Papel cortado em número mínimo de quadrados
Dado um papel retangular de dimensões a x b . A tarefa é cortar todo o papel no mínimo número de quadrado peças. Podemos escolher peças quadradas de qualquer tamanho, mas devem ser cortadas sem sobrepor ou deixar qualquer espaço extra .
Exemplos:
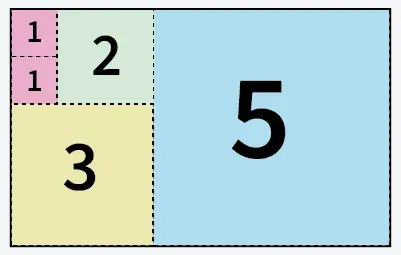
Entrada: uma = 5 b = 8
5 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 5 X 8
Saída: 5
Explicação: Podemos cortar o papel em 5 quadrados: 1 quadrado de tamanho 5x5 1 quadrado de tamanho 3x3 1 quadrado de tamanho 2x2 e 2 quadrados de tamanho 1x1.Entrada: uma = 13 b = 11
6 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 13 X 11
Saída: 6
Explicação: Podemos cortar o papel em 6 quadrados: 1 quadrado de tamanho 7x7 1 quadrado de tamanho 6x6 1 quadrado de tamanho 5x5 2 quadrados de tamanho 4x4 e 1 quadrado de tamanho 1x1.Entrada: uma = 6 b = 7
5 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 6 X 7
Saída: 5
Explicação: Podemos cortar o papel em 5 quadrados: 1 quadrado de tamanho 4x4 2 quadrados de tamanho 3x3 e 2 quadrados de tamanho 3x3.
Índice
- [Abordagem incorreta 1] Usando técnica gananciosa
- [Abordagem incorreta 2] Usando programação dinâmica
- [Abordagem Correta] Usando DFS e Programação Dinâmica
[Abordagem incorreta 1] Usando técnica gananciosa
À primeira vista, pode parecer que o problema pode ser facilmente resolvido cortando primeiro o maior quadrado possível do papel, seguido do corte do maior quadrado do papel restante e assim por diante, até cortarmos todo o papel. Mas esta solução está incorreta.
Por que a abordagem gananciosa não funciona?
Considere um papel de tamanho 6x7 então, se tentarmos cortar o papel com avidez, obteremos 7 quadrados: 1 quadrado de tamanho 6x6 e 6 quadrados de tamanho 1x1 enquanto a solução correta é: 5. Portanto, uma abordagem gananciosa não funcionará.
[Abordagem incorreta 2] Usando programação dinâmica
Programação Dinâmica com cortes verticais ou horizontais: Outra solução que pode parecer correta é usar Programação Dinâmica . Podemos manter uma tabela dp[][] tal que dp[i][j] = número mínimo de quadrados que podem ser cortados de papel de tamanho eu x j . Então para papel de tamanho axb
- Podemos tentar cortá-lo ao longo de cada linha: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) onde k pode estar no intervalo [1 i - 1].
- Podemos tentar cortá-lo ao longo de cada coluna: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) onde k pode estar no intervalo [1 j - 1].
Finalmente, o mínimo de todos os cortes será a resposta. Mas esta solução também está incorreta.
Por que cortar vertical ou horizontalmente com a Abordagem de Programação Dinâmica não funciona?
Isso não funcionará porque estamos assumindo que um corte vertical ou horizontal sempre dividirá o retângulo em duas partes. Considere um papel de tamanho 13x11 então, se tentarmos cortar o papel usando a abordagem DP, obteremos 8 quadrados, mas a resposta correta (como mostrado nos exemplos) é 6. Conseqüentemente, a Programação Dinâmica não funcionará.
[Abordagem Correta] Usando DFS e Programação Dinâmica
C++O ideia é cortar todo o papel usando DFS em baixo para cima maneiras. Em cada etapa, encontre o canto inferior esquerdo do papel e tente cortar quadrados de todos os tamanhos possíveis desse canto. Depois de cortar um quadrado novamente, encontre o canto esquerdo inferior do papel restante para cortar quadrados de todos os tamanhos possíveis e assim por diante. Mas se tentarmos todos os cortes possíveis a partir do canto inferior esquerdo de todos os tamanhos de papel possíveis, isso será bastante ineficiente. Podemos otimizá-lo usando Programação Dinâmica para armazenar cortes mínimos para cada tamanho de papel possível.
Para identificar exclusivamente qualquer tamanho de papel, podemos manter um array remSq[] tal que remSq[i] armazene o número de quadrados restantes de tamanho 1x1 na i-ésima coluna do papel. Portanto, para um papel de tamanho 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Além disso, para encontrar o canto inferior esquerdo, encontraremos o primeiro índice com o máximo de quadrados restantes. Portanto, podemos fazer o hash do valor do array remSq[] para encontrar uma chave exclusiva para todos os valores possíveis do array remSq[].
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include using namespace std ; // function to get the hash key for remSq array int getKey ( vector < int > & remSq int b ) { int base = 1 ; int key = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * base ); base = base * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array int minCutUtil ( vector < int > & remSq int a int b map < int int > & memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( memo . find ( key ) != memo . end ()) return memo [ key ]; int maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ]; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq == 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; vector < int > newRemSq = remSq ; int ans = INT_MAX ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( int i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } return memo [ key ] = ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b int minCut ( int a int b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a == b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns vector < int > remSq ( b a ); map < int int > memo ; return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } int main () { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb cout < < minCut ( a b ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.* ; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey ( int [] remSq int b ) { int base = 1 ; int key = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * base ); base = base * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil ( int [] remSq int a int b Map < Integer Integer > memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( memo . containsKey ( key )) return memo . get ( key ); int maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ] ; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq == 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; int [] newRemSq = Arrays . copyOf ( remSq b ); int ans = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( int i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math . min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } memo . put ( key ans ); return ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut ( int a int b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a == b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int [] remSq = new int [ b ] ; Arrays . fill ( remSq a ); Map < Integer Integer > memo = new HashMap <> (); return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System . out . println ( minCut ( a b )); } }
Python # Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey ( remSq b ): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range ( b ): key += remSq [ i ] * base base = base * ( b + 1 ) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey ( remSq b ) if key in memo : return memo [ key ] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range ( b ): if remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq : maxRemSq = remSq [ i ] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0 : return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq [:] ans = float ( 'inf' ) # Find the ending point of min height while end < b : # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq or newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 : break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range ( start end + 1 ): newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )) end += 1 memo [ key ] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut ( a b ): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b : return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [ a ] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ) if __name__ == '__main__' : # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print ( minCut ( a b ))
C# // C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey ( int [] remSq int b ) { int baseVal = 1 ; int key = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * baseVal ); baseVal = baseVal * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil ( int [] remSq int a int b Dictionary < int int > memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( memo . ContainsKey ( key )) return memo [ key ]; int maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ]; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq == 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; int [] newRemSq = ( int []) remSq . Clone (); int ans = int . MaxValue ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] != maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( int i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math . Min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } memo [ key ] = ans ; return ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut ( int a int b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a == b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int [] remSq = new int [ b ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) remSq [ i ] = a ; Dictionary < int int > memo = new Dictionary < int int > (); return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } static void Main () { int a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console . WriteLine ( minCut ( a b )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey ( remSq b ) { let base = 1 ; let key = 0 ; for ( let i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { key += ( remSq [ i ] * base ); base = base * ( b + 1 ); } return key ; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end ; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey ( remSq b ); if ( key in memo ) return memo [ key ]; let maxRemSq = 0 ; // Find the starting point of min height for ( let i = 0 ; i < b ; i ++ ) { if ( remSq [ i ] > maxRemSq ) { maxRemSq = remSq [ i ]; start = i ; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if ( maxRemSq === 0 ) return 0 ; end = start ; let newRemSq = remSq . slice (); let ans = Infinity ; // Find the ending point of min height while ( end < b ) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1 ; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if ( newRemSq [ end ] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq [ end ] - squareEdge < 0 ) break ; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for ( let i = start ; i <= end ; i ++ ) newRemSq [ i ] = maxRemSq - squareEdge ; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math . min ( ans 1 + minCutUtil ( newRemSq a b memo )); end += 1 ; } memo [ key ] = ans ; return ans ; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut ( a b ) { // if the given rectangle is a square if ( a === b ) return 1 ; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array ( b ). fill ( a ); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil ( remSq a b memo ); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11 ; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console . log ( minCut ( a b ));
Saída
6
Complexidade de tempo: O (a ^ b) para cada uma das b colunas podemos ter a quadrados.
Espaço Auxiliar: O(a^b) devido à memoização que armazena cada estado único.
 5 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 5 X 8
5 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 5 X 8  6 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 13 X 11
6 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 13 X 11  5 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 6 X 7
5 quadrados cortados de papel de tamanho 6 X 7