Java.io.PipedOutputStream klase Java valodā

Java.io.PipedInputStream klase Java valodā

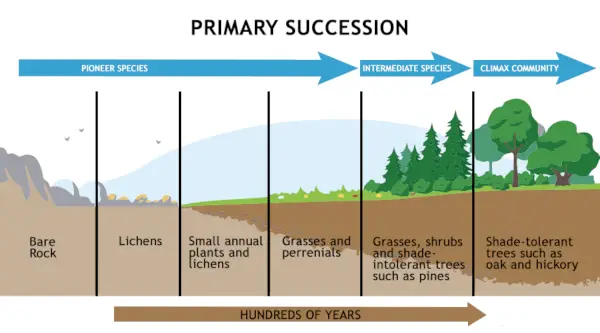
Caurules IO nodrošina saiti starp diviem pavedieniem, kas vienlaikus darbojas JVM. Tāpēc caurules tiek izmantotas gan kā avots, gan galamērķis.
- PipedInputStream tiek arī savienots ar PipedOutputStream. Tātad datus var rakstīt, izmantojot PipedOutputStream, un tos var rakstīt, izmantojot PipedInputStream. Taču, vienlaikus izmantojot abus pavedienus, pavedieni nonāks strupceļā.
- PipedOutputStream sūta caurules galu. Dati tiek ierakstīti PipedOutputStream. Tiek uzskatīts, ka caurule ir pārrauta, ja PipedInputStream, kas lasīja datus, vairs nav.
Deklarācija:
public class PipedOutputStream
extends OutputStream
Konstruktors:
- PipedOutputStream() : izveido PipedOutputStream, ka tā nav savienota.
- PipedOutputStream(PipedOutputStream inStream) : izveido PipedOutputStream, ka tas
ir savienots ar PipedInputStream — 'inStream'.
Metodes:
write() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(int byte) ieraksta norādīto baitu cauruļvadu izvades straumē.
Sintakse :
public void write(int byte)
Parameters :
byte : byte to be written
Return : void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.write(baits[] bufera int offset int maxlen) : java.io.PipedOutputStream.write(baits[] bufera int nobīde int maxlen) ieraksta maksimālus baitus datu no bufera uz cauruļu izvades straumi. Metode bloķē, ja straumē nav ierakstīti baiti.
Sintakse :
public void write(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen)
Parameters :
buffer : data of the buffer
offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'.
maxlen : maximum length of array to be read
Return : void
Exception :
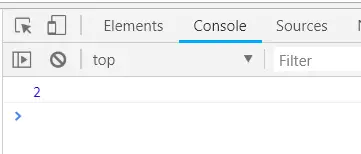
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. JavaIzvade:
Use of write(buffer offset maxlen) : J A V A
- aizvērt() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.close() aizver cauruļu izvades straumi un atbrīvo piešķirtos resursus.
Sintakse :
public void close()
Parameters :
--------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- savienojums(PipedInputStream galamērķis) : java.io.PipedOutputStream.connect(PipedInputStream galamērķis savieno cauruļvadu izvades straumi ar 'galamērķa' cauruļu ievades straumi un gadījumā, ja galamērķis ir caurules ar kādu citu straumes IO izņēmumu
Sintakse :
public void connect(PipedInputStream destination)
Parameters :
destination : the Piped Input Stream to be connected to
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
- flush() : java.io.PipedOutputStream.flush() izskalo izvades straumi.
Sintakse :
public void flush()
Parameters :
------------
Return :
void
Exception :
-> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
Java kods, kas ilustrē PipedOutputStream klases metožu darbību:
JavaIzvade:
Use of flush() method :
G E E K S
Closing the Output stream
Izveidojiet viktorīnu