Resande säljare problem med filial och bunden
Med tanke på en uppsättning städer och avstånd mellan varje par städer är problemet att hitta den kortast möjliga turnén som besöker varje stad exakt en gång och återvänder till utgångspunkten.

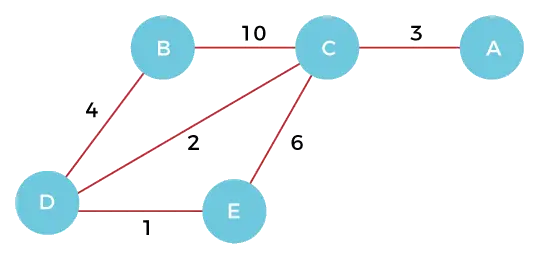
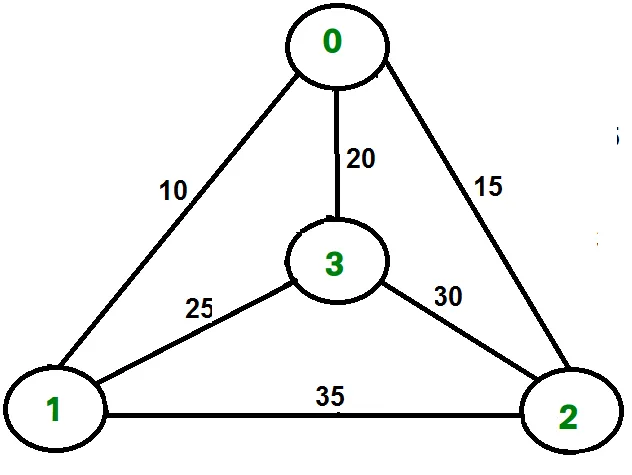
Tänk till exempel på grafen som visas i figuren på höger sida. En TSP-turné i grafen är 0-1-3-2-0. Kostnaden för turnén är 10+25+30+15 vilket är 80.
Vi har diskuterat följande lösningar
1) Naiv och dynamisk programmering
2) Ungefärlig lösning med MST
Gren och bunden lösning
Som framgår av de tidigare artiklarna i gren och bunden metod för aktuell nod i träd beräknar vi en bunden till bästa möjliga lösning som vi kan få om vi ner denna nod. Om den bundna på bästa möjliga lösning i sig är sämre än nuvarande bästa (bäst beräknade hittills) ignorerar vi undertreet som är förankrat med noden.
Observera att kostnaden genom en nod innehåller två kostnader.
1) Kostnad för att nå noden från roten (när vi når en nod har vi denna kostnad beräknad)
2) Kostnader för att nå ett svar från nuvarande nod till ett blad (vi beräknar en gräns för denna kostnad för att bestämma om du ska ignorera undertråd med denna nod eller inte).
- I fall av en maximeringsproblem En övre gräns berättar för oss den maximala möjliga lösningen om vi följer den givna noden. Till exempel i 0/1 ryggsäck vi använde girig tillvägagångssätt för att hitta en övre gräns .
- I fall av en minimeringsproblem En nedre gräns berättar för oss den minsta möjliga lösningen om vi följer den givna noden. Till exempel i Jobbuppdragsproblem Vi får en lägre gräns genom att tilldela en arbetare minst kostnadsarbete.
I gren och bunden är den utmanande delen att räkna ut ett sätt att beräkna en bunden till bästa möjliga lösning. Nedan är en idé som används för att beräkna gränser för resande säljarproblem.
Kostnaden för alla turnéer kan skrivas enligt nedan.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Tänk till exempel på ovanstående graf. Nedan finns lägsta kostnad två kanter intill varje nod.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Nu har vi en idé om beräkning av nedre gräns. Låt oss se hur du tillämpar IT State Space Search Tree. Vi börjar räkna upp alla möjliga noder (helst i lexikografisk ordning)
1. Rotnoden: Utan förlust av generalitet antar vi att vi börjar på Vertex '0' för vilken den nedre gränsen har beräknats ovan.
Hantera nivå 2: Nästa nivå räknar upp alla möjliga vertikaler vi kan gå till (med tanke på att i alla vägar måste ett toppunkt endast inträffa en gång) som är 1 2 3 ... n (Observera att grafen är klar). Tänk på att vi beräknar för Vertex 1 sedan vi flyttade från 0 till 1 vår turné har nu inkluderat kanten 0-1. Detta gör att vi kan göra nödvändiga förändringar i rotens nedre gräns.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Hur fungerar det? För att inkludera kant 0-1 lägger vi kantkostnaden på 0-1 och subtrahera en kantvikt så att den nedre gränsen förblir så snäv som möjligt, vilket skulle vara summan av minsta kanter på 0 och 1 dividerat med 2. Klart kanten subtraheras inte kan vara mindre än detta.
Hantera andra nivåer: När vi går vidare till nästa nivå räknar vi igen alla möjliga toppar. För ovanstående fall som går vidare efter 1 kolla in för 2 3 4 ... n.
Tänk på nedre gränsen för 2 när vi flyttade från 1 till 1 vi inkluderar kanten 1-2 till turnén och ändra den nya nedre gränsen för denna nod.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
Obs: Den enda förändringen i formeln är att den här gången har vi inkluderat den andra minsta kantkostnaden för 1 eftersom minsta kantkostnaden redan har subtraherats på tidigare nivå.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include using namespace std ; const int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. int final_path [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path bool visited [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. int final_res = INT_MAX ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution void copyToFinal ( int curr_path []) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int firstMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int min = INT_MAX ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int secondMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int first = INT_MAX second = INT_MAX ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] void TSPRec ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path []) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level -1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] void TSP ( int adj [ N ][ N ]) { int curr_path [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; memset ( curr_path -1 sizeof ( curr_path )); memset ( visited 0 sizeof ( curr_path )); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound & 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code int main () { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [ N ][ N ] = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); printf ( 'Minimum cost : %d n ' final_res ); printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ]); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited [] = new boolean [ N ] ; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int curr_path [] ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ] ; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] ; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int min = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ] ; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int first = Integer . MAX_VALUE second = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int adj [][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path [] ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] ; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Arrays . fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int adj [][] ) { int curr_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Arrays . fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Arrays . fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [][] = {{ 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); System . out . printf ( 'Minimum cost : %dn' final_res ); System . out . printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { System . out . printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ] ); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Python3 # Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float ( 'inf' ) # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal ( curr_path ): final_path [: N + 1 ] = curr_path [:] final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin ( adj i ): min = maxsize for k in range ( N ): if adj [ i ][ k ] < min and i != k : min = adj [ i ][ k ] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin ( adj i ): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range ( N ): if i == j : continue if adj [ i ][ j ] <= first : second = first first = adj [ i ][ j ] elif ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second and adj [ i ][ j ] != first ): second = adj [ i ][ j ] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited ): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N : # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 : # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]] [ curr_path [ 0 ]] if curr_res < final_res : copyToFinal ( curr_path ) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range ( N ): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 and visited [ i ] == False ): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1 : curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) else : curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res : curr_path [ level ] = i visited [ i ] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited ) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [ False ] * len ( visited ) for j in range ( level ): if curr_path [ j ] != - 1 : visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP ( adj ): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [ - 1 ] * ( N + 1 ) visited = [ False ] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range ( N ): curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math . ceil ( curr_bound / 2 ) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = True curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited ) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [ None ] * ( N + 1 ) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [ False ] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP ( adj ) print ( 'Minimum cost :' final_res ) print ( 'Path Taken : ' end = ' ' ) for i in range ( N + 1 ): print ( final_path [ i ] end = ' ' ) # This code is contributed by ng24_7
C# // C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System ; public class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int [] final_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool [] visited = new bool [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32 . MaxValue ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int [] curr_path ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int min = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int first = Int32 . MaxValue second = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i j ]; } else if ( adj [ i j ] <= second && adj [ i j ] != first ) second = adj [ i j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int [ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int [] curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Array . Fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int [ ] adj ) { int [] curr_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Array . Fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Array . Fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code static public void Main () { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int [ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Minimum cost : ' + final_res ); Console . Write ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { Console . Write ( final_path [ i ] + ' ' ); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
JavaScript const N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array ( N ). fill ( false ); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal ( curr_path ){ for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; } final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin ( adj i ){ let min = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ){ if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i !== k ){ min = adj [ i ][ k ]; } } return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin ( adj i ){ let first = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; let second = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ){ if ( i == j ){ continue ; } if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ){ second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] !== first ){ second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] !== 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] !== 0 && ! visited [ i ]){ let temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ){ curr_bound -= ( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } else { curr_bound -= ( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ){ curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array visited . fill ( false ) for ( var j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP ( adj ) { let curr_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0 ; visited . fill ( false ); // compute initial bound for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ curr_bound += firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i ); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? ( curr_bound / 2 ) + 1 : ( curr_bound / 2 ); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]]; TSP ( adj ); console . log ( `Minimum cost: ${ final_res } ` ); console . log ( `Path Taken: ${ final_path . join ( ' ' ) } ` ); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Output:
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
Avrundningen görs i denna kodrad:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
I gren och bunden TSP -algoritm beräknar vi en lägre gräns för den totala kostnaden för den optimala lösningen genom att lägga till minsta kantkostnader för varje toppunkt och sedan dela med två. Men denna nedre gräns kanske inte är ett heltal. För att få ett heltal nedre gräns kan vi använda avrundning.
I ovanstående kod har Curr_Bound -variabeln den nuvarande nedre gränsen för den totala kostnaden för den optimala lösningen. När vi besöker ett nytt toppunkt på nivånivå beräknar vi en ny nedre bunden New_Bound genom att ta summan av minsta kantkostnader för det nya toppunktet och dess två närmaste grannar. Vi uppdaterar sedan Curr_Bound -variabeln genom att runda New_Bound till närmaste heltal.
Om nivån är 1 rundar vi oss ner till närmaste heltal. Detta beror på att vi bara har besökt ett toppunkt hittills och vi vill vara konservativa i vår uppskattning av den totala kostnaden för den optimala lösningen. Om nivån är större än 1 använder vi en mer aggressiv avrundningsstrategi som tar hänsyn till det faktum att vi redan har besökt vissa vertikaler och därför kan göra en mer exakt uppskattning av den totala kostnaden för den optimala lösningen.
Tidskomplexitet: Det värsta fallet komplexitet i gren och bundet förblir samma som den för brute -styrkan tydligt eftersom vi i värsta fall aldrig får en chans att beskära en nod. I praktiken presterar det mycket bra beroende på TSP: s olika instans. Komplexiteten beror också på valet av avgränsningsfunktionen eftersom det är de som bestämmer hur många noder som ska beskäras.
Referenser:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.ernet.in/dsa/node187.html