Reizende verkoper Probleem met Branch en Bound
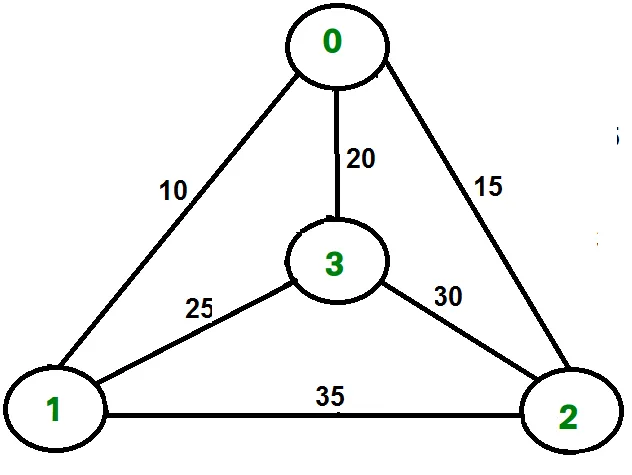
Gegeven een reeks steden en afstand tussen elk paar steden is het probleem om de kortst mogelijke tour te vinden die elke stad precies één keer bezoekt en terugkeert naar het startpunt.

Beschouw bijvoorbeeld de grafiek die in de figuur aan de rechterkant wordt weergegeven. Een TSP-tour in de grafiek is 0-1-3-2-0. De kosten van de tour zijn 10+25+30+15, die 80 is.
We hebben de volgende oplossingen besproken
1) Naïef en dynamisch programmeren
2) Geschatte oplossing met behulp van MST
Tak en gebonden oplossing
Zoals te zien in de vorige artikelen in de tak en gebonden methode voor het huidige knooppunt in de boom, berekenen we een gebonden op de best mogelijke oplossing die we kunnen krijgen als we dit knooppunt verlagen. Als de gebonden op de best mogelijke oplossing zelf slechter is dan het beste (tot nu toe best berekend), negeren we de substructuur die is geworteld met het knooppunt.
Merk op dat de kosten via een knooppunt twee kosten omvatten.
1) Kosten van het bereiken van het knooppunt uit de root (wanneer we een knooppunt bereiken, hebben we deze kosten berekend)
2) Kosten van het bereiken van een antwoord van het huidige knooppunt naar een blad (we berekenen een gebonden op deze kosten om te beslissen of ze subtree met dit knooppunt negeren of niet).
- In het geval van een maximalisatieprobleem Een bovengrens vertelt ons de maximaal mogelijke oplossing als we het gegeven knooppunt volgen. Bijvoorbeeld in 0/1 knapack We hebben de hebzuchtige benadering gebruikt om een bovengrens te vinden .
- In het geval van een Minimalisatieprobleem Een ondergrens vertelt ons de minimaal mogelijke oplossing als we het gegeven knooppunt volgen. Bijvoorbeeld in Taakopdrachtsprobleem We krijgen een ondergrens door de minste kostentaak aan een werknemer toe te wijzen.
In tak en gebonden is het uitdagende deel een manier om een manier te berekenen om een gebonden op de best mogelijke oplossing te berekenen. Hieronder is een idee dat wordt gebruikt om de grenzen te berekenen voor het probleem van de reizende verkoper.
De kosten van elke tour kunnen worden geschreven zoals hieronder.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Beschouw bijvoorbeeld de bovenstaande getoonde grafiek. Hieronder staan minimale kosten twee randen grenzend aan elk knooppunt.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Nu hebben we een idee over berekening van ondergrens. Laten we eens kijken hoe we het moeten toepassen van de staatsruimte -zoekboom. We beginnen alle mogelijke knooppunten op te sommen (bij voorkeur in lexicografische volgorde)
1. Het rootknooppunt: Zonder verlies van algemeenheid gaan we ervan uit dat we beginnen bij hoekpunt '0' waarvoor de ondergrens hierboven is berekend.
Omgaan met niveau 2: Het volgende niveau somt alle mogelijke hoekpunten op waar we naartoe kunnen gaan (houd er rekening mee dat op elk pad een hoekpunt slechts één keer moet plaatsvinden) die 1 2 3 ... n zijn (merk op dat de grafiek voltooid is). Overweeg dat we berekenen voor Vertex 1, omdat we zijn verhuisd van 0 naar 1 onze tour heeft nu de Edge 0-1 opgenomen. Hierdoor kunnen we de nodige wijzigingen aanbrengen in de ondergrens van de wortel.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Hoe werkt het? Om rand 0-1 op te nemen, voegen we de randkosten van 0-1 toe en trekken een randgewicht zodanig af dat de ondergrens zo strak mogelijk blijft, wat de som van de minimale randen van 0 en 1 zou zijn gedeeld door 2. Het is duidelijk dat de rand niet kleiner kan zijn dan dit.
Omgaan met andere niveaus: Terwijl we verder gaan naar het volgende niveau, sommen we opnieuw alle mogelijke hoekpunten. Voor het bovenstaande geval dat verder gaat na 1, kijken we uit voor 2 3 4 ... n.
Overweeg ondergrens voor 2 terwijl we van 1 naar 1 zijn verhuisd, we nemen de rand 1-2 op in de tour en wijzigen de nieuwe ondergrens voor dit knooppunt.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
OPMERKING: De enige wijziging in de formule is dat we deze keer tweede minimale randkosten voor 1 hebben opgenomen omdat de minimale randkosten al in het vorige niveau zijn afgetrokken.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include using namespace std ; const int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. int final_path [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path bool visited [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. int final_res = INT_MAX ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution void copyToFinal ( int curr_path []) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int firstMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int min = INT_MAX ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int secondMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int first = INT_MAX second = INT_MAX ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] void TSPRec ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path []) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level -1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] void TSP ( int adj [ N ][ N ]) { int curr_path [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; memset ( curr_path -1 sizeof ( curr_path )); memset ( visited 0 sizeof ( curr_path )); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound & 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code int main () { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [ N ][ N ] = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); printf ( 'Minimum cost : %d n ' final_res ); printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ]); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited [] = new boolean [ N ] ; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int curr_path [] ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ] ; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] ; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int min = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ] ; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int first = Integer . MAX_VALUE second = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int adj [][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path [] ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] ; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Arrays . fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int adj [][] ) { int curr_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Arrays . fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Arrays . fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [][] = {{ 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); System . out . printf ( 'Minimum cost : %dn' final_res ); System . out . printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { System . out . printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ] ); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Python3 # Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float ( 'inf' ) # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal ( curr_path ): final_path [: N + 1 ] = curr_path [:] final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin ( adj i ): min = maxsize for k in range ( N ): if adj [ i ][ k ] < min and i != k : min = adj [ i ][ k ] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin ( adj i ): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range ( N ): if i == j : continue if adj [ i ][ j ] <= first : second = first first = adj [ i ][ j ] elif ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second and adj [ i ][ j ] != first ): second = adj [ i ][ j ] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited ): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N : # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 : # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]] [ curr_path [ 0 ]] if curr_res < final_res : copyToFinal ( curr_path ) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range ( N ): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 and visited [ i ] == False ): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1 : curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) else : curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res : curr_path [ level ] = i visited [ i ] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited ) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [ False ] * len ( visited ) for j in range ( level ): if curr_path [ j ] != - 1 : visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP ( adj ): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [ - 1 ] * ( N + 1 ) visited = [ False ] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range ( N ): curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math . ceil ( curr_bound / 2 ) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = True curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited ) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [ None ] * ( N + 1 ) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [ False ] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP ( adj ) print ( 'Minimum cost :' final_res ) print ( 'Path Taken : ' end = ' ' ) for i in range ( N + 1 ): print ( final_path [ i ] end = ' ' ) # This code is contributed by ng24_7
C# // C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System ; public class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int [] final_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool [] visited = new bool [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32 . MaxValue ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int [] curr_path ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int min = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int first = Int32 . MaxValue second = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i j ]; } else if ( adj [ i j ] <= second && adj [ i j ] != first ) second = adj [ i j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int [ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int [] curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Array . Fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int [ ] adj ) { int [] curr_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Array . Fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Array . Fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code static public void Main () { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int [ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Minimum cost : ' + final_res ); Console . Write ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { Console . Write ( final_path [ i ] + ' ' ); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
JavaScript const N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array ( N ). fill ( false ); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal ( curr_path ){ for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; } final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin ( adj i ){ let min = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ){ if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i !== k ){ min = adj [ i ][ k ]; } } return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin ( adj i ){ let first = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; let second = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ){ if ( i == j ){ continue ; } if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ){ second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] !== first ){ second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] !== 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] !== 0 && ! visited [ i ]){ let temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ){ curr_bound -= ( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } else { curr_bound -= ( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ){ curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array visited . fill ( false ) for ( var j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP ( adj ) { let curr_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0 ; visited . fill ( false ); // compute initial bound for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ curr_bound += firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i ); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? ( curr_bound / 2 ) + 1 : ( curr_bound / 2 ); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]]; TSP ( adj ); console . log ( `Minimum cost: ${ final_res } ` ); console . log ( `Path Taken: ${ final_path . join ( ' ' ) } ` ); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Uitvoer:
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
De afronding wordt gedaan in deze codelijn:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
In de tak en gebonden TSP -algoritme berekenen we een ondergrens op de totale kosten van de optimale oplossing door de minimale randkosten voor elk hoekpunt op te tellen en vervolgens te delen door twee. Deze ondergrens is echter mogelijk geen geheel getal. Om een integer ondergrens te krijgen, kunnen we afronding gebruiken.
In de bovenstaande code houdt de variabele CURR_Bound de huidige ondergrens vast op de totale kosten van de optimale oplossing. Wanneer we een nieuw hoekpunt op niveau bezoeken, berekenen we een nieuwe lagere bound new_bound door de som te nemen van de minimale voorsprongkosten voor het nieuwe hoekpunt en zijn twee naaste buren. We werken vervolgens de variabele Curr_Bound bij door New_Bound af te ronden op het dichtstbijzijnde gehele getal.
Als het niveau 1 is, komen we af naar het dichtstbijzijnde gehele getal. Dit komt omdat we tot nu toe slechts één hoekpunt hebben bezocht en we conservatief willen zijn in onze schatting van de totale kosten van de optimale oplossing. Als het niveau groter is dan 1, gebruiken we een agressievere afrondingsstrategie die rekening houdt met het feit dat we al enkele hoekpunten hebben bezocht en daarom een meer accurate schatting kunnen maken van de totale kosten van de optimale oplossing.
Tijdcomplexiteit: De complexiteit van het slechtste geval van tak en gebonden blijft hetzelfde als die van de brute kracht duidelijk omdat we in het ergste geval misschien nooit de kans krijgen om een knooppunt te snoeien. Terwijl het in de praktijk zeer goed presteert, afhankelijk van het verschillende exemplaar van de TSP. De complexiteit hangt ook af van de keuze van de grensfunctie, omdat zij degenen zijn die beslissen hoeveel knooppunten moeten worden gesnoeid.
Referenties:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.ernet.in/dsa/node187.html