == n - 1 else right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 bottom [ i ][ j ] = 1 if i == n - 1 else bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 maxPlusSize = 0 # Compute the maximum '+' size for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( n ): if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 : armLength = min ( left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ]) maxPlusSize = max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ) return maxPlusSize if __name__ == '__main__' : # Hardcoded input matrix mat = [ [ 0 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 0 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 1 1 1 0 ] ] print ( findLargestPlus ( mat ))
C# // C# program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming using System ; class GfG { static int FindLargestPlus ( int [] mat ) { int n = mat . GetLength ( 0 ); int [] left = new int [ n n ]; int [] right = new int [ n n ]; int [] top = new int [ n n ]; int [] bottom = new int [ n n ]; // Fill left and top matrices for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i j ] == 1 ) { left [ i j ] = ( j == 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i j ] = ( i == 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i j ] == 1 ) { right [ i j ] = ( j == n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i j ] = ( i == n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 j ] + 1 ; } } } int maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i j ] == 1 ) { int armLength = Math . Min ( Math . Min ( left [ i j ] right [ i j ]) Math . Min ( top [ i j ] bottom [ i j ])); maxPlusSize = Math . Max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } public static void Main () { // Hardcoded input matrix int [] mat = { { 0 1 1 0 1 } { 0 0 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 0 1 } { 0 1 1 1 0 } }; Console . WriteLine ( FindLargestPlus ( mat )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming function findLargestPlus ( mat ) { let n = mat . length ; let left = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); let right = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); let top = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); let bottom = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); // Fill left and top matrices for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { left [ i ][ j ] = ( j === 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i ][ j ] = ( i === 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( let i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( let j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { right [ i ][ j ] = ( j === n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i ][ j ] = ( i === n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } let maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { let armLength = Math . min ( left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ]); maxPlusSize = Math . max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } // Hardcoded input matrix let mat = [ [ 0 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 0 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 1 1 1 0 ] ]; console . log ( findLargestPlus ( mat ));
Sortida
9
Complexitat temporal: O(n²) a causa de quatre passades per calcular les matrius direccionals i una passada final per determinar el "+" més gran. Cada passada triga O(n²) temps que condueix a una complexitat global de O(n²).
Complexitat espacial: O(n²) a causa de quatre matrius auxiliars (esquerra dreta superior inferior) que consumeixen O(n²) espai addicional.