Hierholzerov algoritmus pre orientovaný graf

Daný riadený eulerovský graf je úlohou vytlačiť an Eulerov obvod . Eulerov okruh je cesta, ktorá prechádza každým okrajom grafu presne raz a končí na začiatočnom vrchole.
Poznámka: Daný graf obsahuje Eulerov obvod.
Príklad:
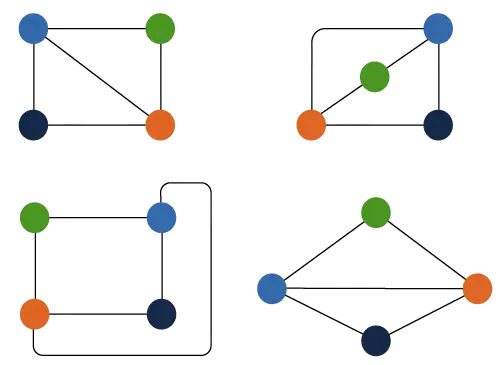
Vstup: Orientovaný graf

výstup: 0 3 4 0 2 1 0
Predpoklady:
- Diskutovali sme o problém zistiť, či je daný graf eulerovský alebo nie pre Neorientovaný graf
- Podmienky pre eulerovský obvod v riadenom grpag: (1) Všetky vrcholy patria do jedného silne prepojeného komponentu. (2) Všetky vrcholy majú rovnaký in-stupeň a vonkajší stupeň. Všimnite si, že pre neorientovaný graf je podmienka iná (všetky vrcholy majú párny stupeň)
Prístup:
- Zvoľte si ľubovoľný počiatočný vrchol v a sledujte stopu hrán z tohto vrcholu, až kým sa nevrátite do v. Nie je možné uviaznuť v inom vrchole ako v, pretože indegre a outdegre každého vrcholu musia byť rovnaké, keď stopa vstupuje do iného vrcholu w, musí tam byť nepoužitá hrana opúšťajúca w. Prehliadka vytvorená týmto spôsobom je uzavretá, ale nemusí pokrývať všetky vrcholy a okraje počiatočného grafu.
- Pokiaľ existuje vrchol u, ktorý patrí k aktuálnej prehliadke, ale má priľahlé okraje, ktoré nie sú súčasťou trasy, začnite ďalšiu trasu od u po nepoužívaných hranách, až kým sa nevrátite do u a pripojte sa k takto vytvorenej trase k predchádzajúcej trase.
Ilustrácia:
Vezmime si príklad vyššie uvedeného grafu s 5 uzlami: adj = {{2 3} {0} {1} {4} {0}}.
- Začnite vo vrchole 0 :
- Aktuálna cesta: [0]
- Okruh: []
- Vrchol 0 → 3 :
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3]
- Okruh: []
- Vertex 3 → 4 :
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4]
- Okruh: []
- Vrchol 4 → 0 :
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4 0]
- Okruh: []
- Vrchol 0 → 2 :
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4 0 2]
- Okruh: []
- Vertex 2 → 1 :
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4 0 2 1]
- Okruh: []
- Vrchol 1 → 0 :
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4 0 2 1 0]
- Okruh: []
- Návrat k vrcholu 0 : Pridajte 0 do obvodu.
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4 0 2 1]
- Okruh: [0]
- Návrat k vrcholu 1 : Pridajte 1 do okruhu.
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4 0 2]
- Okruh: [0 1]
- Späť na vrchol 2 : Pridajte 2 do okruhu.
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4 0]
- Okruh: [0 1 2]
- Návrat k vrcholu 0 : Pridajte 0 do obvodu.
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3 4]
- Okruh: [0 1 2 0]
- Návrat k vrcholu 4 : Pridajte 4 do obvodu.
- Aktuálna cesta: [0 3]
- Okruh: [0 1 2 0 4]
- Návrat k vrcholu 3 : Pridajte 3 do okruhu.
- Aktuálna cesta: [0]
- Okruh: [0 1 2 0 4 3]
- Návrat k vrcholu 0 : Pridajte 0 do obvodu.
- Aktuálna cesta: []
- Okruh: [0 1 2 0 4 3 0]
Nižšie je uvedená implementácia vyššie uvedeného prístupu:
C++ // C++ program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm #include using namespace std ; // Function to print Eulerian circuit vector < int > printCircuit ( vector < vector < int >> & adj ) { int n = adj . size (); if ( n == 0 ) return {}; // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 vector < int > currPath ; currPath . push_back ( 0 ); // list to store final circuit vector < int > circuit ; while ( currPath . size () > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath [ currPath . size () - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. size () > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj [ currNode ]. back (); adj [ currNode ]. pop_back (); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . push_back ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . push_back ( currPath . back ()); currPath . pop_back (); } } // reverse the result vector reverse ( circuit . begin () circuit . end ()); return circuit ; } int main () { vector < vector < int >> adj = {{ 2 3 } { 0 } { 1 } { 4 } { 0 }}; vector < int > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( auto v : ans ) cout < < v < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm import java.util.* ; class GfG { // Function to print Eulerian circuit static List < Integer > printCircuit ( List < List < Integer >> adj ) { int n = adj . size (); if ( n == 0 ) return new ArrayList <> (); // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 List < Integer > currPath = new ArrayList <> (); currPath . add ( 0 ); // list to store final circuit List < Integer > circuit = new ArrayList <> (); while ( currPath . size () > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath . get ( currPath . size () - 1 ); // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj . get ( currNode ). get ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () - 1 ); adj . get ( currNode ). remove ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () - 1 ); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . add ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . add ( currPath . get ( currPath . size () - 1 )); currPath . remove ( currPath . size () - 1 ); } } // reverse the result vector Collections . reverse ( circuit ); return circuit ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { List < List < Integer >> adj = new ArrayList <> (); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 2 3 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 0 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 1 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 4 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 0 ))); List < Integer > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( int v : ans ) System . out . print ( v + ' ' ); System . out . println (); } }
Python # Python program to print Eulerian circuit in given # directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm # Function to print Eulerian circuit def printCircuit ( adj ): n = len ( adj ) if n == 0 : return [] # Maintain a stack to keep vertices # We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 currPath = [ 0 ] # list to store final circuit circuit = [] while len ( currPath ) > 0 : currNode = currPath [ - 1 ] # If there's remaining edge in adjacency list # of the current vertex if len ( adj [ currNode ]) > 0 : # Find and remove the next vertex that is # adjacent to the current vertex nextNode = adj [ currNode ] . pop () # Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . append ( nextNode ) # back-track to find remaining circuit else : # Remove the current vertex and # put it in the circuit circuit . append ( currPath . pop ()) # reverse the result vector circuit . reverse () return circuit if __name__ == '__main__' : adj = [[ 2 3 ] [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 4 ] [ 0 ]] ans = printCircuit ( adj ) for v in ans : print ( v end = ' ' ) print ()
C# // C# program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Function to print Eulerian circuit static List < int > printCircuit ( List < List < int >> adj ) { int n = adj . Count ; if ( n == 0 ) return new List < int > (); // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 List < int > currPath = new List < int > { 0 }; // list to store final circuit List < int > circuit = new List < int > (); while ( currPath . Count > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath [ currPath . Count - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. Count > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj [ currNode ][ adj [ currNode ]. Count - 1 ]; adj [ currNode ]. RemoveAt ( adj [ currNode ]. Count - 1 ); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . Add ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . Add ( currPath [ currPath . Count - 1 ]); currPath . RemoveAt ( currPath . Count - 1 ); } } // reverse the result vector circuit . Reverse (); return circuit ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { List < List < int >> adj = new List < List < int >> { new List < int > { 2 3 } new List < int > { 0 } new List < int > { 1 } new List < int > { 4 } new List < int > { 0 } }; List < int > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); foreach ( int v in ans ) { Console . Write ( v + ' ' ); } Console . WriteLine (); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm // Function to print Eulerian circuit function printCircuit ( adj ) { let n = adj . length ; if ( n === 0 ) return []; // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 let currPath = [ 0 ]; // list to store final circuit let circuit = []; while ( currPath . length > 0 ) { let currNode = currPath [ currPath . length - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. length > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex let nextNode = adj [ currNode ]. pop (); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . push ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . push ( currPath . pop ()); } } // reverse the result vector circuit . reverse (); return circuit ; } let adj = [[ 2 3 ] [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 4 ] [ 0 ]]; let ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( let v of ans ) { console . log ( v ' ' ); }
Výstup
0 3 4 0 2 1 0
Časová zložitosť: O(V + E) kde V je počet vrcholov a E je počet hrán v grafe. Dôvodom je to, že algoritmus vykonáva vyhľadávanie do hĺbky (DFS) a navštevuje každý vrchol a každú hranu presne raz. Takže pre každý vrchol trvá O(1) čas, kým ho navštívi, a pre každú hranu trvá O(1) čas, kým ho prejde.
Zložitosť priestoru : O(V + E) ako algoritmus používa zásobník na uloženie aktuálnej cesty a zoznam na uloženie konečného obvodu. Maximálna veľkosť zásobníka môže byť prinajhoršom V + E, takže priestorová zložitosť je O(V + E).
Vytvoriť kvíz