Java'da Java.io.PipedOutputStream Sınıfı

Java'da Java.io.PipedInputStream sınıfı

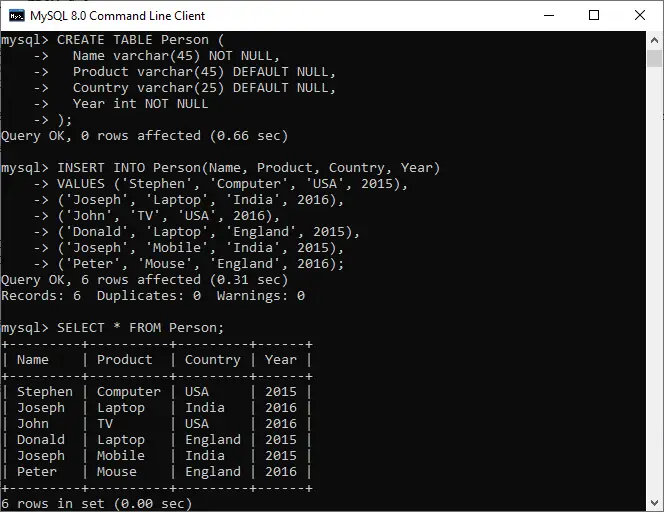
Borular IO'da aynı anda JVM'de çalışan iki iş parçacığı arasında bir bağlantı sağlar. Yani Borular hem kaynak hem de hedef olarak kullanılır.
- PipedInputStream ayrıca PipedOutputStream ile de bağlanır. Yani veriler PipedOutputStream kullanılarak yazılabilir ve PipedInputStream kullanılarak yazılabilir. Ancak her iki iş parçacığını aynı anda kullanmak iş parçacıkları için bir kilitlenme yaratacaktır.
- PipedOutputStream borunun sonunu gönderiyor. Veriler PipedOutputStream'e yazılır. Veriyi okuyan PipedInputStream artık yoksa borunun bozuk olduğu söylenir.
Beyanname:
public class PipedOutputStream
extends OutputStream
Yapıcı:
- PipedOutputStream(): bağlı olmadığı bir PipedOutputStream oluşturur.
- PipedOutputStream(PipedOutputStream inStream): bir PipedOutputStream oluşturur ve
PipedInputStream - 'inStream'e bağlı.
Yöntemler:
write() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(int bayt) Belirtilen bir baytı Borulu Çıkış Akışına yazar.
Sözdizimi:
public void write(int byte)
Parameters :
byte : byte to be written
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) : Java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Verilerin maksimum baytını arabellekten Borulu Çıkış Akışına yazar. Akışa bayt yazılmadığı takdirde yöntem bloke olur.
Sözdizimi:
public void write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen)
Parameters :
buffer : data of the buffer
offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'.
maxlen : maximum length of array to be read
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. JavaÇıkış:
Use of write(buffer offset maxlen) : J A V A
- close() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.close() Borulu Çıkış Akışını kapatır ve tahsis edilen kaynakları serbest bırakır.
Sözdizimi:
public void close()
Parameters :
--------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- connect(PipedInputStream hedefi): Java.io.PipedOutputStream.connect(PipedInputStream hedefi) Borulu Çıkış Akışını 'hedef' Borulu Giriş Akışına bağlar ve 'hedef'in borular olması durumunda başka bir akış IO istisnası atılır
Sözdizimi:
public void connect(PipedInputStream destination)
Parameters :
destination : the Piped Input Stream to be connected to
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- floş() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.flush() Çıkış Akışını temizler.
Sözdizimi:
public void flush()
Parameters :
------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
PipedOutputStream sınıfı yöntemlerinin çalışmasını gösteren Java kodu:
JavaÇıkış:
Use of flush() method :
G E E K S
Closing the Output stream
Test Oluştur