Praca z plikami zip w Pythonie

W tym artykule wyjaśniono, jak można wykonywać różne operacje na pliku ZIP za pomocą prostego programu w języku Python. Co to jest plik zip? ZIP to format pliku archiwum obsługujący bezstratną kompresję danych. Przez kompresję bezstratną rozumiemy, że algorytm kompresji pozwala na doskonałą rekonstrukcję oryginalnych danych na podstawie skompresowanych danych. Zatem plik ZIP to pojedynczy plik zawierający jeden lub więcej skompresowanych plików, co stanowi idealny sposób na zmniejszenie dużych plików i przechowywanie powiązanych plików razem. Dlaczego potrzebujemy plików zip?  Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod w kawałkach:
Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod w kawałkach:  Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python
Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python  Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod dzieląc go na fragmenty:
Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod dzieląc go na fragmenty: 
- Aby zmniejszyć wymagania dotyczące przechowywania.
- Aby poprawić prędkość transferu w przypadku standardowych połączeń.
1. Wyodrębnianie pliku zip
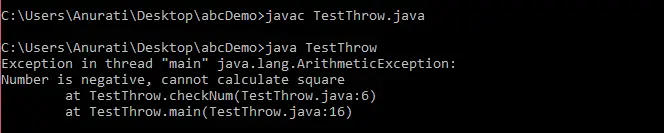
Python # importing required modules from zipfile import ZipFile # specifying the zip file name file_name = 'my_python_files.zip' # opening the zip file in READ mode with ZipFile ( file_name 'r' ) as zip : # printing all the contents of the zip file zip . printdir () # extracting all the files print ( 'Extracting all the files now...' ) zip . extractall () print ( 'Done!' )
The above program extracts a zip file named 'my_python_files.zip' in the same directory as of this python script. The output of above program may look like this:  Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod w kawałkach:
Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod w kawałkach: -
from zipfile import ZipFile
ZipFile is a class of zipfile module for reading and writing zip files. Here we import only class ZipFile from zipfile module. -
with ZipFile(file_name 'r') as zip:
Here a ZipFile object is made by calling ZipFile constructor which accepts zip file name and mode parameters. We create a ZipFile object in CZYTAĆ mode i nadaj mu nazwę zamek błyskawiczny . -
zip.printdir()
katalog wydruku() metoda drukuje spis treści archiwum. -
zip.extractall()
ekstrakt() metoda wyodrębni całą zawartość pliku zip do bieżącego katalogu roboczego. Możesz także zadzwonić ekstrakt() method to extract any file by specifying its path in the zip file. For example:zip.extract('python_files/python_wiki.txt')This will extract only the specified file. If you want to read some specific file you can go like this:data = zip.read(name_of_file_to_read)
2. Zapis do pliku zip
Rozważ katalog (folder) o takim formacie: Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python
Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python # importing required modules from zipfile import ZipFile import os def get_all_file_paths ( directory ): # initializing empty file paths list file_paths = [] # crawling through directory and subdirectories for root directories files in os . walk ( directory ): for filename in files : # join the two strings in order to form the full filepath. filepath = os . path . join ( root filename ) file_paths . append ( filepath ) # returning all file paths return file_paths def main (): # path to folder which needs to be zipped directory = './python_files' # calling function to get all file paths in the directory file_paths = get_all_file_paths ( directory ) # printing the list of all files to be zipped print ( 'Following files will be zipped:' ) for file_name in file_paths : print ( file_name ) # writing files to a zipfile with ZipFile ( 'my_python_files.zip' 'w' ) as zip : # writing each file one by one for file in file_paths : zip . write ( file ) print ( 'All files zipped successfully!' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
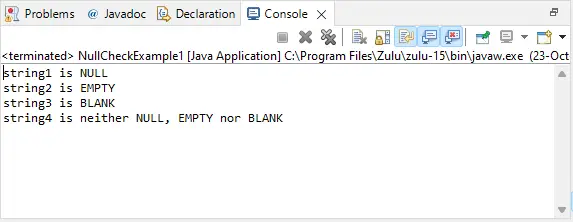
The output of above program looks like this:  Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod dzieląc go na fragmenty:
Spróbujmy zrozumieć powyższy kod dzieląc go na fragmenty: -
def get_all_file_paths(directory): file_paths = [] for root directories files in os.walk(directory): for filename in files: filepath = os.path.join(root filename) file_paths.append(filepath) return file_paths
First of all to get all file paths in our directory we have created this function which uses the os.walk() metoda. W każdej iteracji wszystkie pliki znajdujące się w tym katalogu są dołączane do listy o nazwie ścieżki_plików . Na koniec zwracamy wszystkie ścieżki plików. -
file_paths = get_all_file_paths(directory)
Here we pass the directory to be zipped to the get_all_file_paths() funkcję i uzyskać listę zawierającą wszystkie ścieżki plików. -
with ZipFile('my_python_files.zip''w') as zip:Here we create a ZipFile object in WRITE mode this time. -
for file in file_paths: zip.write(file)
Here we write all the files to the zip file one by one using pisać metoda.
3. Uzyskiwanie wszystkich informacji o pliku ZIP
Python # importing required modules from zipfile import ZipFile import datetime # specifying the zip file name file_name = 'example.zip' # opening the zip file in READ mode with ZipFile ( file_name 'r' ) as zip : for info in zip . infolist (): print ( info . filename ) print ( ' t Modified: t ' + str ( datetime . datetime ( * info . date_time ))) print ( ' t System: tt ' + str ( info . create_system ) + '(0 = Windows 3 = Unix)' ) print ( ' t ZIP version: t ' + str ( info . create_version )) print ( ' t Compressed: t ' + str ( info . compress_size ) + ' bytes' ) print ( ' t Uncompressed: t ' + str ( info . file_size ) + ' bytes' )
The output of above program may look like this: 
for info in zip.infolist():Here informator() metoda tworzy instancję Informacje o ZipInfo class, która zawiera wszystkie informacje o pliku ZIP. Możemy uzyskać dostęp do wszystkich informacji, takich jak data ostatniej modyfikacji plików, system nazw plików, w którym pliki zostały utworzone. Wersja ZIP, rozmiar plików w formie skompresowanej i nieskompresowanej itp. Autorem tego artykułu jest: Nihil Kumar . Utwórz quiz