Algoritmul de ștergere inversă pentru arborele de întindere minimă
 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; } Algoritmul de ștergere inversă este strâns legat de algoritmul lui Kruskal . În algoritmul lui Kruskal ceea ce facem este: Sortați muchiile în ordinea crescătoare a greutăților lor. După sortare, alegem unul câte unul marginile în ordine crescătoare. Includem marginea curentă selectată dacă prin includerea acesteia în arborele de întindere nu formăm niciun ciclu până când nu există muchii V-1 în arborele de întindere unde V = numărul de vârfuri.
În algoritmul de ștergere inversă sortăm toate marginile în scădere ordinea greutăților lor. După sortare, alegem unul câte unul marginile în ordine descrescătoare. Noi includeți marginea curentă selectată dacă excluderea marginii curente cauzează deconectarea în graficul curent . Ideea principală este ștergerea marginii dacă ștergerea acesteia nu duce la deconectarea graficului.
Algoritmul:
- Sortați toate marginile graficului în ordinea necrescătoare a greutăților marginilor.
- Inițializați MST ca grafic original și eliminați marginile suplimentare utilizând pasul 3.
- Alegeți cea mai mare margine de greutate din marginile rămase și verificați dacă ștergerea marginii deconectează graficul sau nu .
Dacă se deconectează, atunci nu ștergem marginea.
În caz contrar, ștergem marginea și continuăm.
Ilustrare:
Să înțelegem cu următorul exemplu:
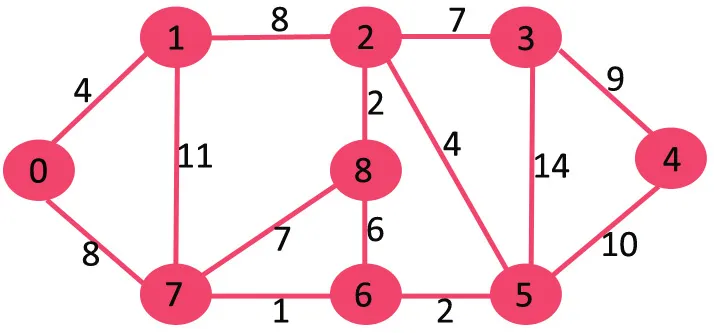
Dacă ștergem cea mai mare margine de greutate a greutății 14, graficul nu devine deconectat, așa că îl eliminăm.
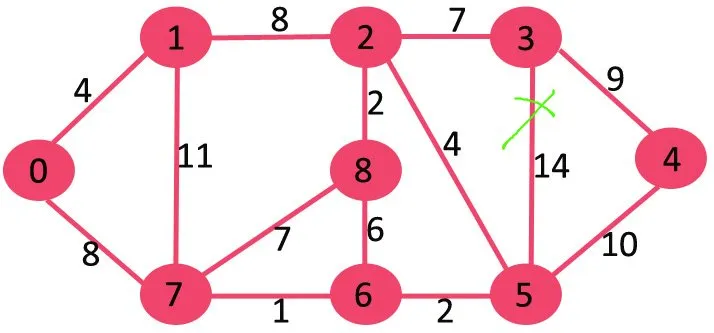
Apoi ștergem 11, deoarece ștergerea nu deconectează graficul.
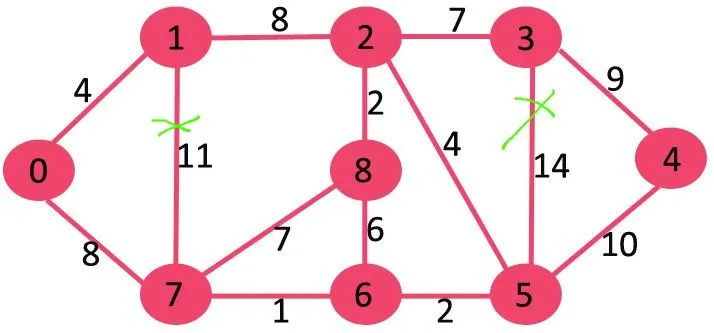
Apoi ștergem 10, deoarece ștergerea nu deconectează graficul.

Următorul este 9. Nu putem șterge 9 deoarece ștergerea acestuia provoacă deconectare.

Continuăm astfel și marginile următoare rămân în MST final.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
Notă: În cazul marginilor cu aceeași greutate, putem alege orice margine a marginilor cu aceeași greutate.
Practică recomandată Algoritmul de ștergere inversă pentru arborele de întindere minimă Încearcă!Implementare:
C++Java// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #includeusing namespace std ; // Creating shortcut for an integer pair typedef pair < int int > iPair ; // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { int V ; // No. of vertices list < int > * adj ; vector < pair < int iPair > > edges ; void DFS ( int v bool visited []); public : Graph ( int V ); // Constructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge ( int u int v int w ); // Returns true if graph is connected bool isConnected (); void reverseDeleteMST (); }; Graph :: Graph ( int V ) { this -> V = V ; adj = new list < int > [ V ]; } void Graph :: addEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ]. push_back ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ]. push_back ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . push_back ({ w { u v }}); } void Graph :: DFS ( int v bool visited []) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex list < int >:: iterator i ; for ( i = adj [ v ]. begin (); i != adj [ v ]. end (); ++ i ) if ( ! visited [ * i ]) DFS ( * i visited ); } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false bool Graph :: isConnected () { bool visited [ V ]; memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not void Graph :: reverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost sort ( edges . begin () edges . end ()); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST cout < < 'Edges in MST n ' ; // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . size () -1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges [ i ]. second . first ; int v = edges [ i ]. second . second ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ]. remove ( v ); adj [ v ]. remove ( u ); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( isConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ]. push_back ( v ); adj [ v ]. push_back ( u ); // This edge is part of MST cout < < '(' < < u < < ' ' < < v < < ') n ' ; mst_wt += edges [ i ]. first ; } } cout < < 'Total weight of MST is ' < < mst_wt ; } // Driver code int main () { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; Graph g ( V ); // making above shown graph g . addEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . addEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . addEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . addEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . addEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . addEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . addEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . addEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . addEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . addEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . addEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . addEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . addEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . addEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . reverseDeleteMST (); return 0 ; } Python3// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.* ; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable < Edge > { int u v w ; Edge ( int u int v int w ) { this . u = u ; this . w = w ; this . v = v ; } public int compareTo ( Edge other ) { return ( this . w - other . w ); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V ; // No. of vertices private List < Integer >[] adj ; private List < Edge > edges ; @SuppressWarnings ({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG ( int v ) // Constructor { V = v ; adj = new ArrayList [ v ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < v ; i ++ ) adj [ i ] = new ArrayList < Integer > (); edges = new ArrayList < Edge > (); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ] . add ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ] . add ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . add ( new Edge ( u v w )); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS ( int v boolean [] visited ) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for ( int i : adj [ v ] ) { if ( ! visited [ i ] ) DFS ( i visited ); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected () { boolean [] visited = new boolean [ V ] ; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) { if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; } return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections . sort ( edges ); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST System . out . println ( 'Edges in MST' ); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . size () - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges . get ( i ). u ; int v = edges . get ( i ). v ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ] . remove ( adj [ u ] . indexOf ( v )); adj [ v ] . remove ( adj [ v ] . indexOf ( u )); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( IsConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ] . add ( v ); adj [ v ] . add ( u ); // This edge is part of MST System . out . println ( '(' + u + ' ' + v + ')' ); mst_wt += edges . get ( i ). w ; } } System . out . println ( 'Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; GFG g = new GFG ( V ); // making above shown graph g . AddEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . AddEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . AddEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . AddEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . ReverseDeleteMST (); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_DeyC## Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph : def __init__ ( self v ): # No. of vertices self . v = v self . adj = [ 0 ] * v self . edges = [] for i in range ( v ): self . adj [ i ] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge ( self u : int v : int w : int ): self . adj [ u ] . append ( v ) # Add w to v’s list. self . adj [ v ] . append ( u ) # Add w to v’s list. self . edges . append (( w ( u v ))) def dfs ( self v : int visited : list ): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self . adj [ v ]: if not visited [ i ]: self . dfs ( i visited ) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected ( self ): visited = [ False ] * self . v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self . dfs ( 0 visited ) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range ( 1 self . v ): if not visited [ i ]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST ( self ): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self . edges . sort ( key = lambda a : a [ 0 ]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print ( 'Edges in MST' ) # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range ( len ( self . edges ) - 1 - 1 - 1 ): u = self . edges [ i ][ 1 ][ 0 ] v = self . edges [ i ][ 1 ][ 1 ] # Remove edge from undirected graph self . adj [ u ] . remove ( v ) self . adj [ v ] . remove ( u ) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self . connected () == False : self . adj [ u ] . append ( v ) self . adj [ v ] . append ( u ) # This edge is part of MST print ( '( %d %d )' % ( u v )) mst_wt += self . edges [ i ][ 0 ] print ( 'Total weight of MST is' mst_wt ) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph ( V ) # making above shown graph g . addEdge ( 0 1 4 ) g . addEdge ( 0 7 8 ) g . addEdge ( 1 2 8 ) g . addEdge ( 1 7 11 ) g . addEdge ( 2 3 7 ) g . addEdge ( 2 8 2 ) g . addEdge ( 2 5 4 ) g . addEdge ( 3 4 9 ) g . addEdge ( 3 5 14 ) g . addEdge ( 4 5 10 ) g . addEdge ( 5 6 2 ) g . addEdge ( 6 7 1 ) g . addEdge ( 6 8 6 ) g . addEdge ( 7 8 7 ) g . reverseDeleteMST () # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552JavaScript// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable < Edge > { public int u v w ; public Edge ( int u int v int w ) { this . u = u ; this . v = v ; this . w = w ; } public int CompareTo ( Edge other ) { return this . w . CompareTo ( other . w ); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V ; // No. of vertices private List < int > [] adj ; private List < Edge > edges ; public Graph ( int v ) // Constructor { V = v ; adj = new List < int > [ v ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < v ; i ++ ) adj [ i ] = new List < int > (); edges = new List < Edge > (); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ]. Add ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ]. Add ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . Add ( new Edge ( u v w )); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS ( int v bool [] visited ) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach ( int i in adj [ v ]) { if ( ! visited [ i ]) DFS ( i visited ); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected () { bool [] visited = new bool [ V ]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) { if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; } return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges . Sort (); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST Console . WriteLine ( 'Edges in MST' ); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . Count - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges [ i ]. u ; int v = edges [ i ]. v ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ]. Remove ( v ); adj [ v ]. Remove ( u ); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( IsConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ]. Add ( v ); adj [ v ]. Add ( u ); // This edge is part of MST Console . WriteLine ( '({0} {1})' u v ); mst_wt += edges [ i ]. w ; } } Console . WriteLine ( 'Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt ); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main ( string [] args ) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; Graph g = new Graph ( V ); // making above shown graph g . AddEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . AddEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . AddEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . AddEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . ReverseDeleteMST (); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
IeșireEdges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37Complexitatea timpului: O((E*(V+E)) + E log E) unde E este numărul de muchii.
Complexitatea spațiului: O(V+E) unde V este numărul de vârfuri și E este numărul de muchii. Folosim lista de adiacență pentru a stoca graficul, așa că avem nevoie de spațiu proporțional cu O(V+E).
Note:
- Implementarea de mai sus este o implementare simplă/naivă a algoritmului de ștergere inversă și poate fi optimizată la O(E log V (log log V) 3 ) [Sursa: O săptămână ]. Dar această complexitate optimizată a timpului este încă mai mică decât Prim şi Kruskal Algoritmi pentru MST.
- Implementarea de mai sus modifică graficul original. Putem crea o copie a graficului dacă graficul original trebuie păstrat.
Creați un test