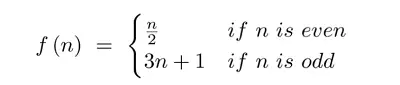Hierholcera algoritms virzītajam grafikam

Ņemot vērā virzītu Eilera grafiku, uzdevums ir izdrukāt an Eilera ķēde . Eilera ķēde ir ceļš, kas šķērso katru grafika malu precīzi vienu reizi un ceļš beidzas sākuma virsotnē.
Piezīme: Dotajā grafikā ir Eilera ķēde.
Piemērs:
Ievade: virzīts grafiks

Izvade: 0 3 4 0 2 1 0
Priekšnosacījumi:
- Mēs esam apsprieduši Problēma, kā noskaidrot, vai dotais grafs ir vai nav nevirzītam grafikam
- Nosacījumi Eilera ķēdei virzītā grpag: (1) Visas virsotnes pieder vienam stingri savienotam komponentam. (2) Visām virsotnēm ir vienāds iekšējais un ārējais grāds. Ņemiet vērā, ka nevirzītam grafikam nosacījums ir atšķirīgs (visām virsotnēm ir pāra pakāpe)
Pieeja:
- Izvēlieties jebkuru sākuma virsotni v un sekojiet malu takai no šīs virsotnes līdz atgriešanās pie v. Nav iespējams iestrēgt nevienā virsotnē, izņemot v, jo katras virsotnes pakāpei un ārpuses pakāpei jābūt vienādai, kad taka ieiet citā virsotnē w, ir jābūt neizmantotai malai, kas atstāj w. Šādā veidā izveidotā ekskursija ir slēgta, taču tā var neaptvert visas sākotnējā grafika virsotnes un malas.
- Kamēr pastāv virsotne u, kas pieder pašreizējam ceļojumam, bet kurai ir blakus esošās malas, kas nav maršruta daļa, sāciet citu taku no u, sekojot neizmantotajām malām, līdz atgriežaties pie u un pievienojiet šādā veidā izveidoto tūri iepriekšējam ceļojumam.
Ilustrācija:
Iepriekš minētās diagrammas piemērs ar 5 mezgliem: adj = {{2 3} {0} {1} {4} {0}}.
- Sāciet ar virsotni 0 :
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0]
- Ķēde: []
- Virsotne 0 → 3 :
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3]
- Ķēde: []
- Virsotne 3 → 4 :
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4]
- Ķēde: []
- Virsotne 4 → 0 :
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4 0]
- Ķēde: []
- Virsotne 0 → 2 :
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4 0 2]
- Ķēde: []
- Virsotne 2 → 1 :
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4 0 2 1]
- Ķēde: []
- Virsotne 1 → 0 :
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4 0 2 1 0]
- Ķēde: []
- Atgriezties uz virsotni 0 : pievienojiet ķēdei 0.
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4 0 2 1]
- Ķēde: [0]
- Atgriezties uz 1. virsotni : pievienojiet ķēdei 1.
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4 0 2]
- Ķēde: [0 1]
- Atgriezties uz 2. virsotni : pievienojiet ķēdei 2.
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4 0]
- Ķēde: [0 1 2]
- Atgriezties uz virsotni 0 : pievienojiet ķēdei 0.
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3 4]
- Ķēde: [0 1 2 0]
- Atgriezties uz 4. virsotni : pievienojiet ķēdei 4.
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0 3]
- Ķēde: [0 1 2 0 4]
- Atgriezties uz 3. virsotni : pievienojiet ķēdei 3.
- Pašreizējais ceļš: [0]
- Ķēde: [0 1 2 0 4 3]
- Atgriezties uz virsotni 0 : pievienojiet ķēdei 0.
- Pašreizējais ceļš: []
- Ķēde: [0 1 2 0 4 3 0]
Tālāk ir norādīta iepriekš minētās pieejas īstenošana.
C++ // C++ program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm #include using namespace std ; // Function to print Eulerian circuit vector < int > printCircuit ( vector < vector < int >> & adj ) { int n = adj . size (); if ( n == 0 ) return {}; // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 vector < int > currPath ; currPath . push_back ( 0 ); // list to store final circuit vector < int > circuit ; while ( currPath . size () > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath [ currPath . size () - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. size () > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj [ currNode ]. back (); adj [ currNode ]. pop_back (); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . push_back ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . push_back ( currPath . back ()); currPath . pop_back (); } } // reverse the result vector reverse ( circuit . begin () circuit . end ()); return circuit ; } int main () { vector < vector < int >> adj = {{ 2 3 } { 0 } { 1 } { 4 } { 0 }}; vector < int > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( auto v : ans ) cout < < v < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm import java.util.* ; class GfG { // Function to print Eulerian circuit static List < Integer > printCircuit ( List < List < Integer >> adj ) { int n = adj . size (); if ( n == 0 ) return new ArrayList <> (); // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 List < Integer > currPath = new ArrayList <> (); currPath . add ( 0 ); // list to store final circuit List < Integer > circuit = new ArrayList <> (); while ( currPath . size () > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath . get ( currPath . size () - 1 ); // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj . get ( currNode ). get ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () - 1 ); adj . get ( currNode ). remove ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () - 1 ); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . add ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . add ( currPath . get ( currPath . size () - 1 )); currPath . remove ( currPath . size () - 1 ); } } // reverse the result vector Collections . reverse ( circuit ); return circuit ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { List < List < Integer >> adj = new ArrayList <> (); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 2 3 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 0 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 1 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 4 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 0 ))); List < Integer > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( int v : ans ) System . out . print ( v + ' ' ); System . out . println (); } }
Python # Python program to print Eulerian circuit in given # directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm # Function to print Eulerian circuit def printCircuit ( adj ): n = len ( adj ) if n == 0 : return [] # Maintain a stack to keep vertices # We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 currPath = [ 0 ] # list to store final circuit circuit = [] while len ( currPath ) > 0 : currNode = currPath [ - 1 ] # If there's remaining edge in adjacency list # of the current vertex if len ( adj [ currNode ]) > 0 : # Find and remove the next vertex that is # adjacent to the current vertex nextNode = adj [ currNode ] . pop () # Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . append ( nextNode ) # back-track to find remaining circuit else : # Remove the current vertex and # put it in the circuit circuit . append ( currPath . pop ()) # reverse the result vector circuit . reverse () return circuit if __name__ == '__main__' : adj = [[ 2 3 ] [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 4 ] [ 0 ]] ans = printCircuit ( adj ) for v in ans : print ( v end = ' ' ) print ()
C# // C# program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Function to print Eulerian circuit static List < int > printCircuit ( List < List < int >> adj ) { int n = adj . Count ; if ( n == 0 ) return new List < int > (); // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 List < int > currPath = new List < int > { 0 }; // list to store final circuit List < int > circuit = new List < int > (); while ( currPath . Count > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath [ currPath . Count - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. Count > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj [ currNode ][ adj [ currNode ]. Count - 1 ]; adj [ currNode ]. RemoveAt ( adj [ currNode ]. Count - 1 ); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . Add ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . Add ( currPath [ currPath . Count - 1 ]); currPath . RemoveAt ( currPath . Count - 1 ); } } // reverse the result vector circuit . Reverse (); return circuit ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { List < List < int >> adj = new List < List < int >> { new List < int > { 2 3 } new List < int > { 0 } new List < int > { 1 } new List < int > { 4 } new List < int > { 0 } }; List < int > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); foreach ( int v in ans ) { Console . Write ( v + ' ' ); } Console . WriteLine (); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm // Function to print Eulerian circuit function printCircuit ( adj ) { let n = adj . length ; if ( n === 0 ) return []; // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 let currPath = [ 0 ]; // list to store final circuit let circuit = []; while ( currPath . length > 0 ) { let currNode = currPath [ currPath . length - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. length > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex let nextNode = adj [ currNode ]. pop (); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . push ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . push ( currPath . pop ()); } } // reverse the result vector circuit . reverse (); return circuit ; } let adj = [[ 2 3 ] [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 4 ] [ 0 ]]; let ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( let v of ans ) { console . log ( v ' ' ); }
Izvade
0 3 4 0 2 1 0
Laika sarežģītība: O(V + E) kur V ir virsotņu skaits un E ir grafa šķautņu skaits. Iemesls tam ir tāpēc, ka algoritms veic dziļuma meklēšanu (DFS) un apmeklē katru virsotni un katru malu tieši vienu reizi. Tātad katrai virsotnei ir nepieciešams O(1) laiks, lai to apmeklētu, un katrai malai ir nepieciešams O(1) laiks, lai to šķērsotu.
Telpas sarežģītība: O(V + E) kā algoritms izmanto kaudzi, lai saglabātu pašreizējo ceļu, un sarakstu, lai saglabātu galīgo ķēdi. Sliktākajā gadījumā maksimālais kaudzes izmērs var būt V + E, tāpēc telpas sarežģītība ir O(V + E).
Izveidojiet viktorīnu