Atritināts saistītais saraksts | 1. komplekts (ievads)
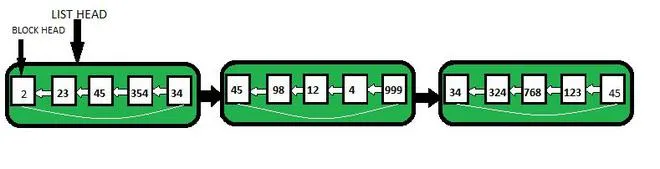
Tāpat kā masīvs un saistītais saraksts, arī atritinātais saistītais saraksts ir lineāra datu struktūra un ir saistīta saraksta variants.
Kāpēc mums ir nepieciešams atritināts saistīto sarakstu?
Viena no lielākajām saistīto sarakstu priekšrocībām salīdzinājumā ar masīviem ir tāda, ka elementa ievietošana jebkurā vietā aizņem tikai O(1). Tomēr galvenais ir tas, ka, lai meklētu elementu saistītajā sarakstā, nepieciešams O(n). Tātad, lai atrisinātu meklēšanas problēmu, t.i., samazinātu elementa meklēšanas laiku, tika izvirzīta atritinātu saistīto sarakstu koncepcija. Atritinātais saistītais saraksts aptver gan masīva, gan saistītā saraksta priekšrocības, jo tas samazina atmiņas izmaksas salīdzinājumā ar vienkāršiem saistītiem sarakstiem, katrā mezglā saglabājot vairākus elementus, un tam ir arī ātra ievietošana un dzēšana, tāpat kā saistītam sarakstam.


Priekšrocības:
- Kešatmiņas darbības dēļ lineārā meklēšana ir daudz ātrāka atritinātos saistītos sarakstos.
- Salīdzinot ar parasto saistīto sarakstu, tas prasa mazāk vietas norāžu/atsauču uzglabāšanai.
- Tā veic tādas darbības kā ievietošanas dzēšana un šķērsošana ātrāk nekā parastie saistītie saraksti (jo meklēšana ir ātrāka).
Trūkumi:
- Katra mezgla pieskaitāmās izmaksas ir salīdzinoši lielākas nekā atsevišķi saistītie saraksti. Skatiet mezgla piemēru zemāk esošajā kodā
Piemērs: Pieņemsim, ka mums ir 8 elementi, tāpēc sqrt (8) = 2,82, kas noapaļo līdz 3. Tātad katrā blokā tiks saglabāti 3 elementi. Tādējādi, lai saglabātu 8 elementus, tiks izveidoti 3 bloki, no kuriem pirmajos divos blokos tiks saglabāti 3 elementi, bet pēdējā blokā - 2 elementi.
Kā meklēšana kļūst labāka atritinātos saistītos sarakstos?
Tātad, ņemot vērā iepriekš minēto piemēru, ja mēs vēlamies meklēt 7. elementu sarakstā, mēs šķērsojam bloku sarakstu uz to, kurā ir 7. elements. Tas aizņem tikai O(sqrt(n)), jo mēs atradām, ka tas nepārsniedz sqrt(n) blokus.
Vienkārša ieviešana:
Tālāk esošā programma izveido vienkāršu atritinātu saistīto sarakstu ar 3 mezgliem, kas satur mainīgu skaitu elementu katrā. Tas arī šķērso izveidoto sarakstu.
C++ // C++ program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include using namespace std ; #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public : int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) cout < < n -> array [ i ] < < ' ' ; // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { Node * head = NULL ; Node * second = NULL ; Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; } // This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C // C program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include #include #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node struct Node { int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; struct Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( struct Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' n -> array [ i ]); // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { struct Node * head = NULL ; struct Node * second = NULL ; struct Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); second = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); third = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static final int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node static class Node { int numElements ; int [] array = new int [ maxElements ] ; Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) System . out . print ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Python3 # Python3 program to implement unrolled # linked list and traversing it. maxElements = 4 # Unrolled Linked List Node class Node : def __init__ ( self ): self . numElements = 0 self . array = [ 0 for i in range ( maxElements )] self . next = None # Function to traverse an unrolled linked list # and print all the elements def printUnrolledList ( n ): while ( n != None ): # Print elements in current node for i in range ( n . numElements ): print ( n . array [ i ] end = ' ' ) # Move to next node n = n . next # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : head = None second = None third = None # Allocate 3 Nodes head = Node () second = Node () third = Node () # Let us put some values in second # node (Number of values must be # less than or equal to # maxElement) head . numElements = 3 head . array [ 0 ] = 1 head . array [ 1 ] = 2 head . array [ 2 ] = 3 # Link first Node with the second Node head . next = second # Let us put some values in second node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) second . numElements = 3 second . array [ 0 ] = 4 second . array [ 1 ] = 5 second . array [ 2 ] = 6 # Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third # Let us put some values in third node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 third . array [ 0 ] = 7 third . array [ 1 ] = 8 third . array [ 2 ] = 9 third . next = None printUnrolledList ( head ) # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# // C# program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. using System ; class GFG { static readonly int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public int numElements ; public int [] array = new int [ maxElements ]; public Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) Console . Write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void Main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. const maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { constructor () { this . numElements = 0 ; this . array = new Array ( maxElements ); this . next = null ; } } // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements function printUnrolledList ( n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( var i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) document . write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes var head = null ; var second = null ; var third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); < /script>
Izvade
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Sarežģītības analīze:
Šajā rakstā mēs esam iepazīstinājuši ar izritinātu sarakstu un tā priekšrocībām. Mēs arī esam parādījuši, kā šķērsot sarakstu. Nākamajā rakstā mēs detalizēti apspriedīsim ievietošanas dzēšanu un maxElements/numElements vērtības.
Ievietošana atritinātajā saistīto sarakstā
Izveidojiet viktorīnu
Jums Varētu Patikt
Top Raksti
Kategorija
Interesanti Raksti