Classe Java.io.FilterOutputStream em Java
Classe java.io.FilterInputStream em Java

Java.io.FilterOutputStream class é a superclasse de todas as classes que filtram os fluxos de saída. O método write() da classe FilterOutputStream filtra os dados e os grava na filtragem de fluxo subjacente, que é feita dependendo dos Streams.
Declaração:
public class FilterOutputStream extends OutputStream
Construtores:
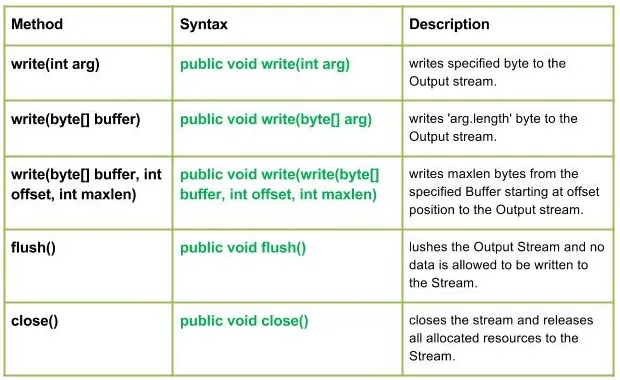
Métodos:
Sintaxe:
public void write(int arg) Parameters : arg : Source Bytes Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
// Java program illustrating the working of work(int arg) // method import java.io.* ; import java.lang.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // OutputStream FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream // initially null OutputStream geek_out = null ; FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null ; // FileInputStream used here FileInputStream geekinput = null ; char c ; int a ; try { // create output streams geek_out = new FileOutputStream ( 'GEEKS.txt' ); geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream ( geek_out ); // write(int arg) : Used to write 'M' in the file // - 'ABC.txt' geek_filter . write ( 77 ); // Flushes the Output Stream geek_filter . flush (); // Creating Input Stream geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'GEEKS.txt' ); // read() method of FileInputStream : // reading the bytes and converting next bytes to int a = geekinput . read (); /* Since read() converts bytes to int so we convert int to char for our program output*/ c = ( char ) a ; // print character System . out . println ( 'Character written by' + ' FilterOutputStream : ' + c ); } catch ( IOException except ) { // if any I/O error occurs System . out . print ( 'Write Not working properly' ); } finally { // releases any system resources associated with // the stream if ( geek_out != null ) geek_out . close (); if ( geek_filter != null ) geek_filter . close (); } } }
No programa que usei GEEKS.txt file o programa criará um novo arquivo com o nome fornecido no código e escreverá nele.
Saída :
Character written by FilterOutputStream : M
Sintaxe:
public void write(byte[] arg) Parameters : buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
// Java program illustrating the working of work(byte // buffer) method import java.io.* ; import java.lang.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // OutputStream FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream // initially null OutputStream geek_out = null ; FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null ; // FileInputStream used here FileInputStream geekinput = null ; byte [] buffer = { 77 79 72 73 84 }; char c ; int a ; try { // create output streams geek_out = new FileOutputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream ( geek_out ); // writes buffer to the output stream geek_filter . write ( buffer ); // forces byte contents to written out to the stream geek_filter . flush (); // create input streams geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); while (( a = geekinput . read ()) !=- 1 ) { // converts integer to the character c = ( char ) a ; // prints System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( IOException except ) { // if any I/O error occurs System . out . print ( 'Write Not working properly' ); } finally { // releases any system resources associated // with the stream if ( geek_out != null ) geek_out . close (); if ( geek_filter != null ) geek_filter . close (); } } }
No programa que eu uso GEEKS.txt file o programa criará um novo arquivo com o nome fornecido no código e escreverá nele.
Saída :
MOHIT
Sintaxe:
public void write(write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream Return : buffer : Source Buffer to be written offset : Starting offset maxlen : max no. of bytes to be written to the Output Stream Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
Sintaxe:
public void flush() Parameters : ------ Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
Sintaxe:
public void close() Parameters : ------ Return : void Exception : In case any I/O error occurs.
Programa Java ilustrando: métodos write (byte [] buffer int offset int maxlen) flush () close ()
// Java program illustrating the working of // write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) // flush() close() method import java.io.* ; import java.lang.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { // OutputStream FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream // initially null OutputStream geek_out = null ; FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null ; // FileInputStream used here FileInputStream geekinput = null ; byte [] buffer = { 65 66 77 79 72 73 84 }; char c ; int a ; try { // create output streams geek_out = new FileOutputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream ( geek_out ); // write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) : // writes buffer to the output stream // Here offset = 2 so it won't read first two bytes // then maxlen = 5 so it will print max of 5 characters geek_filter . write ( buffer 2 5 ); // forces byte contents to written out to the stream geek_filter . flush (); // create input streams geekinput = new FileInputStream ( 'ABC.txt' ); while (( a = geekinput . read ()) !=- 1 ) { // converts integer to the character c = ( char ) a ; // prints System . out . print ( c ); } } catch ( IOException except ) { // if any I/O error occurs System . out . print ( 'Write Not working properly' ); } finally { // releases any system resources associated // with the stream if ( geek_out != null ) geek_out . close (); if ( geek_filter != null ) geek_filter . close (); } } }
Observação :
No programa que eu uso GEEKS.txt file o programa criará um novo arquivo com o nome fornecido no código e escreverá nele.
Saída :
MOHIT
Você Pode Gostar
Principais Artigos
Categoria
Artigos Interessantes