기사가 체스판에 남아 있을 확률

주어진 n*n 체스판 그리고 기사 위치 (xy) 기사가 움직일 때마다 8개의 가능한 움직임 중 하나를 균일하게 선택합니다. 무작위의 (그 말이 체스판에서 벗어나더라도) 움직임 거기. 기사 계속 정확히 만들어질 때까지 움직인다 케이 움직이거나 가지고 있다 이사했다 체스판. 과제는 찾다 그만큼 개연성 그 기사는 유적 에 판자 그 후에 중지됨 움직이는.
메모: 체스 기사는 8개의 가능한 움직임을 만들 수 있습니다. 각 이동은 기본 방향의 두 셀, 직교 방향의 한 셀입니다.
예:
입력: n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 1
산출: 0.25
설명: 기사는 (0 0)에서 시작하고 한 단계를 밟은 후 (1 2) 및 (2 1)의 8개 위치 중 2개 위치에만 보드 내부에 놓이게 됩니다. 따라서 확률은 2/8 = 0.25가 됩니다.입력 : n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3
산출: 0.125입력: n = 4 x = 1 y = 2 k = 4
산출: 0.024414
목차
- Top-Down Dp(Memoization) 사용 - O(n*n*k) 시간 및 O(n*n*k) 공간
- 상향식 Dp(표) 사용 - O(n*n*k) 시간 및 O(n*n*k) 공간
- 공간 최적화 Dp - O(n*n*k) 시간 및 O(n*n) 공간 사용
Top-Down Dp(Memoization) 사용 - O(n*n*k) 시간 및 O(n*n*k) 공간
C++k번 이동한 후에도 기사가 체스판에 남아 있을 확률은 k - 1번 이동한 후 이전 8개 위치에 있는 기사가 있을 확률의 평균과 같습니다. 마찬가지로 k-1번 이동한 후의 확률은 k-2번 이동한 후 확률의 평균에 따라 달라집니다. 아이디어는 사용하는 것입니다 메모이제이션 이전 이동의 확률을 저장하고 평균을 찾아 최종 결과를 계산합니다.
그렇게 하려면 3차원 배열 메모[][][] 어디 메모[i][j][k] k번 이동한 후 기사가 셀(i j)에 있을 확률을 저장합니다. k가 0이면 즉, 초기 상태에 도달합니다. 1을 반환 그렇지 않으면 이전 8개 위치를 탐색하고 해당 확률의 평균을 구합니다.
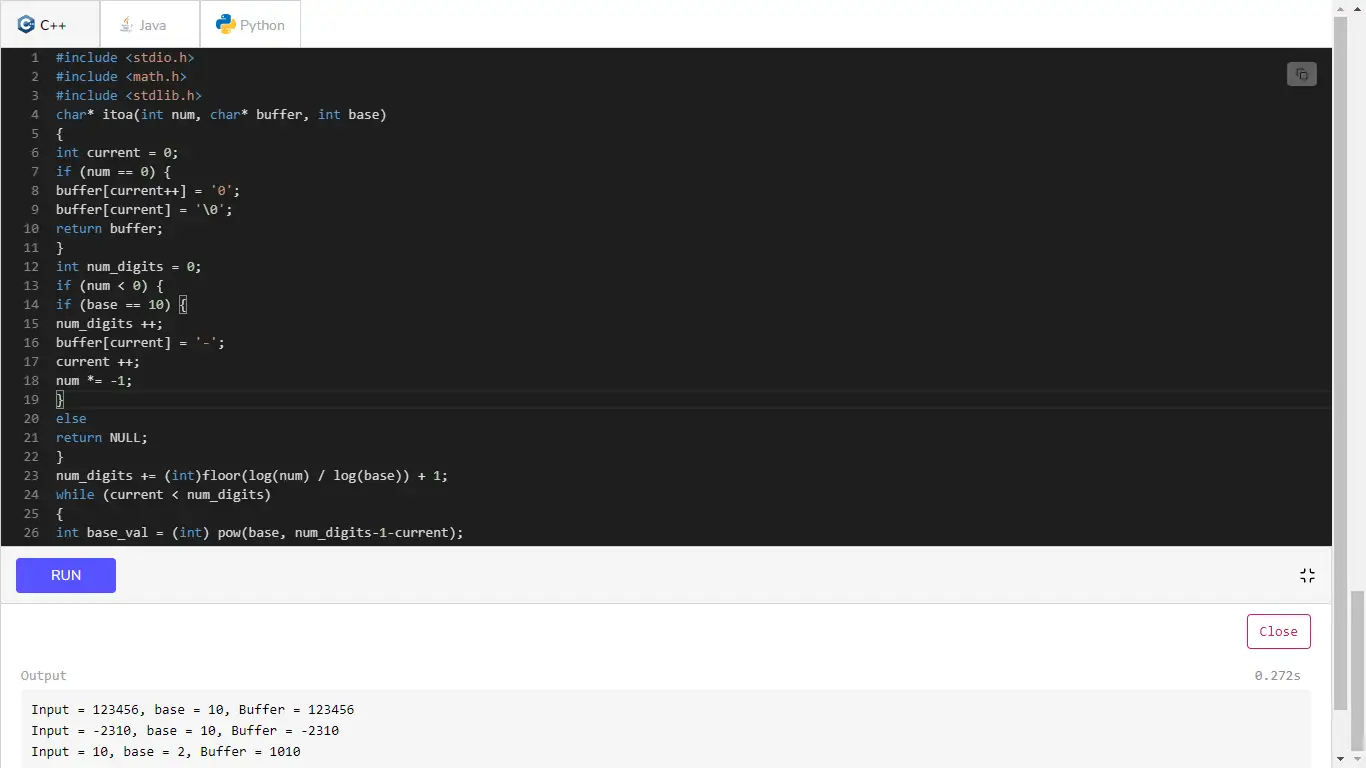
// C++ program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard #include using namespace std ; // recursive function to calculate // knight probability double knightProbability ( int n int x int y int k vector < vector < vector < double >>> & memo ){ // Base case initial probability if ( k == 0 ) return 1.0 ; // check if already calculated if ( memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] != -1 ) return memo [ x ][ y ][ k ]; vector < vector < int >> directions = {{ 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 -1 } { 1 -2 } { -1 -2 } { -2 -1 } { -2 1 } { -1 2 }}; memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = 0 ; double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (xy) for ( auto d : directions ){ int u = x + d [ 0 ]; int v = y + d [ 1 ]; // if this position lie inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) cur += knightProbability ( n u v k -1 memo ) / 8.0 ; } return memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = cur ; } // Function to find the probability double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // Initialize memo to store results vector < vector < vector < double >>> memo ( n vector < vector < double >> ( n vector < double > ( k + 1 -1 ))); return knightProbability ( n x y k memo ); } int main (){ int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; cout < < findProb ( n x y k ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard class GfG { // recursive function to calculate // knight probability static double knightProbability ( int n int x int y int k double [][][] memo ) { // Base case initial probability if ( k == 0 ) return 1.0 ; // check if already calculated if ( memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] != - 1 ) return memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] ; int [][] directions = {{ 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 - 1 } { 1 - 2 } { - 1 - 2 } { - 2 - 1 } { - 2 1 } { - 1 2 }}; memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = 0 ; double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (x y) for ( int [] d : directions ) { int u = x + d [ 0 ] ; int v = y + d [ 1 ] ; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) cur += knightProbability ( n u v k - 1 memo ) / 8.0 ; } return memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = cur ; } // Function to find the probability static double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // Initialize memo to store results double [][][] memo = new double [ n ][ n ][ k + 1 ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { for ( int m = 0 ; m <= k ; m ++ ) { memo [ i ][ j ][ m ] = - 1 ; } } } return knightProbability ( n x y k memo ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; System . out . println ( findProb ( n x y k )); } }
Python # Python program to find the probability of the # knight to remain inside the chessboard # recursive function to calculate # knight probability def knightProbability ( n x y k memo ): # Base case initial probability if k == 0 : return 1.0 # check if already calculated if memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] != - 1 : return memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] directions = [ [ 1 2 ] [ 2 1 ] [ 2 - 1 ] [ 1 - 2 ] [ - 1 - 2 ] [ - 2 - 1 ] [ - 2 1 ] [ - 1 2 ] ] memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = 0 cur = 0.0 # for every position reachable from (x y) for d in directions : u = x + d [ 0 ] v = y + d [ 1 ] # if this position lies inside the board if 0 <= u < n and 0 <= v < n : cur += knightProbability ( n u v k - 1 memo ) / 8.0 memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = cur return cur # Function to find the probability def findProb ( n x y k ): # Initialize memo to store results memo = [[[ - 1 for _ in range ( k + 1 )] for _ in range ( n )] for _ in range ( n )] return knightProbability ( n x y k memo ) n x y k = 8 0 0 3 print ( findProb ( n x y k ))
C# // C# program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard using System ; class GfG { // recursive function to calculate // knight probability static double KnightProbability ( int n int x int y int k double [] memo ) { // Base case initial probability if ( k == 0 ) return 1.0 ; // check if already calculated if ( memo [ x y k ] != - 1 ) return memo [ x y k ]; int [] directions = {{ 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 - 1 } { 1 - 2 } { - 1 - 2 } { - 2 - 1 } { - 2 1 } { - 1 2 }}; memo [ x y k ] = 0 ; double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (x y) for ( int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i ++ ) { int u = x + directions [ i 0 ]; int v = y + directions [ i 1 ]; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) { cur += KnightProbability ( n u v k - 1 memo ) / 8.0 ; } } return memo [ x y k ] = cur ; } // Function to find the probability static double FindProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // Initialize memo to store results double [] memo = new double [ n n k + 1 ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { for ( int m = 0 ; m <= k ; m ++ ) { memo [ i j m ] = - 1 ; } } } return KnightProbability ( n x y k memo ); } static void Main () { int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; Console . WriteLine ( FindProb ( n x y k )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard // recursive function to calculate // knight probability function knightProbability ( n x y k memo ) { // Base case initial probability if ( k === 0 ) return 1.0 ; // check if already calculated if ( memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] !== - 1 ) return memo [ x ][ y ][ k ]; const directions = [ [ 1 2 ] [ 2 1 ] [ 2 - 1 ] [ 1 - 2 ] [ - 1 - 2 ] [ - 2 - 1 ] [ - 2 1 ] [ - 1 2 ] ]; memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = 0 ; let cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (x y) for ( let d of directions ) { const u = x + d [ 0 ]; const v = y + d [ 1 ]; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) { cur += knightProbability ( n u v k - 1 memo ) / 8.0 ; } } return memo [ x ][ y ][ k ] = cur ; } // Function to find the probability function findProb ( n x y k ) { // Initialize memo to store results const memo = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( k + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ))); return knightProbability ( n x y k memo ). toFixed ( 6 ); } const n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; console . log ( findProb ( n x y k ));
산출
0.125
상향식 Dp(표) 사용 - O(n*n*k) 시간 및 O(n*n*k) 공간
C++위의 접근 방식은 다음을 사용하여 최적화할 수 있습니다. 상향식 재귀 스택에 필요한 추가 공간을 줄이는 표입니다. 아이디어는 3을 유지하는 것입니다 D 배열 dp[][][] 어디 dp[i][j][k] 기사가 감방에 있을 확률을 저장합니다. (나는 j) ~ 후에 케이 움직인다. 초기화 0번째 상태 DP 가치있는 1 . 이후의 각 이동에 대해 개연성 기사의 것입니다 동일한 에게 평균 확률의 이전의 이후 8자리 k-1 움직인다.
// C++ program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard #include using namespace std ; // Function to find the probability double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // Initialize dp to store results of each step vector < vector < vector < double >>> dp ( n vector < vector < double >> ( n vector < double > ( k + 1 ))); // Initialize dp for step 0 for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { dp [ i ][ j ][ 0 ] = 1.0 ; } } vector < vector < int >> directions = { { 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 -1 } { 1 -2 } { -1 -2 } { -2 -1 } { -2 1 } { -1 2 } }; for ( int move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (xy) for ( auto d : directions ) { int u = i + d [ 0 ]; int v = j + d [ 1 ]; // if this position lie inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) cur += dp [ u ][ v ][ move - 1 ] / 8.0 ; } // store the result dp [ i ][ j ][ move ] = cur ; } } } // return the result return dp [ x ][ y ][ k ]; } int main (){ int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; cout < < findProb ( n x y k ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard import java.util.* ; class GfG { // Function to find the probability static double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // Initialize dp to store results of each step double [][][] dp = new double [ n ][ n ][ k + 1 ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { dp [ i ][ j ][ 0 ] = 1 ; } } int [][] directions = { { 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 - 1 } { 1 - 2 } { - 1 - 2 } { - 2 - 1 } { - 2 1 } { - 1 2 } }; for ( int move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (x y) for ( int [] d : directions ) { int u = i + d [ 0 ] ; int v = j + d [ 1 ] ; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) { cur += dp [ u ][ v ][ move - 1 ] / 8.0 ; } } // store the result dp [ i ][ j ][ move ] = cur ; } } } // return the result return dp [ x ][ y ][ k ] ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; System . out . println ( findProb ( n x y k )); } }
Python # Python program to find the probability of the # knight to remain inside the chessboard # Function to find the probability def findProb ( n x y k ): # Initialize dp to store results of each step dp = [[[ 0 for _ in range ( k + 1 )] for _ in range ( n )] for _ in range ( n )] for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( n ): dp [ i ][ j ][ 0 ] = 1.0 directions = [[ 1 2 ] [ 2 1 ] [ 2 - 1 ] [ 1 - 2 ] [ - 1 - 2 ] [ - 2 - 1 ] [ - 2 1 ] [ - 1 2 ]] for move in range ( 1 k + 1 ): # find probability for cell (i j) for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( n ): cur = 0.0 # for every position reachable from (x y) for d in directions : u = i + d [ 0 ] v = j + d [ 1 ] # if this position lies inside the board if 0 <= u < n and 0 <= v < n : cur += dp [ u ][ v ][ move - 1 ] / 8.0 # store the result dp [ i ][ j ][ move ] = cur # return the result return dp [ x ][ y ][ k ] if __name__ == '__main__' : n x y k = 8 0 0 3 print ( findProb ( n x y k ))
C# // C# program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard using System ; class GfG { // Function to find the probability static double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // Initialize dp to store results of each step double [] dp = new double [ n n k + 1 ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { dp [ i j 0 ] = 1.0 ; } } int [] directions = {{ 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 - 1 } { 1 - 2 } { - 1 - 2 } { - 2 - 1 } { - 2 1 } { - 1 2 }}; for ( int move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (x y) for ( int d = 0 ; d < directions . GetLength ( 0 ); d ++ ) { int u = i + directions [ d 0 ]; int v = j + directions [ d 1 ]; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) { cur += dp [ u v move - 1 ] / 8.0 ; } } // store the result dp [ i j move ] = cur ; } } } // return the result return dp [ x y k ]; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; Console . WriteLine ( findProb ( n x y k )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard // Function to find the probability function findProb ( n x y k ) { // Initialize dp to store results of each step let dp = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( k + 1 ). fill ( 0 )) ); // Initialize dp for step 0 for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { dp [ i ][ j ][ 0 ] = 1.0 ; } } let directions = [[ 1 2 ] [ 2 1 ] [ 2 - 1 ] [ 1 - 2 ] [ - 1 - 2 ] [ - 2 - 1 ] [ - 2 1 ] [ - 1 2 ]]; for ( let move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { let cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (x y) for ( let d of directions ) { let u = i + d [ 0 ]; let v = j + d [ 1 ]; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) { cur += dp [ u ][ v ][ move - 1 ] / 8.0 ; } } // store the result dp [ i ][ j ][ move ] = cur ; } } } // return the result return dp [ x ][ y ][ k ]. toFixed ( 6 ); } let n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; console . log ( findProb ( n x y k ));
산출
0.125
공간 최적화 Dp - O(n*n*k) 시간 및 O(n*n) 공간 사용
C++위의 접근 방식 필요하다 오직 이전의 계산할 확률의 상태 현재의 이렇게 상태 오직 그만큼 이전의 매장을 보관해야 합니다. 아이디어는 두 개를 만드는 것입니다 2차원 배열 prevMove[][] 그리고 현재이동[][] 어디
- prevMove[i][j]는 기사가 이전 이동까지 (i j)에 있을 확률을 저장합니다. 초기 상태는 값 1로 초기화됩니다.
- currMove[i][j]는 현재 상태의 확률을 저장합니다.
위의 접근 방식과 유사하게 작동합니다. 끝 각 반복의 이전이동[][] 업데이트 값이 저장된 상태에서 현재이동[][].
// C++ program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard #include using namespace std ; // Function to find the probability double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // dp to store results of previous move vector < vector < double >> prevMove ( n vector < double > ( n 1 )); // dp to store results of current move vector < vector < double >> currMove ( n vector < double > ( n 0 )); vector < vector < int >> directions = { { 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 -1 } { 1 -2 } { -1 -2 } { -2 -1 } { -2 1 } { -1 2 } }; for ( int move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (xy) for ( auto d : directions ) { int u = i + d [ 0 ]; int v = j + d [ 1 ]; // if this position lie inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) cur += prevMove [ u ][ v ] / 8.0 ; } // store the result currMove [ i ][ j ] = cur ; } } // update previous state prevMove = currMove ; } // return the result return prevMove [ x ][ y ]; } int main (){ int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; cout < < findProb ( n x y k ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard class GfG { // Function to find the probability static double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // dp to store results of previous move double [][] prevMove = new double [ n ][ n ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { prevMove [ i ][ j ] = 1.0 ; } } // dp to store results of current move double [][] currMove = new double [ n ][ n ] ; int [][] directions = { { 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 - 1 } { 1 - 2 } { - 1 - 2 } { - 2 - 1 } { - 2 1 } { - 1 2 } }; for ( int move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (xy) for ( int [] d : directions ) { int u = i + d [ 0 ] ; int v = j + d [ 1 ] ; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) cur += prevMove [ u ][ v ] / 8.0 ; } // store the result currMove [ i ][ j ] = cur ; } } // update previous state for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { System . arraycopy ( currMove [ i ] 0 prevMove [ i ] 0 n ); } } // return the result return prevMove [ x ][ y ] ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; System . out . println ( findProb ( n x y k )); } }
Python # Python program to find the probability of the # knight to remain inside the chessboard def findProb ( n x y k ): # dp to store results of previous move prevMove = [[ 1.0 ] * n for _ in range ( n )] # dp to store results of current move currMove = [[ 0.0 ] * n for _ in range ( n )] directions = [ [ 1 2 ] [ 2 1 ] [ 2 - 1 ] [ 1 - 2 ] [ - 1 - 2 ] [ - 2 - 1 ] [ - 2 1 ] [ - 1 2 ] ] for move in range ( 1 k + 1 ): # find probability for cell (i j) for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( n ): cur = 0.0 # for every position reachable from (xy) for d in directions : u v = i + d [ 0 ] j + d [ 1 ] # if this position lies inside the board if 0 <= u < n and 0 <= v < n : cur += prevMove [ u ][ v ] / 8.0 # store the result currMove [ i ][ j ] = cur # update previous state prevMove = [ row [:] for row in currMove ] # return the result return prevMove [ x ][ y ] if __name__ == '__main__' : n x y k = 8 0 0 3 print ( findProb ( n x y k ))
C# // C# program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard using System ; class GfG { // Function to find the probability static double findProb ( int n int x int y int k ) { // dp to store results of previous move double [] prevMove = new double [ n n ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) prevMove [ i j ] = 1.0 ; // dp to store results of current move double [] currMove = new double [ n n ]; int [] directions = { { 1 2 } { 2 1 } { 2 - 1 } { 1 - 2 } { - 1 - 2 } { - 2 - 1 } { - 2 1 } { - 1 2 } }; for ( int move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { double cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (xy) for ( int d = 0 ; d < directions . GetLength ( 0 ); d ++ ) { int u = i + directions [ d 0 ]; int v = j + directions [ d 1 ]; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) cur += prevMove [ u v ] / 8.0 ; } // store the result currMove [ i j ] = cur ; } } // update previous state Array . Copy ( currMove prevMove n * n ); } // return the result return prevMove [ x y ]; } static void Main () { int n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; Console . WriteLine ( findProb ( n x y k )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find the probability of the // knight to remain inside the chessboard function findProb ( n x y k ) { // dp to store results of previous move let prevMove = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 1.0 )); // dp to store results of current move let currMove = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0.0 )); const directions = [ [ 1 2 ] [ 2 1 ] [ 2 - 1 ] [ 1 - 2 ] [ - 1 - 2 ] [ - 2 - 1 ] [ - 2 1 ] [ - 1 2 ] ]; for ( let move = 1 ; move <= k ; move ++ ) { // find probability for cell (i j) for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { let cur = 0.0 ; // for every position reachable from (xy) for ( let d of directions ) { let u = i + d [ 0 ]; let v = j + d [ 1 ]; // if this position lies inside the board if ( u >= 0 && u < n && v >= 0 && v < n ) cur += prevMove [ u ][ v ] / 8.0 ; } // store the result currMove [ i ][ j ] = cur ; } } // update previous state prevMove = currMove . map ( row => [... row ]); } // return the result return prevMove [ x ][ y ]. toFixed ( 6 ); } let n = 8 x = 0 y = 0 k = 3 ; console . log ( findProb ( n x y k ));
산출
0.125퀴즈 만들기