Pares de verificação com determinado produto


Dada uma matriz arr [] de n inteiros distintos e um alvo Valor A tarefa é verificar se há um par de elementos na matriz cujo produto é igual ao destino.
Exemplos:
Entrada: arr [] = [1 5 7 -1 5] Alvo = 35
Saída: verdadeiro
Explicação: Como 5* 7 = 35 A resposta é verdadeira.Entrada: arr [] = [-10 20 9 -40] alvo = 30
Saída: falso
Explicação: Nenhum par existe com o produto 30
Tabela de conteúdo
- [Abordagem ingênua] gerando todos os pares possíveis - o (n^2) tempo e o (1) espaço
- [Abordagem melhor] Usando a técnica de dois ponteiros - o (n log (n)) tempo e o (1) espaço
- [Abordagem esperada] Usando hashset - o (n) tempo e o (n) espaço
[Abordagem ingênua] gerando todos os pares possíveis - O (n 2 ) Tempo e O (1) Espaço
C++A abordagem muito básica é gerar todos os pares possíveis e verificar se existe algum par cujo produto é igual ao valor alvo determinado e depois retornar verdadeiro . Se não existir esse par, retorne falso .
#include using namespace std ; // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target bool isProduct ( vector < int > & arr long long target ) { int n = arr . size (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( 1L L * arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; cout < < isProduct ( arr target ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
C #include #include // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target bool isProduct ( int arr [] int n long long target ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( 1L L * arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } int main () { int arr [] = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; int n = sizeof ( arr ) / sizeof ( arr [ 0 ]); printf ( '%d n ' isProduct ( arr n target )); return 0 ; }
Java class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target static boolean isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { int n = arr . length ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if (( long ) arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; System . out . println ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
Python # Function to check if any pair exists whose product # equals the target def is_product ( arr target ): n = len ( arr ) for i in range ( n - 1 ): for j in range ( i + 1 n ): if arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target : return True return False arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ] target = 35 print ( is_product ( arr target ))
C# using System ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target static bool IsProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { int n = arr . Length ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if (( long ) arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] == target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } static void Main () { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; Console . WriteLine ( IsProduct ( arr target )); } }
JavaScript // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target function isProduct ( arr target ) { let n = arr . length ; for ( let i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( arr [ i ] * arr [ j ] === target ) { return true ; } } } return false ; } let arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ]; let target = 35 ; console . log ( isProduct ( arr target ));
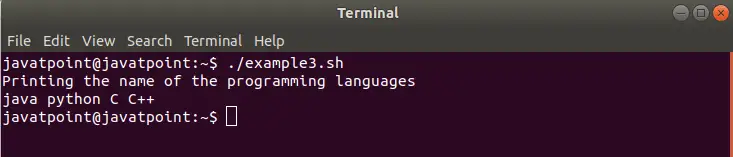
Saída
1
Complexidade do tempo: O (n²) para usar dois loops aninhados
Espaço auxiliar: O(1)
[Abordagem melhor] Usando a técnica de dois ponteiros - o (n log (n)) tempo e o (1) espaço
C++Também podemos usar a técnica de dois pontos para esse problema, mas é aplicável apenas a dados classificados. Então primeiro classifique a matriz e mantenha dois ponteiros um ponteiro no começo ( esquerda ) e outro no final ( certo ) da matriz. Em seguida, verifique o produto dos elementos nesses dois indicadores:
- Se o produto é igual ao alvo Encontramos o par.
- Se o produto for menor que o alvo mova o esquerda ponteiro para o certo para aumentar o produto.
- Se o produto for maior que o alvo mova o certo ponteiro para o esquerda Para diminuir o produto.
#include using namespace std ; // Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. bool isProduct ( vector < int > & arr long long target ) { // Sort the array sort ( arr . begin () arr . end ()); int left = 0 right = arr . size () - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long long currProd = 1L L * arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; cout < < isProduct ( arr target ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
C #include #include #include // Function to compare two integers (used in qsort) int compare ( const void * a const void * b ) { return ( * ( int * ) a - * ( int * ) b ); } // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. bool isProduct ( int arr [] int n long long target ) { // Sort the array qsort ( arr n sizeof ( int ) compare ); int left = 0 right = n - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long long currProd = ( long long ) arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } int main () { int arr [] = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; int n = sizeof ( arr ) / sizeof ( arr [ 0 ]); printf ( '%d n ' isProduct ( arr n target )); return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.Arrays ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. static boolean isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Sort the array Arrays . sort ( arr ); int left = 0 right = arr . length - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long currProd = ( long ) arr [ left ] * arr [ right ] ; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; System . out . println ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
Python # Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. def isProduct ( arr target ): # Sort the array arr . sort () left right = 0 len ( arr ) - 1 while left < right : # Calculate the current product currProd = arr [ left ] * arr [ right ] # If the product matches the target return True. if currProd == target : return True # Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if currProd > target : right -= 1 else : left += 1 return False if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ] target = 35 print ( isProduct ( arr target ))
C# using System ; using System.Linq ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. static bool isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Sort the array Array . Sort ( arr ); int left = 0 right = arr . Length - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product long currProd = ( long ) arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd == target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; Console . WriteLine ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
JavaScript // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. function isProduct ( arr target ) { // Sort the array arr . sort (( a b ) => a - b ); let left = 0 right = arr . length - 1 ; while ( left < right ) { // Calculate the current product let currProd = arr [ left ] * arr [ right ]; // If the product matches the target return true. if ( currProd === target ) return true ; // Move the pointers based on comparison with target. if ( currProd > target ) right -- ; else left ++ ; } return false ; } let arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ]; let target = 35 ; console . log ( isProduct ( arr target ));
Saída
1
Complexidade do tempo: O (n log (n)) para classificar a matriz
Espaço auxiliar: O(1)
[Abordagem esperada] Usando hashset - o (n) tempo e o (n) espaço
C++Podemos usar um Conjunto de hash Para procurar com eficiência. À medida que iteramos através da matriz, verificamos se cada número é um fator do alvo. Se for, então vemos se seu fator correspondente já está no conjunto. Se sim, voltamos verdadeiro ; Caso contrário, adicionamos o número atual ao conjunto e continuamos.
#include #include #include using namespace std ; // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. bool isProduct ( vector < int > & arr long long target ) { // Use an unordered set to store previously seen numbers. unordered_set < int > st ; for ( int num : arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 return true. if ( target == 0 && num == 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of the target. if ( target % num == 0 ) { int secondNum = target / num ; // If the secondNum has been seen before return true. if ( st . find ( secondNum ) != st . end ()) { return true ; } // Mark the current number as seen. st . insert ( num ); } } return false ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 1 5 7 -1 5 }; long long target = 35 ; cout < < isProduct ( arr target ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.HashSet ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. static boolean isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Use a hash set to store previously seen numbers. HashSet < Integer > set = new HashSet <> (); for ( int num : arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 // return true. if ( target == 0 && num == 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of // the target. if ( target % num == 0 ) { int secondNum = ( int )( target / num ); // If the secondNum has been seen before // return true. if ( set . contains ( secondNum )) return true ; // Mark the current number as seen. set . add ( num ); } } return false ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; System . out . println ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
Python # Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals the target. def isProduct ( arr target ): # Use a set to store previously seen numbers. st = set () for num in arr : # If target is 0 and current number is 0 return True. if target == 0 and num == 0 : return True # Check if current number can be a factor of the target. if target % num == 0 : secondNum = target // num # If the secondNum has been seen before return True. if secondNum in st : return True # Mark the current number as seen. st . add ( num ) return False if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ] target = 35 print ( isProduct ( arr target ))
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Function to check if any pair exists whose product // equals the target. static bool isProduct ( int [] arr long target ) { // Use a hash set to store previously seen numbers. HashSet < int > set = new HashSet < int > (); foreach ( int num in arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 // return true. if ( target == 0 && num == 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of // the target. if ( target % num == 0 ) { int secondNum = ( int )( target / num ); // If the secondNum has been seen before // return true. if ( set . Contains ( secondNum )) return true ; // Mark the current number as seen. set . Add ( num ); } } return false ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int [] arr = { 1 5 7 - 1 5 }; long target = 35 ; Console . WriteLine ( isProduct ( arr target )); } }
JavaScript // Function to check if any pair exists whose product equals // the target. function isProduct ( arr target ) { // Use a set to store previously seen numbers. let seen = new Set (); for ( let num of arr ) { // If target is 0 and current number is 0 return // true. if ( target === 0 && num === 0 ) return true ; // Check if current number can be a factor of the // target. if ( target % num === 0 ) { let secondNum = target / num ; // If the secondNum has been seen before return // true. if ( seen . has ( secondNum )) return true ; // Mark the current number as seen. seen . add ( num ); } } return false ; } let arr = [ 1 5 7 - 1 5 ]; let target = 35 ; console . log ( isProduct ( arr target ));
Saída
1
Complexidade do tempo: O (n) para iteração única
Espaço auxiliar: O (n) para armazenar elementos no conjunto de hash