Reisende selgerproblem ved hjelp av filial og bundet
Gitt et sett med byer og avstand mellom hvert par byer, er problemet å finne den kortest mulige turen som besøker hver by nøyaktig en gang og vender tilbake til utgangspunktet.

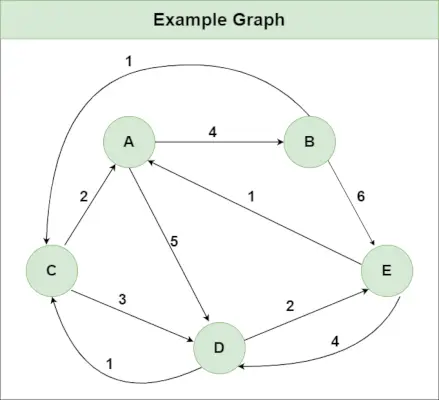
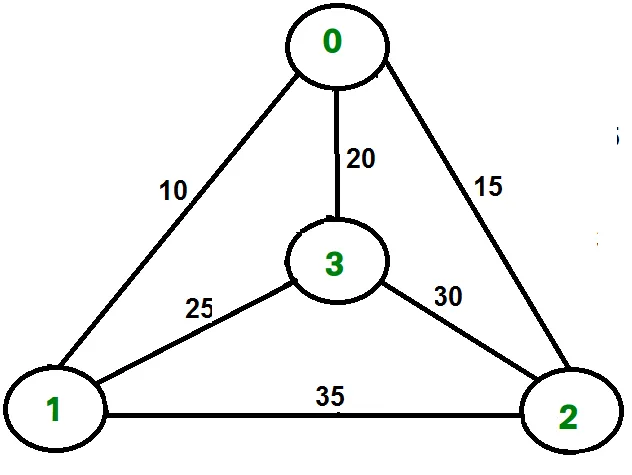
Tenk for eksempel på grafen som er vist på figuren på høyre side. En TSP-tur i grafen er 0-1-3-2-0. Kostnaden for turen er 10+25+30+15 som er 80.
Vi har diskutert følgende løsninger
1) Naiv og dynamisk programmering
2) Omtrentlig løsning ved bruk av MST
Gren og bundet løsning
Som det fremgår av de tidligere artiklene i gren og bundet metode for gjeldende node i treet, beregner vi en bundet på best mulig løsning som vi kan få hvis vi ned denne noden. Hvis den bundne best mulig løsning i seg selv er verre enn nåværende best (best beregnet så langt), ignorerer vi undertræren forankret med noden.
Merk at kostnadene gjennom en node inkluderer to kostnader.
1) Kostnad for å nå noden fra roten (når vi når en node, har vi denne kostnaden beregnet)
2) Kostnad for å nå et svar fra gjeldende node til et blad (vi beregner en bundet av denne kostnaden for å bestemme om vi skal ignorere undertrekk med denne noden eller ikke).
- I tilfeller av en Maksimeringsproblem En øvre grense forteller oss den maksimale mulige løsningen hvis vi følger den gitte noden. For eksempel i 0/1 ryggsekk Vi brukte grådig tilnærming for å finne en øvre grense .
- I tilfeller av en minimeringsproblem En undergrense forteller oss minst mulig løsning hvis vi følger den gitte noden. For eksempel i Jobboppgaveproblem Vi får en lavere grense ved å tildele minst kostnadsjobb til en arbeider.
I gren og bundet er den utfordrende delen å finne ut en måte å beregne en bundet på best mulig løsning. Nedenfor er en idé som brukes til å beregne grenser for reisende selgerproblem.
Kostnad for en hvilken som helst tur kan skrives som nedenfor.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Tenk for eksempel ovennevnte graf. Nedenfor er minimumskostnad to kanter ved siden av hver node.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Nå har vi en ide om beregning av undergrensen. La oss se hvordan vi kan bruke det State Space Search Tree. Vi begynner å oppregne alle mulige noder (helst i leksikografisk rekkefølge)
1. Rotnoden: Uten tap av generalitet antar vi at vi begynner på Vertex '0' som den nedre grensen er beregnet ovenfor.
Håndtere nivå 2: Det neste nivået oppregner alle mulige hjørner vi kan gå til (husk at i hvilken som helst bane må en toppunkt bare skje en gang) som er 1 2 3 ... n (merk at grafen er fullført). Tenk på at vi beregner for toppunkt 1 siden vi flyttet fra 0 til 1-turen vår nå har inkludert kanten 0-1. Dette gjør at vi kan gjøre nødvendige endringer i den nedre grensen av roten.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Hvordan fungerer det? For å inkludere kant 0-1 legger vi til kantkostnaden på 0-1 og trekker fra en kantvekt slik at den nedre grensen forblir så tett som mulig som vil være summen av minimumskantene på 0 og 1 delt på 2.. Klart kanten kan trukket ut kan ikke være mindre enn dette.
Håndtere andre nivåer: Når vi går videre til neste nivå, oppregner vi igjen alle mulige hjørner. For ovennevnte sak som går videre etter 1, sjekker vi ut 2 3 4 ... n.
Tenk på undergrensen for 2 når vi flyttet fra 1 til 1, inkluderer vi kanten 1-2 til turen og endrer den nye nedre grensen for denne noden.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
Merk: Den eneste endringen i formelen er at vi denne gangen har inkludert andre minimumskostnader for 1 fordi minimumskostnadene allerede er trukket fra på tidligere nivå.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include using namespace std ; const int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. int final_path [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path bool visited [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. int final_res = INT_MAX ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution void copyToFinal ( int curr_path []) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int firstMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int min = INT_MAX ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int secondMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int first = INT_MAX second = INT_MAX ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] void TSPRec ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path []) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level -1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] void TSP ( int adj [ N ][ N ]) { int curr_path [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; memset ( curr_path -1 sizeof ( curr_path )); memset ( visited 0 sizeof ( curr_path )); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound & 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code int main () { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [ N ][ N ] = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); printf ( 'Minimum cost : %d n ' final_res ); printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ]); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited [] = new boolean [ N ] ; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int curr_path [] ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ] ; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] ; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int min = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ] ; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int first = Integer . MAX_VALUE second = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int adj [][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path [] ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] ; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Arrays . fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int adj [][] ) { int curr_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Arrays . fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Arrays . fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [][] = {{ 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); System . out . printf ( 'Minimum cost : %dn' final_res ); System . out . printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { System . out . printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ] ); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Python3 # Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float ( 'inf' ) # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal ( curr_path ): final_path [: N + 1 ] = curr_path [:] final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin ( adj i ): min = maxsize for k in range ( N ): if adj [ i ][ k ] < min and i != k : min = adj [ i ][ k ] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin ( adj i ): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range ( N ): if i == j : continue if adj [ i ][ j ] <= first : second = first first = adj [ i ][ j ] elif ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second and adj [ i ][ j ] != first ): second = adj [ i ][ j ] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited ): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N : # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 : # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]] [ curr_path [ 0 ]] if curr_res < final_res : copyToFinal ( curr_path ) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range ( N ): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 and visited [ i ] == False ): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1 : curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) else : curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res : curr_path [ level ] = i visited [ i ] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited ) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [ False ] * len ( visited ) for j in range ( level ): if curr_path [ j ] != - 1 : visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP ( adj ): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [ - 1 ] * ( N + 1 ) visited = [ False ] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range ( N ): curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math . ceil ( curr_bound / 2 ) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = True curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited ) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [ None ] * ( N + 1 ) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [ False ] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP ( adj ) print ( 'Minimum cost :' final_res ) print ( 'Path Taken : ' end = ' ' ) for i in range ( N + 1 ): print ( final_path [ i ] end = ' ' ) # This code is contributed by ng24_7
C# // C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System ; public class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int [] final_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool [] visited = new bool [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32 . MaxValue ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int [] curr_path ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int min = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int first = Int32 . MaxValue second = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i j ]; } else if ( adj [ i j ] <= second && adj [ i j ] != first ) second = adj [ i j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int [ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int [] curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Array . Fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int [ ] adj ) { int [] curr_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Array . Fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Array . Fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code static public void Main () { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int [ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Minimum cost : ' + final_res ); Console . Write ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { Console . Write ( final_path [ i ] + ' ' ); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
JavaScript const N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array ( N ). fill ( false ); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal ( curr_path ){ for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; } final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin ( adj i ){ let min = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ){ if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i !== k ){ min = adj [ i ][ k ]; } } return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin ( adj i ){ let first = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; let second = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ){ if ( i == j ){ continue ; } if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ){ second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] !== first ){ second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] !== 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] !== 0 && ! visited [ i ]){ let temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ){ curr_bound -= ( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } else { curr_bound -= ( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ){ curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array visited . fill ( false ) for ( var j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP ( adj ) { let curr_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0 ; visited . fill ( false ); // compute initial bound for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ curr_bound += firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i ); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? ( curr_bound / 2 ) + 1 : ( curr_bound / 2 ); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]]; TSP ( adj ); console . log ( `Minimum cost: ${ final_res } ` ); console . log ( `Path Taken: ${ final_path . join ( ' ' ) } ` ); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Utgang:
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
Avrundingen gjøres i denne kodelinjen:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
I grenen og bundet TSP -algoritmen beregner vi en nedre grense for den totale kostnaden for den optimale løsningen ved å legge opp minimumskantkostnadene for hvert toppunkt og deretter dele med to. Imidlertid er det ikke sikkert at denne undergrensen er et heltall. For å få et heltall undergrensen kan vi bruke avrunding.
I koden ovenfor holder Curr_bound -variabelen den nåværende nedre grensen på den totale kostnaden for den optimale løsningen. Når vi besøker et nytt toppunkt på nivånivå, beregner vi en ny lavere bundet New_Bound ved å ta summen av minimumskostnadene for det nye toppunktet og dens to nærmeste naboer. Vi oppdaterer deretter Curr_bound -variabelen ved å avrunde New_Bound til nærmeste heltall.
Hvis nivået er 1, runder vi ned til nærmeste heltall. Dette er fordi vi bare har besøkt ett toppunkt så langt, og vi ønsker å være konservative i vårt estimat av den totale kostnaden for den optimale løsningen. Hvis nivået er større enn 1, bruker vi en mer aggressiv avrundingsstrategi som tar hensyn til det faktum at vi allerede har besøkt noen hjørner og derfor kan gjøre et mer nøyaktig estimat av den totale kostnaden for den optimale løsningen.
Tidskompleksitet: Det verste tilfellet kompleksitet av gren og bundet forblir den samme som for brute force tydelig fordi vi i verste fall aldri får en sjanse til å beskjære en node. Mens den i praksis fungerer veldig bra avhengig av den forskjellige forekomsten av TSP. Kompleksiteten avhenger også av valget av avgrensningsfunksjonen som de er de som bestemmer hvor mange noder som skal beskjæres.
Referanser:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.net.in/dsa/node187.html