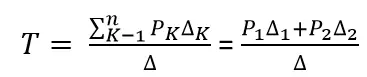АЛГОРИТМ ПЕТЕРСОН-а за међусобно искључење | Сет 2 (ЦПУ циклуси и меморијска ограда)
Проблем: С обзиром на 2 процеса И и Ј, морате да напишете програм који може гарантовати међусобно искључење између њих двоје без икакве додатне хардверске подршке.
Расипање ЦПУ Цлоцк Цицлес-а
У лаику појмовима када је нит чекала да се окрене, завршила је дуготрајна петља која је тестирала услов милионе пута у секунди тако непотребно израчунавање. Постоји бољи начин да се чека и то је познато као 'принос' .
Да бисмо разумели шта нам је потребно да дубоко копамо у начину рада процеса у Линуку. Овде је поменута идеја је поједностављена верзија планера Стварна имплементација има пуно компликација.
Размотрите следећи пример
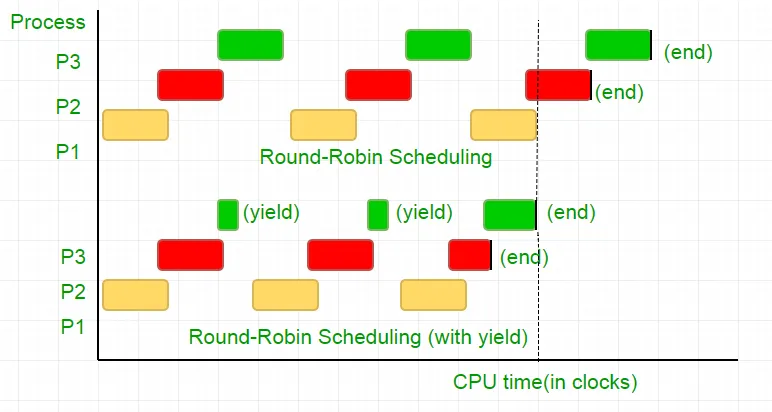
Постоје три процеса П1 П2 и П3. Процесс П3 је такав да има ио време Слично слично ономе у нашем кодексу који није тако корисно рачунање и постоји од петље само када П2 заврши његово извршење. Планинар их све ставља у округли робин ред. Сада реците да је брзина сата процесора 1000000 / сек и додељује 100 сатова у сваком поступку у свакој итерацији. Затим ће се први П1 покренути за 100 сатова (0,0001 секунди), а затим П2 (0,0001 секунди), пошто не постоји више процеса овог циклуса понавља се до П2, а затим је уследио П3-ова и на крају, а затим је уследила и на крају П3.
Ово је комплетан отпад циклуса 100 ЦПУ-а. Да бисте избегли да се међусобно одустанемо од временског времена ЦПУ-а, тј. Принос који се у суштини завршава овај пут, и распоред преузме следећи процес који је следећи процес покренуо. Сада тестирамо своје стање једном кад се одрекнемо ЦПУ-а. С обзиром на наш тест траје 25 циклуса сата уштедемо 75% нашег рачунања у времену. Да ово графички постави

С обзиром на брзину сата процесора као 1МХз, ово је пуно штедње!.
Различите дистрибуције пружају различиту функцију за постизање ове функције. Линук пружа сцхед_ииелд () .
void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] = 1 ; turn = 1 - self ; while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Only change is the addition of // sched_yield() call sched_yield (); }
Меморијска ограда.
Кодекс у ранијем водичу можда је радио на већини система, али није 100% тачно. Логика је била савршена, али најмодерније ЦПУ-у запошљава оптимизације перформанси које могу резултирати извршењем извршења ванредне наруџбе. Ово преуређивање меморијских операција (оптерећења и продавнице) обично препазиће у једној нити извршења, али може проузроковати непредвидиво понашање у истодобним програмима.
Размислите о овом примеру
while ( f == 0 ); // Memory fence required here print x ;
У горњем примеру преводилац разматра 2 изјаве као независно једни од других и на тај начин покушава повећати ефикасност кодекса поновним наручивањем којих могу довести до проблема са истодобним програмима. Да бисте избегли ово место меморијску ограду да дате наговештајник компајлеру о могућем односу између изјава широм баријере.
Дакле, редослед изјава
застава [селф] = 1;
ред = 1-себство;
док (претвори чек у услов)
принос ();
мора бити потпуно исти како би закључали рад у супротном, завршиће у стању застоја.
Да би се осигурало да се овај преводила пружају упутство које спречавају наручивање изјава широм ове баријере. У случају ГЦЦ-а то је __Синц_Синцхронизе () .
Дакле, модификовани код постаје
Потпуна примена у Ц:
// Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp // Use below command to compile: // g++ -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include std :: atomic < int > flag [ 2 ]; std :: atomic < int > turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. std :: atomic_thread_fence ( std :: memory_order_seq_cst ); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. std :: this_thread :: yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; std :: cout < < 'Thread Entered: ' < < self < < std :: endl ; lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) std :: thread t1 ( func 0 ); std :: thread t2 ( func 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); std :: cout < < 'Actual Count: ' < < ans < < ' | Expected Count: ' < < MAX * 2 < < std :: endl ; return 0 ; }
C // Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c // Use below command to compile: // gcc -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include 'mythreads.h' int flag [ 2 ]; int turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. __sync_synchronize (); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. sched_yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void * func ( void * s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = ( int * ) s ; printf ( 'Thread Entered: %d n ' self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { pthread_t p1 p2 ; // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) Pthread_create ( & p1 NULL func ( void * ) 0 ); Pthread_create ( & p2 NULL func ( void * ) 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. Pthread_join ( p1 NULL ); Pthread_join ( p2 NULL ); printf ( 'Actual Count: %d | Expected Count:' ' %d n ' ans MAX * 2 ); return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger ; public class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static AtomicInteger [] flag = new AtomicInteger [ 2 ] ; static AtomicInteger turn = new AtomicInteger (); static final int MAX = 1000000000 ; static int ans = 0 ; static void lockInit () { flag [ 0 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 1 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 0 ] . set ( 0 ); flag [ 1 ] . set ( 0 ); turn . set ( 0 ); } static void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 1 ); turn . set ( 1 - self ); // Memory fence to prevent the reordering of instructions beyond this barrier. // In Java volatile variables provide this guarantee implicitly. // No direct equivalent to atomic_thread_fence is needed. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] . get () == 1 && turn . get () == 1 - self ) Thread . yield (); } static void unlock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 0 ); } static void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; System . out . println ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Initialize the lock lockInit (); // Create two threads (both run func) Thread t1 = new Thread (() -> func ( 0 )); Thread t2 = new Thread (() -> func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); try { // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } System . out . println ( 'Actual Count: ' + ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + MAX * 2 ); } }
Python import threading flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 MAX = 10 ** 9 ans = 0 def lock_init (): # This function initializes the lock by resetting the flags and turn. global flag turn flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 def lock ( self ): # This function is executed before entering the critical section. It sets the flag for the current thread and gives the turn to the other thread. global flag turn flag [ self ] = 1 turn = 1 - self while flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 and turn == 1 - self : pass def unlock ( self ): # This function is executed after leaving the critical section. It resets the flag for the current thread. global flag flag [ self ] = 0 def func ( s ): # This function is executed by each thread. It locks the critical section increments the shared variable and then unlocks the critical section. global ans self = s print ( f 'Thread Entered: { self } ' ) lock ( self ) for _ in range ( MAX ): ans += 1 unlock ( self ) def main (): # This is the main function where the threads are created and started. lock_init () t1 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 0 )) t2 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 1 )) t1 . start () t2 . start () t1 . join () t2 . join () print ( f 'Actual Count: { ans } | Expected Count: { MAX * 2 } ' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static flag = [ 0 0 ]; static turn = 0 ; static MAX = 1000000000 ; static ans = 0 ; // Function to acquire the lock static async lock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 1 ; PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn = 1 - self ; // Asynchronous loop with a small delay to yield while ( PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn == 1 - self ) { await new Promise ( resolve => setTimeout ( resolve 0 )); } } // Function to release the lock static unlock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // Function representing the critical section static func ( s ) { let i = 0 ; let self = s ; console . log ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); // Lock the critical section PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . lock ( self ). then (() => { // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX ; i ++ ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans ++ ; } // Release the lock PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . unlock ( self ); }); } // Main function static main () { // Create two threads (both run func) const t1 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 0 )); const t2 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); // Wait for the threads to end. setTimeout (() => { console . log ( 'Actual Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX * 2 ); } 1000 ); // Delay for a while to ensure threads finish } } // Define a simple Thread class for simulation class Thread { constructor ( func ) { this . func = func ; } start () { this . func (); } } // Run the main function PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . main ();
C++ // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include // Function to lock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was locked successfully } // Function to unlock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was unlocked successfully } // Function to create a pthread void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was created successfully } // Function to join a pthread void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was joined successfully } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
C // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert // statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
Python import threading import ctypes # Function to lock a thread lock def Thread_lock ( lock ): lock . acquire () # Acquire the lock # No need for assert in Python acquire will raise an exception if it fails # Function to unlock a thread lock def Thread_unlock ( lock ): lock . release () # Release the lock # No need for assert in Python release will raise an exception if it fails # Function to create a thread def Thread_create ( target args = ()): thread = threading . Thread ( target = target args = args ) thread . start () # Start the thread # No need for assert in Python thread.start() will raise an exception if it fails # Function to join a thread def Thread_join ( thread ): thread . join () # Wait for the thread to finish # No need for assert in Python thread.join() will raise an exception if it fails
Излаз:
Thread Entered: 1
Thread Entered: 0
Actual Count: 2000000000 | Expected Count: 2000000000