Ceļojošā pārdevēja problēma, izmantojot filiāli un saistošu
Ņemot vērā pilsētu kopumu un attālumu starp katru pilsētu pāri, problēma ir atrast pēc iespējas īsāku ekskursiju, kas katru pilsētu tieši vienu reizi apmeklē un atgriežas sākuma punktā.

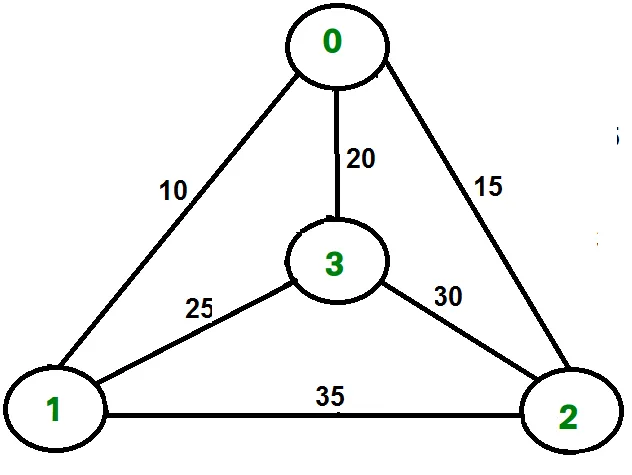
Piemēram, apsveriet diagrammu, kas parādīta attēlā labajā pusē. TSP tūre grafikā ir 0-1-3-2-0. Ekskursijas izmaksas ir 10+25+30+15, kas ir 80.
Mēs esam apsprieduši šādus risinājumus
1) Naiva un dinamiska programmēšana
2) Aptuvenais risinājums, izmantojot MST
Zars un saistītais šķīdums
Kā redzams iepriekšējos rakstos filiālē un iesietā metodē pašreizējam mezglam kokā, mēs aprēķinām iesieto labāko iespējamo risinājumu, ko mēs varam iegūt, ja mēs pa šo mezglu. Ja pats iespējamais iespējamais risinājums ir sliktāks nekā pašreizējais labākais (vislabāk aprēķināts līdz šim), tad mēs ignorējam subreju, kas sakņojas ar mezglu.
Ņemiet vērā, ka izmaksas caur mezglu ietver divas izmaksas.
1) Mezgla sasniegšanas izmaksas no saknes (kad mēs sasniedzam mezglu, mums ir aprēķinātas šīs izmaksas)
2) Atbildes sasniegšanas izmaksas no pašreizējā mezgla uz lapu (mēs aprēķinām saistošās šīs izmaksas, lai izlemtu, vai ignorēt apakštēlu ar šo mezglu vai nē).
- A Maksimizācijas problēma Augšējā robeža mums norāda maksimālu iespējamo risinājumu, ja sekojam dotajam mezglam. Piemēram 0/1 mugursoma Mēs izmantojām alkatīgu pieeju, lai atrastu augšējo robežu Apvidū
- A samazināšanas problēma Apakšējā robeža mums norāda minimālo iespējamo risinājumu, ja sekojam dotajam mezglam. Piemēram Darba uzdevuma problēma Mēs saņemam zemāku robežu, piešķirot darbiniekam vismazāko izmaksu darbu.
Filiālē un saistībā ar to, ka izaicinošā daļa ir izdomāt veidu, kā aprēķināt labāko iespējamo risinājumu. Zemāk ir ideja, ko izmanto, lai aprēķinātu ceļojošā pārdevēja problēmas robežas.
Jebkuras ekskursijas izmaksas var uzrakstīt, kā norādīts zemāk.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Piemēram, apsveriet iepriekš parādīto grafiku. Zemāk ir minimālās izmaksas divas malas, kas atrodas blakus katram mezglam.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Tagad mums ir ideja par apakšējās robežas aprēķināšanu. Ļaujiet mums redzēt, kā to pielietot, stāvokļa kosmosa meklēšanas koks. Mēs sākam uzskaitīt visus iespējamos mezglus (vēlams leksikogrāfiskā secībā)
1. Saknes mezgls: Nezaudējot vispārīgumu, mēs pieņemam, ka mēs sākam ar virsotni “0”, par kuru zemākā robeža ir aprēķināta iepriekš.
Darbs ar 2. līmeni: Nākamais līmenis uzskaita visas iespējamās virsotnes, uz kurām mēs varam doties (paturot prātā, ka jebkurā ceļā virsotnei jānotiek tikai vienu reizi), kas ir 1 2 3 ... n (ņemiet vērā, ka grafiks ir pabeigts). Apsveriet, ka mēs aprēķinām 1. virsotni, jo mēs pārcēlāmies no 0 līdz 1, mūsu ekskursija tagad ir iekļāvusi malu 0-1. Tas ļauj mums veikt nepieciešamās izmaiņas saknes apakšējā robežā.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Kā tas darbojas? Lai iekļautu malu 0-1, mēs pievienojam malas izmaksas 0-1 un atņemiet malas svaru tā, lai apakšējā robeža paliek pēc iespējas saspringtāka, kas būtu minimālo malu summa 0 un 1, dalīta ar 2. Skaidrs, ka atņemtā mala nevar būt mazāka par šo.
Darbs ar citiem līmeņiem: Pārejot uz nākamo līmeni, mēs atkal uzskaitām visas iespējamās virsotnes. Iepriekš minētajam gadījumam, kas iet tālāk pēc 1, mēs pārbaudām 2 3 4 ... n.
Apsveriet apakšējo robežu 2, kad mēs pārvietojāmies no 1 līdz 1, mēs iekļaujam malu 1-2 uz ekskursiju un mainām jauno apakšējo robežu šim mezglam.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
Piezīme: vienīgās izmaiņas formulā ir tā, ka šoreiz mēs esam iekļāvuši otro minimālo malu izmaksas par 1, jo minimālās malas izmaksas jau ir atņemtas iepriekšējā līmenī.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include using namespace std ; const int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. int final_path [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path bool visited [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. int final_res = INT_MAX ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution void copyToFinal ( int curr_path []) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int firstMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int min = INT_MAX ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int secondMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int first = INT_MAX second = INT_MAX ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] void TSPRec ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path []) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level -1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] void TSP ( int adj [ N ][ N ]) { int curr_path [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; memset ( curr_path -1 sizeof ( curr_path )); memset ( visited 0 sizeof ( curr_path )); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound & 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code int main () { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [ N ][ N ] = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); printf ( 'Minimum cost : %d n ' final_res ); printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ]); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited [] = new boolean [ N ] ; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int curr_path [] ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ] ; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] ; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int min = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ] ; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int first = Integer . MAX_VALUE second = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int adj [][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path [] ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] ; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Arrays . fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int adj [][] ) { int curr_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Arrays . fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Arrays . fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [][] = {{ 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); System . out . printf ( 'Minimum cost : %dn' final_res ); System . out . printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { System . out . printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ] ); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Python3 # Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float ( 'inf' ) # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal ( curr_path ): final_path [: N + 1 ] = curr_path [:] final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin ( adj i ): min = maxsize for k in range ( N ): if adj [ i ][ k ] < min and i != k : min = adj [ i ][ k ] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin ( adj i ): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range ( N ): if i == j : continue if adj [ i ][ j ] <= first : second = first first = adj [ i ][ j ] elif ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second and adj [ i ][ j ] != first ): second = adj [ i ][ j ] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited ): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N : # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 : # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]] [ curr_path [ 0 ]] if curr_res < final_res : copyToFinal ( curr_path ) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range ( N ): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 and visited [ i ] == False ): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1 : curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) else : curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res : curr_path [ level ] = i visited [ i ] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited ) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [ False ] * len ( visited ) for j in range ( level ): if curr_path [ j ] != - 1 : visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP ( adj ): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [ - 1 ] * ( N + 1 ) visited = [ False ] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range ( N ): curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math . ceil ( curr_bound / 2 ) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = True curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited ) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [ None ] * ( N + 1 ) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [ False ] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP ( adj ) print ( 'Minimum cost :' final_res ) print ( 'Path Taken : ' end = ' ' ) for i in range ( N + 1 ): print ( final_path [ i ] end = ' ' ) # This code is contributed by ng24_7
C# // C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System ; public class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int [] final_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool [] visited = new bool [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32 . MaxValue ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int [] curr_path ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int min = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int first = Int32 . MaxValue second = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i j ]; } else if ( adj [ i j ] <= second && adj [ i j ] != first ) second = adj [ i j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int [ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int [] curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Array . Fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int [ ] adj ) { int [] curr_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Array . Fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Array . Fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code static public void Main () { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int [ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Minimum cost : ' + final_res ); Console . Write ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { Console . Write ( final_path [ i ] + ' ' ); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
JavaScript const N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array ( N ). fill ( false ); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal ( curr_path ){ for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; } final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin ( adj i ){ let min = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ){ if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i !== k ){ min = adj [ i ][ k ]; } } return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin ( adj i ){ let first = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; let second = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ){ if ( i == j ){ continue ; } if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ){ second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] !== first ){ second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] !== 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] !== 0 && ! visited [ i ]){ let temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ){ curr_bound -= ( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } else { curr_bound -= ( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ){ curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array visited . fill ( false ) for ( var j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP ( adj ) { let curr_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0 ; visited . fill ( false ); // compute initial bound for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ curr_bound += firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i ); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? ( curr_bound / 2 ) + 1 : ( curr_bound / 2 ); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]]; TSP ( adj ); console . log ( `Minimum cost: ${ final_res } ` ); console . log ( `Path Taken: ${ final_path . join ( ' ' ) } ` ); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Izlaide:
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
Noapaļošana tiek veikta šajā koda rindā:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
Filiālajā un saistītajā TSP algoritmā mēs aprēķinām zemāku robežu no optimālā šķīduma kopējām izmaksām, saskaitot katras virsotnes minimālās malas izmaksas un pēc tam dalot ar diviem. Tomēr šī apakšējā robeža var nebūt vesels skaitlis. Lai iegūtu veselu skaitli apakšējo robežu, mēs varam izmantot noapaļošanu.
Iepriekš minētajā kodā mainīgais Curr_bound ir pašreizējā zemākā robeža uz optimālā risinājuma kopējām izmaksām. Apmeklējot jaunu virsotni līmenī, mēs aprēķinām jaunu apakšējo robežu New_bound, ņemot vērā minimālo malu izmaksu summu jaunajai virsotnei un tās diviem tuvākajiem kaimiņiem. Pēc tam mēs atjauninām mainīgo Curr_Bound, noapaļojot New_bound līdz tuvākajam veselam skaitlim.
Ja līmenis ir 1, mēs noapaļojam līdz tuvākajam veselam skaitlim. Tas ir tāpēc, ka līdz šim mēs esam apmeklējuši tikai vienu virsotni, un mēs vēlamies būt konservatīvi, aplēsot optimālā risinājuma kopējās izmaksas. Ja līmenis ir lielāks par 1, mēs izmantojam agresīvāku noapaļošanas stratēģiju, kurā ņemts vērā fakts, ka mēs jau esam apmeklējuši dažas virsotnes, un tāpēc varam precīzāk novērtēt optimālā risinājuma kopējās izmaksas.
Laika sarežģītība: Sliktākā filiāles un saistītā gadījuma sarežģītība ir skaidri tāda pati kā brutālā spēka dēļ, jo sliktākajā gadījumā mēs nekad nevaram iegūt iespēju apgriezt mezglu. Tā kā praksē tas darbojas ļoti labi atkarībā no atšķirīgā TSP gadījuma. Sarežģītība ir atkarīga arī no ierobežojošās funkcijas izvēles, jo tās ir tās, kas izlemj, cik mezglu atgūt.
Atsauces:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.ernet.in/dsa/node187.html