Efektywnie projektuj zapytania wstawiające, usuwające i medianujące w zestawie
Biorąc pod uwagę początkowo pusty zbiór i liczbę zapytań na jego temat, każdy z możliwych typów:
- Wstawianie „x” odbywa się za pomocą aktualizacji (1 0 10^6 x 1). Należy zauważyć, że korzeń drzewa jest przekazywany jako indeks początkowy jako 0 i indeks końcowy jako 10^6, dzięki czemu wszystkie zakresy posiadające x zostaną zaktualizowane.
- Usuwanie „x” odbywa się za pomocą aktualizacji (1 0 10^6 x -1). Należy zauważyć, że korzeń drzewa jest przekazywany jako indeks początkowy jako 0 i indeks końcowy jako 10^6, dzięki czemu wszystkie zakresy posiadające x zostaną zaktualizowane.
Przykład:
Input : Insert 1 Insert 4 Insert 7 Median Output : The first three queries should insert 1 4 and 7 into an empty set. The fourth query should return 4 (median of 1 4 7).
Dla celów poglądowych zakładamy, co następuje, ale założenia te nie stanowią ograniczeń omawianej tutaj metody:
1. W każdym przypadku wszystkie elementy są różne i żaden z nich nie występuje więcej niż raz.
2. Zapytanie o medianę wykonujemy tylko wtedy, gdy w zbiorze znajduje się nieparzysta liczba elementów. (w przypadku liczb parzystych będziemy musieli wykonać dwa zapytania na naszym drzewie segmentowym)
3. Elementy w zestawie mieszczą się w zakresie od 1 do +10^6.
Metoda 1 (naiwna)
W naiwnej implementacji możemy wykonać dwa pierwsze zapytania w O(1), a ostatnie zapytanie w O(max_elem), gdzie max_elem jest maksymalnym elementem wszystkich czasów (w tym usuniętymi elementami).
Załóżmy tablicę liczyć[] (o rozmiarze 10^6 + 1), aby zachować liczbę każdego elementu w podzbiorze. Poniżej znajdują się proste i oczywiste algorytmy dla 3 zapytań:
Wstaw zapytanie x:
count[x]++; if (x > max_elem) max_elem = x; n++;
Usuń x zapytanie:
if (count[x] > 0) count[x]--; n--;
Mediana zapytania:
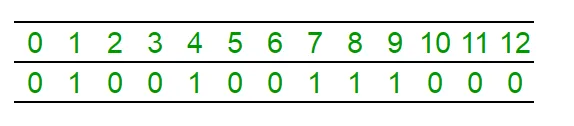
sum = 0; i = 0; while( sum <= n / 2 ) { i++; sum += count[i]; } median = i; return median; Ilustracja tablicy count[] reprezentującej zbiór {1 4 7 8 9}, w którym elementem mediany jest „7”:

Zapytanie „Mediana” ma na celu znalezienie (n + 1)/2-tej „1” w tablicy, w tym przypadku trzeciej „1”; teraz robimy to samo, używając drzewa segmentowego.
Metoda 2 (przy użyciu Drzewo segmentowe )
Wykonujemy drzewo segmentowe do przechowywania sumy przedziałów, gdzie przedział [a b] reprezentuje liczbę elementów znajdujących się w zbiorze aktualnie w zakresie [a b]. Na przykład, jeśli rozważymy powyższy przykład zapytanie (3 7) zwraca 2 zapytanie (4 4) zwraca 1 zapytanie (5 5) zwraca 0.
Zapytania wstawiające i usuwające są proste i oba można zaimplementować za pomocą funkcji update(int x int diff) (dodaje „diff” przy indeksie „x”)
Algorytm
// adds ‘diff’ at index ‘x’ update(node a b x diff) // If leaf node If a == b and a == x segmentTree[node] += diff // If non-leaf node and x lies in its range If x is in [a b] // Update children recursively update(2*node a (a + b)/2 x diff) update(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b x diff) // Update node segmentTree[node] = segmentTree[2 * node] + segmentTree[2 * node + 1]
Działa powyższa funkcja rekurencyjna O(log(max_elem)) (w tym przypadku max_elem wynosi 10^6) i służy zarówno do wstawiania, jak i usuwania za pomocą następujących wywołań:
Teraz funkcja znajdowania indeksu z k-tym „1”, gdzie „k” w tym przypadku zawsze będzie wynosić (n + 1) / 2. Będzie to działać podobnie do wyszukiwania binarnego, możesz o nim myśleć jak o rekursywnej funkcji wyszukiwania binarnego w drzewie segmentów.
Weźmy przykład, aby zrozumieć, że nasz zbiór ma obecnie elementy { 1 4 7 8 9 } i dlatego jest reprezentowany przez następujące drzewo segmentowe.
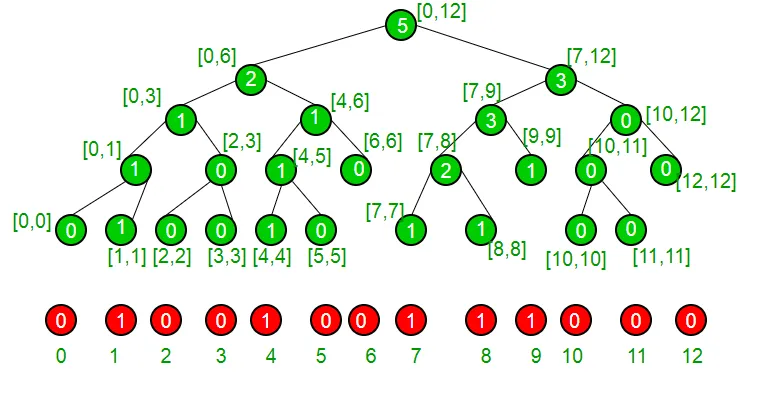
Jeśli jesteśmy w węźle innym niż liść, jesteśmy pewni, że ma on oboje dzieci. Widzimy, czy lewe dziecko ma większą lub równą liczbę jedynek jak „k”. Jeśli tak, jesteśmy pewni, że nasz indeks leży w lewym poddrzewie. W przeciwnym razie, jeśli lewe poddrzewo ma mniejszą liczbę jedynek niż k, to jesteśmy pewni, że nasz indeks leży w prawym poddrzewie. Robimy to rekurencyjnie, aby dotrzeć do naszego indeksu i stamtąd go zwracamy.
Algorytm
1.findKth(node a b k) 2. If a != b 3. If segmentTree[ 2 * node ] >= k 4. return findKth(2*node a (a + b)/2 k) 5. else 6. return findKth(2*node + 1 (a + b)/2 + 1 b k - segmentTree[ 2 * node ]) 7. else 8. return a
Działa powyższa funkcja rekurencyjna O(log(max_elem) ) .
// A C++ program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree #include #define maxn 3000005 #define max_elem 1000000 using namespace std ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. int segmentTree [ maxn ]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. void update ( int node int a int b int x int diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' is in its // range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree int findKth ( int node int a int b int k ) { // non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 k ); // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]); } // if at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return ( segmentTree [ node ]) ? a : -1 ; } // insert x in the set void insert ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // delete x from the set void delete ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x -1 ); } // returns median element of the set with odd // cardinality only int median () { int k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code int main () { insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); cout < < 'Median for the set {147} = ' < < median () < < endl ; insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); cout < < 'Median for the set {14789} = ' < < median () < < endl ; delete ( 1 ); delete ( 8 ); cout < < 'Median for the set {479} = ' < < median () < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree import java.io.* ; class GFG { public static int maxn = 3000005 ; public static int max_elem = 1000000 ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int [] segmentTree = new int [ maxn ] ; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update ( int node int a int b int x int diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ] ; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth ( int node int a int b int k ) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) { return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 k ); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ] ); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return ( segmentTree [ node ] != 0 ) ? a : - 1 ; } // Insert x in the set public static void insert ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median () { int k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); System . out . println ( 'Median for the set {147} = ' + median ()); insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); System . out . println ( 'Median for the set {14789} = ' + median ()); delete ( 1 ); delete ( 8 ); System . out . println ( 'Median for the set {479} = ' + median ()); } } // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Python3 # A Python3 program to implement insert delete and # median queries using segment tree maxn = 3000005 max_elem = 1000000 # A global array to store segment tree. # Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. segmentTree = [ 0 for i in range ( maxn )] # Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. # Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and # 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored # in current node. # 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. def update ( node a b x diff ): global segmentTree # If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b and a == x ): # add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff return # If current node is non-leaf and 'x' is in its # range if ( x >= a and x <= b ): # update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) // 2 x diff ) update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) // 2 + 1 b x diff ) # Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ] # Returns k'th node in segment tree def findKth ( node a b k ): global segmentTree # non-leaf node will definitely have both # children left and right if ( a != b ): # If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ): return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) // 2 k ) # If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) // 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]) # if at a leaf node return the index it stores # information about return a if ( segmentTree [ node ]) else - 1 # insert x in the set def insert ( x ): update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ) # delete x from the set def delete ( x ): update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ) # returns median element of the set with odd # cardinality only def median (): k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) // 2 return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__' : insert ( 1 ) insert ( 4 ) insert ( 7 ) print ( 'Median for the set {147} =' median ()) insert ( 8 ) insert ( 9 ) print ( 'Median for the set {14789} =' median ()) delete ( 1 ) delete ( 8 ) print ( 'Median for the set {479} =' median ()) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C# // A C# program to implement insert delete // and median queries using segment tree using System ; class GFG { public static int maxn = 3000005 ; public static int max_elem = 1000000 ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. public static int [] segmentTree = new int [ maxn ]; // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. public static void update ( int node int a int b int x int diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree public static int findKth ( int node int a int b int k ) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) { return findKth ( node * 2 a ( a + b ) / 2 k ); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 ( a + b ) / 2 + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it // stores information about if ( segmentTree [ node ] != 0 ) { return a ; } else { return - 1 ; } } // Insert x in the set public static void insert ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // Delete x from the set public static void delete ( int x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only public static int median () { int k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code static public void Main () { insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Median for the set {147} = ' + median ()); insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Median for the set {14789} = ' + median ()); delete ( 1 ); delete ( 8 ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Median for the set {479} = ' + median ()); } } // This code is contributed by rag2127
JavaScript < script > // A Javascript program to implement insert delete and // median queries using segment tree let maxn = 3000005 ; let max_elem = 1000000 ; // A global array to store segment tree. // Note: Since it is global all elements are 0. let segmentTree = new Array ( maxn ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < maxn ; i ++ ) { segmentTree [ i ] = 0 ; } // Update 'node' and its children in segment tree. // Here 'node' is index in segmentTree[] 'a' and // 'b' are starting and ending indexes of range stored // in current node. // 'diff' is the value to be added to value 'x'. function update ( node a b x diff ) { // If current node is a leaf node if ( a == b && a == x ) { // Add 'diff' and return segmentTree [ node ] += diff ; return ; } // If current node is non-leaf and 'x' // is in its range if ( x >= a && x <= b ) { // Update both sub-trees left and right update ( node * 2 a Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) x diff ); update ( node * 2 + 1 Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) + 1 b x diff ); // Finally update current node segmentTree [ node ] = segmentTree [ node * 2 ] + segmentTree [ node * 2 + 1 ]; } } // Returns k'th node in segment tree function findKth ( node a b k ) { // Non-leaf node will definitely have both // children; left and right if ( a != b ) { // If kth element lies in the left subtree if ( segmentTree [ node * 2 ] >= k ) { return findKth ( node * 2 a Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) k ); } // If kth one lies in the right subtree return findKth ( node * 2 + 1 Math . floor (( a + b ) / 2 ) + 1 b k - segmentTree [ node * 2 ]); } // If at a leaf node return the index it stores // information about return ( segmentTree [ node ] != 0 ) ? a : - 1 ; } // Insert x in the set function insert ( x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x 1 ); } // Delete x from the set function delet ( x ) { update ( 1 0 max_elem x - 1 ); } // Returns median element of the set // with odd cardinality only function median () { let k = ( segmentTree [ 1 ] + 1 ) / 2 ; return findKth ( 1 0 max_elem k ); } // Driver code insert ( 1 ); insert ( 4 ); insert ( 7 ); document . write ( 'Median for the set {147} = ' + median () + '
' ); insert ( 8 ); insert ( 9 ); document . write ( 'Median for the set {14789} = ' + median () + '
' ); delet ( 1 ); delet ( 8 ); document . write ( 'Median for the set {479} = ' + median () + '
' ); // This code is contributed by unknown2108 < /script>
Wyjście:
Median for the set {147} = 4 Median for the set {14789} = 7 Median for the set {479} = 7
Wniosek:
Uruchomione są wszystkie trzy zapytania O(log(max_elem) ) w tym przypadku max_elem = 10^6, więc log(max_elem) jest w przybliżeniu równy 20.
Drzewo segmentowe wykorzystuje O(max_elem) przestrzeń.
Gdyby nie było zapytania o usunięcie, problem można było rozwiązać również za pomocą znanego algorytmu Tutaj .
Może Ci Się Spodobać
Najpopularniejsze Artykuły
Kategoria
Ciekawe Artykuły