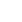
Garākā apakšsecība, kurā starpība starp blakus esošajām ir viena


Dota a ray arr[] no izmērs n uzdevums ir atrast garākā secība tāds, ka absolūta atšķirība starp blakus esošie elementi ir 1.
Piemēri:
Ievade: arr[] = [10 9 4 5 4 8 6]
Izvade: 3
Paskaidrojums: Trīs iespējamās 3. garuma apakšsecības ir [10 9 8] [4 5 4] un [4 5 6], kur blakus esošo elementu absolūtā atšķirība ir 1. Nevarēja izveidot derīgu garāku apakšsecību.
Ievade: arr[] = [1 2 3 4 5]
Izvade: 5
Paskaidrojums: Visus elementus var iekļaut derīgajā apakšsecībā.
Rekursijas izmantošana - O(2^n) laiks un O(n) telpa
C++Par rekursīvā pieeja mēs apsvērsim divi gadījumi katrā solī:
- Ja elements atbilst nosacījumam ( absolūta atšķirība starp blakus esošajiem elementiem ir 1) mēs ietver to secībā un pārejiet uz nākamais elements.
- citādi mēs izlaist uz strāva elementu un pāriet uz nākamo.
Matemātiski atkārtošanās attiecības izskatīsies šādi:
- garākaisSubseq(arr idx prev) = max (garākais apakšsekv.(arr idx + 1 iepriekš) 1 + garākais apakšsekv.(arr idx + 1 idx))
Pamata gadījums:
- Kad idx == arr.size() mums ir sasniegts masīva beigas tā atgriezt 0 (jo nevar iekļaut vairāk elementu).
// C++ program to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements is one using // recursion. #include using namespace std ; int subseqHelper ( int idx int prev vector < int >& arr ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx == arr . size ()) { return 0 ; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index int noTake = subseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr ); // Take the current element if the condition is met int take = 0 ; if ( prev == -1 || abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) == 1 ) { take = 1 + subseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr ); } // Return the maximum of the two options return max ( take noTake ); } // Function to find the longest subsequence int longestSubseq ( vector < int >& arr ) { // Start recursion from index 0 // with no previous element return subseqHelper ( 0 -1 arr ); } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 }; cout < < longestSubseq ( arr ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements is one using // recursion. import java.util.ArrayList ; class GfG { // Helper function to recursively find the subsequence static int subseqHelper ( int idx int prev ArrayList < Integer > arr ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx == arr . size ()) { return 0 ; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index int noTake = subseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr ); // Take the current element if the condition is met int take = 0 ; if ( prev == - 1 || Math . abs ( arr . get ( idx ) - arr . get ( prev )) == 1 ) { take = 1 + subseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr ); } // Return the maximum of the two options return Math . max ( take noTake ); } // Function to find the longest subsequence static int longestSubseq ( ArrayList < Integer > arr ) { // Start recursion from index 0 // with no previous element return subseqHelper ( 0 - 1 arr ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { ArrayList < Integer > arr = new ArrayList <> (); arr . add ( 10 ); arr . add ( 9 ); arr . add ( 4 ); arr . add ( 5 ); arr . add ( 4 ); arr . add ( 8 ); arr . add ( 6 ); System . out . println ( longestSubseq ( arr )); } }
Python # Python program to find the longest subsequence such that # the difference between adjacent elements is one using # recursion. def subseq_helper ( idx prev arr ): # Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if idx == len ( arr ): return 0 # Skip the current element and move to the next index no_take = subseq_helper ( idx + 1 prev arr ) # Take the current element if the condition is met take = 0 if prev == - 1 or abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) == 1 : take = 1 + subseq_helper ( idx + 1 idx arr ) # Return the maximum of the two options return max ( take no_take ) def longest_subseq ( arr ): # Start recursion from index 0 # with no previous element return subseq_helper ( 0 - 1 arr ) if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 ] print ( longest_subseq ( arr ))
C# // C# program to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements is one using // recursion. using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Helper function to recursively find the subsequence static int SubseqHelper ( int idx int prev List < int > arr ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx == arr . Count ) { return 0 ; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index int noTake = SubseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr ); // Take the current element if the condition is met int take = 0 ; if ( prev == - 1 || Math . Abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) == 1 ) { take = 1 + SubseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr ); } // Return the maximum of the two options return Math . Max ( take noTake ); } // Function to find the longest subsequence static int LongestSubseq ( List < int > arr ) { // Start recursion from index 0 // with no previous element return SubseqHelper ( 0 - 1 arr ); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { List < int > arr = new List < int > { 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 }; Console . WriteLine ( LongestSubseq ( arr )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find the longest subsequence // such that the difference between adjacent elements // is one using recursion. function subseqHelper ( idx prev arr ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx === arr . length ) { return 0 ; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index let noTake = subseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr ); // Take the current element if the condition is met let take = 0 ; if ( prev === - 1 || Math . abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) === 1 ) { take = 1 + subseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr ); } // Return the maximum of the two options return Math . max ( take noTake ); } function longestSubseq ( arr ) { // Start recursion from index 0 // with no previous element return subseqHelper ( 0 - 1 arr ); } const arr = [ 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 ]; console . log ( longestSubseq ( arr ));
Izvade
3
Izmantojot no augšas uz leju DP (atgādināšana ) - O(n^2) Laiks un O(n^2) Kosmoss
Ja mēs uzmanīgi pamanām, mēs varam novērot, ka iepriekš minētajam rekursīvajam risinājumam ir šādas divas īpašības Dinamiskā programmēšana :
1. Optimāla apakšstruktūra: Risinājums, lai atrastu garāko secību, lai atšķirība starp blakus esošajiem elementiem var iegūt no mazāku apakšproblēmu optimālajiem risinājumiem. Konkrēti jebkuram idx (pašreizējais indekss) un iepriekj (iepriekšējais indekss apakšsecībā) mēs varam izteikt rekursīvo attiecību šādi:
- apakšseqHelper(idx prev) = max (apakšsekpalīdzētājs(idx + 1 iepriekš) 1 + subseqHelper(idx + 1 idx))
2. Apakšproblēmas, kas pārklājas: Īstenojot a rekursīvs pieeja problēmas risināšanai, mēs novērojam, ka daudzas apakšproblēmas tiek aprēķinātas vairākas reizes. Piemēram, skaitļojot subseqHelper(0-1) masīvam arr = [10 9 4 5] apakšproblēma subseqHelper (2-1) var tikt aprēķināts vairākas reizes. Lai izvairītos no šīs atkārtošanās, mēs izmantojam iegaumēšanu, lai saglabātu iepriekš aprēķināto apakšproblēmu rezultātus.
Rekursīvais risinājums ietver divi parametri:
- idx (pašreizējais indekss masīvā).
- iepriekj (pēdējā iekļautā elementa indekss apakšsecībā).
Mums ir jāizseko abi parametri tāpēc mēs izveidojam a 2D masīva piezīme no izmērs (n) x (n+1) . Mēs inicializējam 2D masīva piezīme ar -1 lai norādītu, ka vēl nav aprēķinātas apakšproblēmas. Pirms rezultāta aprēķināšanas mēs pārbaudām, vai vērtība ir piezīme[idx][iepriekšējā+1] ir -1. Ja tā, mēs aprēķinām un veikals rezultāts. Pretējā gadījumā mēs atgriežam saglabāto rezultātu.
C++ // C++ program to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements is one using // recursion with memoization. #include using namespace std ; // Helper function to recursively find the subsequence int subseqHelper ( int idx int prev vector < int >& arr vector < vector < int >>& memo ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx == arr . size ()) { return 0 ; } // Check if the result is already computed if ( memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] != -1 ) { return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ]; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index int noTake = subseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr memo ); // Take the current element if the condition is met int take = 0 ; if ( prev == -1 || abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) == 1 ) { take = 1 + subseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr memo ); } // Store the result in the memo table return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] = max ( take noTake ); } // Function to find the longest subsequence int longestSubseq ( vector < int >& arr ) { int n = arr . size (); // Create a memoization table initialized to -1 vector < vector < int >> memo ( n vector < int > ( n + 1 -1 )); // Start recursion from index 0 with no previous element return subseqHelper ( 0 -1 arr memo ); } int main () { // Input array of integers vector < int > arr = { 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 }; cout < < longestSubseq ( arr ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements is one using // recursion with memoization. import java.util.ArrayList ; import java.util.Arrays ; class GfG { // Helper function to recursively find the subsequence static int subseqHelper ( int idx int prev ArrayList < Integer > arr int [][] memo ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx == arr . size ()) { return 0 ; } // Check if the result is already computed if ( memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] != - 1 ) { return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] ; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index int noTake = subseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr memo ); // Take the current element if the condition is met int take = 0 ; if ( prev == - 1 || Math . abs ( arr . get ( idx ) - arr . get ( prev )) == 1 ) { take = 1 + subseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr memo ); } // Store the result in the memo table memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] = Math . max ( take noTake ); // Return the stored result return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] ; } // Function to find the longest subsequence static int longestSubseq ( ArrayList < Integer > arr ) { int n = arr . size (); // Create a memoization table initialized to -1 int [][] memo = new int [ n ][ n + 1 ] ; for ( int [] row : memo ) { Arrays . fill ( row - 1 ); } // Start recursion from index 0 // with no previous element return subseqHelper ( 0 - 1 arr memo ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { ArrayList < Integer > arr = new ArrayList <> (); arr . add ( 10 ); arr . add ( 9 ); arr . add ( 4 ); arr . add ( 5 ); arr . add ( 4 ); arr . add ( 8 ); arr . add ( 6 ); System . out . println ( longestSubseq ( arr )); } }
Python # Python program to find the longest subsequence such that # the difference between adjacent elements is one using # recursion with memoization. def subseq_helper ( idx prev arr memo ): # Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if idx == len ( arr ): return 0 # Check if the result is already computed if memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] != - 1 : return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] # Skip the current element and move to the next index no_take = subseq_helper ( idx + 1 prev arr memo ) # Take the current element if the condition is met take = 0 if prev == - 1 or abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) == 1 : take = 1 + subseq_helper ( idx + 1 idx arr memo ) # Store the result in the memo table memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] = max ( take no_take ) # Return the stored result return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] def longest_subseq ( arr ): n = len ( arr ) # Create a memoization table initialized to -1 memo = [[ - 1 for _ in range ( n + 1 )] for _ in range ( n )] # Start recursion from index 0 with # no previous element return subseq_helper ( 0 - 1 arr memo ) if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 ] print ( longest_subseq ( arr ))
C# // C# program to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements is one using // recursion with memoization. using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Helper function to recursively find the subsequence static int SubseqHelper ( int idx int prev List < int > arr int [] memo ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx == arr . Count ) { return 0 ; } // Check if the result is already computed if ( memo [ idx prev + 1 ] != - 1 ) { return memo [ idx prev + 1 ]; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index int noTake = SubseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr memo ); // Take the current element if the condition is met int take = 0 ; if ( prev == - 1 || Math . Abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) == 1 ) { take = 1 + SubseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr memo ); } // Store the result in the memoization table memo [ idx prev + 1 ] = Math . Max ( take noTake ); // Return the stored result return memo [ idx prev + 1 ]; } // Function to find the longest subsequence static int LongestSubseq ( List < int > arr ) { int n = arr . Count ; // Create a memoization table initialized to -1 int [] memo = new int [ n n + 1 ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) { memo [ i j ] = - 1 ; } } // Start recursion from index 0 with no previous element return SubseqHelper ( 0 - 1 arr memo ); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { List < int > arr = new List < int > { 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 }; Console . WriteLine ( LongestSubseq ( arr )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find the longest subsequence // such that the difference between adjacent elements // is one using recursion with memoization. function subseqHelper ( idx prev arr memo ) { // Base case: if index reaches the end of the array if ( idx === arr . length ) { return 0 ; } // Check if the result is already computed if ( memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] !== - 1 ) { return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ]; } // Skip the current element and move to the next index let noTake = subseqHelper ( idx + 1 prev arr memo ); // Take the current element if the condition is met let take = 0 ; if ( prev === - 1 || Math . abs ( arr [ idx ] - arr [ prev ]) === 1 ) { take = 1 + subseqHelper ( idx + 1 idx arr memo ); } // Store the result in the memoization table memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ] = Math . max ( take noTake ); // Return the stored result return memo [ idx ][ prev + 1 ]; } function longestSubseq ( arr ) { let n = arr . length ; // Create a memoization table initialized to -1 let memo = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n + 1 ). fill ( - 1 )); // Start recursion from index 0 with no previous element return subseqHelper ( 0 - 1 arr memo ); } const arr = [ 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 ]; console . log ( longestSubseq ( arr ));
Izvade
3
Augšupējas DP (tabulācijas) izmantošana - O(n) Laiks un O(n) Kosmoss
Pieeja ir līdzīga rekursīvs metodi, bet tā vietā, lai rekursīvi sadalītu problēmu, mēs iteratīvi veidojam risinājumu a no apakšas uz augšu.
Tā vietā, lai izmantotu rekursiju, mēs izmantojam a hashmap balstīta dinamiskās programmēšanas tabula (dp), lai saglabātu garumi no garākajām apakšsekvencēm. Tas palīdz mums efektīvi aprēķināt un atjaunināt secība garumi visām iespējamām masīva elementu vērtībām.
C++Dinamiskās programmēšanas saistība:
dp[x] pārstāv garums no garākās apakšsecības, kas beidzas ar elementu x.
Katram elementam arr[i] masīvā: Ja arr[i] + 1 vai arr[i] - 1 pastāv dp:
- dp[arr[i]] = 1 + max (dp[arr[i] + 1] dp[arr[i] - 1]);
Tas nozīmē, ka mēs varam paplašināt apakšsekvences, kas beidzas ar arr[i] + 1 vai arr[i] - 1 autors ieskaitot arr[i].
Pretējā gadījumā sāciet jaunu secību:
- dp[arr[i]] = 1;
// C++ program to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements is one using // Tabulation. #include using namespace std ; int longestSubseq ( vector < int >& arr ) { int n = arr . size (); // Base case: if the array has only // one element if ( n == 1 ) { return 1 ; } // Map to store the length of the longest subsequence unordered_map < int int > dp ; int ans = 1 ; // Loop through the array to fill the map // with subsequence lengths for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { // Check if the current element is adjacent // to another subsequence if ( dp . count ( arr [ i ] + 1 ) > 0 || dp . count ( arr [ i ] - 1 ) > 0 ) { dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 + max ( dp [ arr [ i ] + 1 ] dp [ arr [ i ] - 1 ]); } else { dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 ; } // Update the result with the maximum // subsequence length ans = max ( ans dp [ arr [ i ]]); } return ans ; } int main () { vector < int > arr = { 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 }; cout < < longestSubseq ( arr ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java code to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements // is one using Tabulation. import java.util.HashMap ; import java.util.ArrayList ; class GfG { static int longestSubseq ( ArrayList < Integer > arr ) { int n = arr . size (); // Base case: if the array has only one element if ( n == 1 ) { return 1 ; } // Map to store the length of the longest subsequence HashMap < Integer Integer > dp = new HashMap <> (); int ans = 1 ; // Loop through the array to fill the map // with subsequence lengths for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { // Check if the current element is adjacent // to another subsequence if ( dp . containsKey ( arr . get ( i ) + 1 ) || dp . containsKey ( arr . get ( i ) - 1 )) { dp . put ( arr . get ( i ) 1 + Math . max ( dp . getOrDefault ( arr . get ( i ) + 1 0 ) dp . getOrDefault ( arr . get ( i ) - 1 0 ))); } else { dp . put ( arr . get ( i ) 1 ); } // Update the result with the maximum // subsequence length ans = Math . max ( ans dp . get ( arr . get ( i ))); } return ans ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { ArrayList < Integer > arr = new ArrayList <> (); arr . add ( 10 ); arr . add ( 9 ); arr . add ( 4 ); arr . add ( 5 ); arr . add ( 4 ); arr . add ( 8 ); arr . add ( 6 ); System . out . println ( longestSubseq ( arr )); } }
Python # Python code to find the longest subsequence such that # the difference between adjacent elements is # one using Tabulation. def longestSubseq ( arr ): n = len ( arr ) # Base case: if the array has only one element if n == 1 : return 1 # Dictionary to store the length of the # longest subsequence dp = {} ans = 1 for i in range ( n ): # Check if the current element is adjacent to # another subsequence if arr [ i ] + 1 in dp or arr [ i ] - 1 in dp : dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 + max ( dp . get ( arr [ i ] + 1 0 ) dp . get ( arr [ i ] - 1 0 )) else : dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 # Update the result with the maximum # subsequence length ans = max ( ans dp [ arr [ i ]]) return ans if __name__ == '__main__' : arr = [ 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 ] print ( longestSubseq ( arr ))
C# // C# code to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements // is one using Tabulation. using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { static int longestSubseq ( List < int > arr ) { int n = arr . Count ; // Base case: if the array has only one element if ( n == 1 ) { return 1 ; } // Map to store the length of the longest subsequence Dictionary < int int > dp = new Dictionary < int int > (); int ans = 1 ; // Loop through the array to fill the map with // subsequence lengths for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { // Check if the current element is adjacent to // another subsequence if ( dp . ContainsKey ( arr [ i ] + 1 ) || dp . ContainsKey ( arr [ i ] - 1 )) { dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 + Math . Max ( dp . GetValueOrDefault ( arr [ i ] + 1 0 ) dp . GetValueOrDefault ( arr [ i ] - 1 0 )); } else { dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 ; } // Update the result with the maximum // subsequence length ans = Math . Max ( ans dp [ arr [ i ]]); } return ans ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { List < int > arr = new List < int > { 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 }; Console . WriteLine ( longestSubseq ( arr )); } }
JavaScript // Function to find the longest subsequence such that // the difference between adjacent elements // is one using Tabulation. function longestSubseq ( arr ) { const n = arr . length ; // Base case: if the array has only one element if ( n === 1 ) { return 1 ; } // Object to store the length of the // longest subsequence let dp = {}; let ans = 1 ; // Loop through the array to fill the object // with subsequence lengths for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { // Check if the current element is adjacent to // another subsequence if (( arr [ i ] + 1 ) in dp || ( arr [ i ] - 1 ) in dp ) { dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 + Math . max ( dp [ arr [ i ] + 1 ] || 0 dp [ arr [ i ] - 1 ] || 0 ); } else { dp [ arr [ i ]] = 1 ; } // Update the result with the maximum // subsequence length ans = Math . max ( ans dp [ arr [ i ]]); } return ans ; } const arr = [ 10 9 4 5 4 8 6 ]; console . log ( longestSubseq ( arr ));
Izvade
3Izveidojiet viktorīnu