Odległość najbliższej komórki mającej 1 w macierzy binarnej

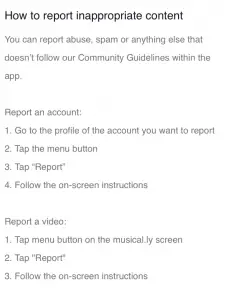
Biorąc pod uwagę plik binarny siatka[][] . Znajdź odległość najbliższego 1 w siatce dla każdej komórki.
Odległość jest obliczana jako |tj 1 - I 2 | + |j 1 - J 2 | gdzie ja 1 J 1 to numer wiersza i numer kolumny bieżącej komórki oraz i 2 J 2 to numer wiersza i numer kolumny najbliższej komórki o wartości 1.
Notatka: W siatce powinna znajdować się co najmniej jedna komórka o wartości 1.
Przykłady:
Wejście: siatka[][] = [[0 1 1 0]
[1 1 0 0]
[0 0 1 1]]
Wyjście: [[1 0 0 1]
[0 0 1 1]
[1 1 0 0]]
Wyjaśnienie:
komórka (0 1) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (0 0) - odległość = |0-0| + |0-1| = 1
komórka (0 2) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (0 3) - odległość = |0-0| + |3-2| = 1
komórka (1 0) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (0 0) - odległość = |1-0| + |0-0| = 1
komórka (1 1) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (1 2) - odległość = |1-1| + |1-2| = 1
komórka (2 2) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (2 1) - odległość = |2-2| + |2-1| = 1
komórka (2 3) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (1 3) - odległość = |2-1| + |3-3| = 1
Reszta to komórki mające 1, więc ich odległość od najbliższej komórki mającej 1 wynosi 0.Wejście: siatka[][] = [[1 0 1]
[1 1 0]
[1 0 0]]
Wyjście: [[0 1 0]
[0 0 1]
[0 1 2]]
Wyjaśnienie:
komórka (0 0) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (0 1) - odległość = |0-0| + |0-1| = 1
komórka (0 2) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (0 1) - odległość = |0-0| + |2-1| = 1
komórka (1 0) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (0 1) - odległość = |1-0| + |0-1| = 2
komórka (1 1) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (1 2) - odległość = |1-1| + |1-2| = 1
komórka (2 0) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (2 1) - odległość = |2-2| + |2-1| = 1
komórka (2 2) ma najbliższą 1 w komórce (2 1) - odległość = |2-2| + |2-1| = 1
Reszta to komórki mające 1, więc ich odległość od najbliższej komórki mającej 1 wynosi 0.
Spis treści
- [Podejście naiwne] - O((n*m)^2) Czas i O(n * m) Przestrzeń
- [Podejście oczekiwane] — Korzystanie z wyszukiwania wszerz — O(n * m) czasu i O(n * m) przestrzeni
[Podejście naiwne] - O((n*m)^2) Czas i O(n * m) Przestrzeń
C++Pomysł polega na tym, aby przejść przez całą siatkę i obliczyć odległość każdej komórki z dokładnością do 1:
- Jeśli komórka zawiera 1, jej odległość wynosi 0.
- Jeśli komórka zawiera 0, przemierzamy całą siatkę, aby znaleźć najbliższą komórkę zawierającą 1.
- Dla każdej komórki 0 oblicz odległość Manhattanu do wszystkich komórek z liczbą 1 i przyjmij odległość minimalną.
Zapisz tę minimalną odległość w odpowiedniej komórce macierzy wyników. Powtórz tę czynność dla wszystkich komórek siatki.
//Driver Code Starts #include #include #include using namespace std ; //Driver Code Ends vector < vector < int >> nearest ( vector < vector < int >> & grid ) { int n = grid . size (); int m = grid [ 0 ]. size (); vector < vector < int >> ans ( n vector < int > ( m INT_MAX )); // visit each cell of the grid for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // if the cell has 1 // then the distance is 0 if ( grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 ; continue ; } // iterate over all the cells // and find the distance of the nearest 1 for ( int k = 0 ; k < n ; k ++ ) { for ( int l = 0 ; l < m ; l ++ ) { if ( grid [ k ][ l ] == 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = min ( ans [ i ][ j ] abs ( i - k ) + abs ( j - l )); } } } } } return ans ; } //Driver Code Starts int main () { vector < vector < int >> grid = {{ 0 1 1 0 } { 1 1 0 0 } { 0 0 1 1 }}; vector < vector < int >> ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < ans . size (); i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < ans [ i ]. size (); j ++ ) { cout < < ans [ i ][ j ] < < ' ' ; } cout < < endl ; } return 0 ; } //Driver Code Ends
Java //Driver Code Starts import java.util.ArrayList ; class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nearest ( int [][] grid ) { int n = grid . length ; int m = grid [ 0 ] . length ; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer > > ans = new ArrayList <> (); // initialize all cells with maximum value for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { ArrayList < Integer > row = new ArrayList <> (); for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { row . add ( Integer . MAX_VALUE ); } ans . add ( row ); } // visit each cell of the grid for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // if the cell has 1 distance is 0 if ( grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { ans . get ( i ). set ( j 0 ); continue ; } // iterate over all cells to find nearest 1 for ( int k = 0 ; k < n ; k ++ ) { for ( int l = 0 ; l < m ; l ++ ) { if ( grid [ k ][ l ] == 1 ) { int distance = Math . abs ( i - k ) + Math . abs ( j - l ); if ( distance < ans . get ( i ). get ( j )) { ans . get ( i ). set ( j distance ); } } } } } } return ans ; } //Driver Code Starts public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [][] grid = { { 0 1 1 0 } { 1 1 0 0 } { 0 0 1 1 } }; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer > > ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > row : ans ) { for ( Integer val : row ) { System . out . print ( val + ' ' ); } System . out . println (); } } } //Driver Code Ends
Python def nearest ( grid ): n = len ( grid ) m = len ( grid [ 0 ]) ans = [[ float ( 'inf' )] * m for _ in range ( n )] # visit each cell of the grid for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( m ): # if the cell has 1 # then the distance is 0 if grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 : ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 continue # iterate over all the cells # and find the distance of the nearest 1 for k in range ( n ): for l in range ( m ): if grid [ k ][ l ] == 1 : ans [ i ][ j ] = min ( ans [ i ][ j ] abs ( i - k ) + abs ( j - l )) return ans #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == '__main__' : grid = [[ 0 1 1 0 ] [ 1 1 0 0 ] [ 0 0 1 1 ]] ans = nearest ( grid ) for i in range ( len ( ans )): for j in range ( len ( ans [ i ])): print ( ans [ i ][ j ] end = ' ' ) print () #Driver Code Ends
C# //Driver Code Starts using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { //Driver Code Ends static List < List < int > > nearest ( int [ ] grid ) { int n = grid . GetLength ( 0 ); int m = grid . GetLength ( 1 ); List < List < int > > ans = new List < List < int > > (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { List < int > row = new List < int > (); for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { row . Add ( int . MaxValue ); } ans . Add ( row ); } // Visit each cell of the grid for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // If the cell has 1 distance is 0 if ( grid [ i j ] == 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 ; continue ; } // iterate over all the cells // and find the distance of the nearest 1 for ( int k = 0 ; k < n ; k ++ ) { for ( int l = 0 ; l < m ; l ++ ) { if ( grid [ k l ] == 1 ) { int distance = Math . Abs ( i - k ) + Math . Abs ( j - l ); if ( distance < ans [ i ][ j ]) { ans [ i ][ j ] = distance ; } } } } } } return ans ; } //Driver Code Starts static void Main () { int [ ] grid = { { 0 1 1 0 } { 1 1 0 0 } { 0 0 1 1 } }; List < List < int > > ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < ans . Count ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < ans [ i ]. Count ; j ++ ) { Console . Write ( ans [ i ][ j ] + ' ' ); } Console . WriteLine (); } } } //Driver Code Ends
JavaScript function nearest ( grid ) { let n = grid . length ; let m = grid [ 0 ]. length ; let ans = new Array ( n ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { ans [ i ] = new Array ( m ). fill ( Infinity ); } // visit each cell of the grid for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // if the cell has 1 // then the distance is 0 if ( grid [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 ; continue ; } // iterate over all the cells // and find the distance of the nearest 1 for ( let k = 0 ; k < n ; k ++ ) { for ( let l = 0 ; l < m ; l ++ ) { if ( grid [ k ][ l ] === 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = Math . min ( ans [ i ][ j ] Math . abs ( i - k ) + Math . abs ( j - l )); } } } } } return ans ; } // Driver Code //Driver Code Starts let grid = [ [ 0 1 1 0 ] [ 1 1 0 0 ] [ 0 0 1 1 ] ]; let ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < ans . length ; i ++ ) { console . log ( ans [ i ]. join ( ' ' )); } //Driver Code Ends
Wyjście
1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
[Podejście oczekiwane] — Korzystanie z wyszukiwania wszerz — O(n * m) czasu i O(n * m) przestrzeni
C++Problem można skutecznie rozwiązać, stosując podejście BFS z wieloma źródłami. Każda komórka siatki traktowana jest jako węzeł, którego krawędzie łączą sąsiednie komórki (góra, dół, lewy, prawy). Zamiast przeprowadzać oddzielne wyszukiwanie dla każdej komórki 0, kolejkujemy wszystkie komórki zawierające na początku 1 i wykonujemy pojedynczy BFS z tych wielu źródeł jednocześnie. W miarę jak BFS rozwija się warstwa po warstwie, aktualizujemy odległość każdej nieodwiedzonej komórki 0, aby była o jeden większa niż odległość jej rodzica. Gwarantuje to, że każda komórka otrzyma minimalną odległość do najbliższej 1 w optymalny i efektywny sposób.
//Driver Code Starts #include #include #include #include using namespace std ; //Driver Code Ends vector < vector < int >> nearest ( vector < vector < int >> & grid ) { int n = grid . size (); int m = grid [ 0 ]. size (); vector < vector < int >> ans ( n vector < int > ( m INT_MAX )); // to store the indices of the cells having 1 queue < pair < int int >> q ; // visit each cell of the grid for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // if the cell has 1 // then the distance is 0 if ( grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 ; q . push ({ i j }); } } } // iterate over all the cells // and find the distance of the nearest 1 while ( ! q . empty ()) { int len = q . size (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < len ; i ++ ) { int x = q . front (). first ; int y = q . front (). second ; q . pop (); // check all the four directions vector < vector < int >> directions = {{ 0 1 } { 0 -1 } { 1 0 } { -1 0 }}; for ( int j = 0 ; j < directions . size (); j ++ ) { int dx = directions [ j ][ 0 ]; int dy = directions [ j ][ 1 ]; // if the cell is within the grid // and the distance is not calculated yet if ( x + dx >= 0 && x + dx < n && y + dy >= 0 && y + dy < m && ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] == INT_MAX ) { ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] = ans [ x ][ y ] + 1 ; q . push ({ x + dx y + dy }); } } } } return ans ; } //Driver Code Starts int main () { vector < vector < int >> grid = {{ 0 1 1 0 } { 1 1 0 0 } { 0 0 1 1 }}; vector < vector < int >> ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < ans . size (); i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < ans [ i ]. size (); j ++ ) { cout < < ans [ i ][ j ] < < ' ' ; } cout < < endl ; } return 0 ; } //Driver Code Ends
Java //Driver Code Starts import java.util.ArrayList ; import java.util.Queue ; import java.util.LinkedList ; import java.util.Arrays ; class GfG { //Driver Code Ends static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nearest ( int [][] grid ) { int n = grid . length ; int m = grid [ 0 ] . length ; int [][] ans = new int [ n ][ m ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { Arrays . fill ( ans [ i ] Integer . MAX_VALUE ); } // to store the indices of the cells having 1 Queue < int []> q = new LinkedList <> (); // visit each cell of the grid for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // if the cell has 1 // then the distance is 0 if ( grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 ; q . add ( new int [] { i j }); } } } // iterate over all the cells // and find the distance of the nearest 1 while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) { int len = q . size (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < len ; i ++ ) { int [] front = q . poll (); int x = front [ 0 ] ; int y = front [ 1 ] ; // check all the four directions int [][] directions = {{ 0 1 } { 0 - 1 } { 1 0 } { - 1 0 }}; for ( int j = 0 ; j < directions . length ; j ++ ) { int dx = directions [ j ][ 0 ] ; int dy = directions [ j ][ 1 ] ; // if the cell is within the grid // and the distance is not calculated yet if ( x + dx >= 0 && x + dx < n && y + dy >= 0 && y + dy < m && ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] == Integer . MAX_VALUE ) { ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] = ans [ x ][ y ] + 1 ; q . add ( new int [] { x + dx y + dy }); } } } } ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> result = new ArrayList <> (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { ArrayList < Integer > row = new ArrayList <> (); for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { row . add ( ans [ i ][ j ] ); } result . add ( row ); } return result ; } //Driver Code Starts public static void main ( String [] args ) { int [][] grid = {{ 0 1 1 0 } { 1 1 0 0 } { 0 0 1 1 }}; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > row : ans ) { for ( int val : row ) { System . out . print ( val + ' ' ); } System . out . println (); } } } //Driver Code Ends
Python #Driver Code Starts from collections import deque import sys #Driver Code Ends def nearest ( grid ): n = len ( grid ) m = len ( grid [ 0 ]) ans = [[ sys . maxsize for _ in range ( m )] for _ in range ( n )] # to store the indices of the cells having 1 q = deque () # visit each cell of the grid for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( m ): # if the cell has 1 # then the distance is 0 if grid [ i ][ j ] == 1 : ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 q . append (( i j )) # iterate over all the cells # and find the distance of the nearest 1 while q : len_q = len ( q ) for _ in range ( len_q ): x y = q . popleft () # check all the four directions directions = [( 0 1 ) ( 0 - 1 ) ( 1 0 ) ( - 1 0 )] for dx dy in directions : # if the cell is within the grid # and the distance is not calculated yet if 0 <= x + dx < n and 0 <= y + dy < m and ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] == sys . maxsize : ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] = ans [ x ][ y ] + 1 q . append (( x + dx y + dy )) return ans #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == '__main__' : grid = [[ 0 1 1 0 ] [ 1 1 0 0 ] [ 0 0 1 1 ]] ans = nearest ( grid ) for row in ans : print ( ' ' . join ( map ( str row ))) #Driver Code Ends
C# //Driver Code Starts using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static List < List < int >> nearest ( int [] grid ) { int n = grid . GetLength ( 0 ); int m = grid . GetLength ( 1 ); int [] ans = new int [ n m ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { ans [ i j ] = int . MaxValue ; } } // to store the indices of the cells having 1 Queue < Tuple < int int >> q = new Queue < Tuple < int int >> (); // visit each cell of the grid for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // if the cell has 1 // then the distance is 0 if ( grid [ i j ] == 1 ) { ans [ i j ] = 0 ; q . Enqueue ( new Tuple < int int > ( i j )); } } } // iterate over all the cells // and find the distance of the nearest 1 while ( q . Count > 0 ) { int len = q . Count ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < len ; i ++ ) { var node = q . Dequeue (); int x = node . Item1 ; int y = node . Item2 ; // check all the four directions int [] directions = new int [] { { 0 1 } { 0 - 1 } { 1 0 } { - 1 0 } }; for ( int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j ++ ) { int dx = directions [ j 0 ]; int dy = directions [ j 1 ]; // if the cell is within the grid // and the distance is not calculated yet if ( x + dx >= 0 && x + dx < n && y + dy >= 0 && y + dy < m && ans [ x + dx y + dy ] == int . MaxValue ) { ans [ x + dx y + dy ] = ans [ x y ] + 1 ; q . Enqueue ( new Tuple < int int > ( x + dx y + dy )); } } } } // Convert 2D array to List > before returning
List < List < int >> result = new List < List < int >> (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { List < int > row = new List < int > (); for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { row . Add ( ans [ i j ]); } result . Add ( row ); } return result ; } //Driver Code Starts static void Main () { int [] grid = new int [] { { 0 1 1 0 } { 1 1 0 0 } { 0 0 1 1 } }; List < List < int >> ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < ans . Count ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < ans [ i ]. Count ; j ++ ) { Console . Write ( ans [ i ][ j ] + ' ' ); } Console . WriteLine (); } } } //Driver Code Ends
JavaScript //Driver Code Starts const Denque = require ( 'denque' ); //Driver Code Ends function nearest ( grid ) { let n = grid . length ; let m = grid [ 0 ]. length ; // Initialize answer matrix with Infinity let ans = []; for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { ans . push ( new Array ( m ). fill ( Infinity )); } // to store the indices of the cells having 1 let q = new Denque (); // visit each cell of the grid for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // if the cell has 1 // then the distance is 0 if ( grid [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { ans [ i ][ j ] = 0 ; q . push ([ i j ]); } } } // iterate over all the cells // and find the distance of the nearest 1 while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) { let [ x y ] = q . shift (); // check all the four directions let directions = [ [ 0 1 ] [ 0 - 1 ] [ 1 0 ] [ - 1 0 ] ]; for ( let dir of directions ) { let dx = dir [ 0 ]; let dy = dir [ 1 ]; // if the cell is within the grid // and the distance is not calculated yet if ( x + dx >= 0 && x + dx < n && y + dy >= 0 && y + dy < m && ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] === Infinity ) { ans [ x + dx ][ y + dy ] = ans [ x ][ y ] + 1 ; q . push ([ x + dx y + dy ]); } } } return ans ; } //Driver Code Starts // Driver Code let grid = [ [ 0 1 1 0 ] [ 1 1 0 0 ] [ 0 0 1 1 ] ]; let ans = nearest ( grid ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < ans . length ; i ++ ) { console . log ( ans [ i ]. join ( ' ' )); } //Driver Code Ends
Wyjście
1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0Utwórz quiz