동적 메모리용 C++의 new 및 delete 연산자

C/C++에서 동적 메모리 할당은 프로그래머가 수동으로 메모리 할당을 수행하는 것을 의미합니다. 동적으로 할당된 메모리는 다음에 할당됩니다. 더미, 비정적 및 지역 변수는 메모리를 할당받습니다. 스택 (인용하다 메모리 레이아웃 C 프로그램 자세한 내용은).
애플리케이션이란 무엇입니까?
- 동적으로 할당된 메모리의 한 가지 용도는 가변 크기의 메모리를 할당하는 것입니다. 이는 다음을 제외하고는 컴파일러 할당 메모리로는 가능하지 않습니다. 가변 길이 배열 .
- 가장 중요한 용도는 프로그래머에게 제공되는 유연성입니다. 필요할 때마다, 더 이상 필요하지 않을 때마다 메모리를 자유롭게 할당하고 할당 해제할 수 있습니다. 이러한 유연성이 도움이 되는 경우가 많이 있습니다. 그러한 사례의 예는 다음과 같습니다. 나무 , 등.
일반 변수에 할당된 메모리와 어떻게 다릅니까?
int a, char str[10] 등과 같은 일반 변수의 경우 메모리가 자동으로 할당 및 할당 해제됩니다. int *p = new int[10]과 같이 동적으로 할당된 메모리의 경우 더 이상 필요하지 않을 때 메모리 할당을 해제하는 것은 프로그래머의 책임입니다. 프로그래머가 메모리 할당을 해제하지 않으면 메모리 누수 (프로그램이 종료될 때까지 메모리 할당이 해제되지 않습니다.)
C++에서 메모리는 어떻게 할당/할당 취소됩니까?
C는 malloc()과 calloc() 런타임에 동적으로 메모리를 할당하는 함수와 free() 함수를 사용하여 동적으로 할당된 메모리를 해제합니다. C++에서는 이러한 함수를 지원하며 두 개의 연산자도 있습니다. 새로운 그리고 삭제, 더 좋고 쉬운 방법으로 메모리를 할당하고 해제하는 작업을 수행합니다.
새로운 운영자
new 연산자는 Free Store에 대한 메모리 할당 요청을 나타냅니다. 충분한 메모리를 사용할 수 있으면 new 연산자는 메모리를 초기화하고 새로 할당되고 초기화된 메모리의 주소를 포인터 변수에 반환합니다.
new 연산자를 사용하는 구문
pointer-variable = new data-type;
여기서 포인터 변수는 데이터 유형 유형의 포인터입니다. 데이터 유형은 배열을 포함한 모든 내장 데이터 유형이거나 구조 및 클래스를 포함한 사용자 정의 데이터 유형일 수 있습니다.
예:
// Pointer initialized with NULL // Then request memory for the variable int *p = NULL; p = new int; OR // Combine declaration of pointer // and their assignment int *p = new int;C++
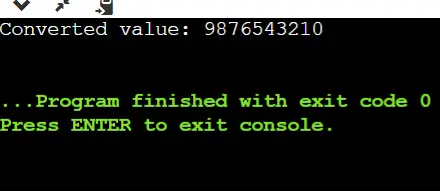
// C++ program to demonstrate how to create dynamic variable // using new #include #include using namespace std; int main() { // pointer to store the address returned by the new int* ptr; // allocating memory for integer ptr = new int; // assigning value using dereference operator *ptr = 10; // printing value and address cout < < 'Address: ' < < ptr < < endl; cout < < 'Value: ' < < *ptr; return 0; } 산출
Address: 0x162bc20 Value: 10
메모리 초기화: new 연산자를 사용하여 내장 데이터 유형에 대한 메모리를 초기화할 수도 있습니다. 사용자 정의 데이터 유형의 경우 값을 초기화하려면 생성자가 필요합니다(데이터 유형을 입력으로 사용). 다음은 두 데이터 유형의 초기화 예입니다.
pointer-variable = new data-type(value);
예:
C++ // C++ program to illustrate how to initialize a dynamic // variable with allocation #include #include using namespace std; // Custom data type with constructor to take initial value struct cust { int p; cust(int q) : p(q) { } cust() = default; }; int main() { // creating inbuit data types with initial value int* p = new int(25); float* q = new float(75.25); // Works fine, doesn’t require constructor cust* var1 = new cust; // OR // Works fine, doesn’t require constructor var1 = new cust(); // Notice error if you comment this line cust* var = new cust(25); cout < < *p < < ' ' < < *q < < ' ' < < var->피; 0을 반환합니다. } 산출
25 75.25 25
메모리 블록을 할당합니다. new 연산자는 유형의 메모리 블록(배열)을 할당하는 데에도 사용됩니다. 데이터 형식 .
pointer-variable = new data-type[size];
여기서 size(변수)는 배열의 요소 수를 지정합니다.
예:
int *p = new int[10]
int 유형의 연속 10개 정수에 대한 메모리를 동적으로 할당하고 top(포인터)에 할당된 시퀀스의 첫 번째 요소에 대한 포인터를 반환합니다. p[0]은 첫 번째 요소를 참조하고, p[1]은 두 번째 요소를 참조하는 방식입니다.

일반 배열 선언과 new 사용
일반 배열을 선언하는 것과 new를 사용하여 메모리 블록을 할당하는 것에는 차이가 있습니다. 가장 중요한 차이점은 일반 배열이 컴파일러에 의해 할당 해제된다는 것입니다(배열이 로컬인 경우 함수가 반환되거나 완료될 때 할당이 해제됩니다). 그러나 동적으로 할당된 배열은 프로그래머가 할당을 취소하거나 프로그램이 종료될 때까지 항상 그대로 유지됩니다.
런타임 중에 충분한 메모리를 사용할 수 없으면 어떻게 되나요?
힙에 할당할 메모리가 충분하지 않은 경우 새 요청은 std::bad_alloc 유형의 예외를 발생시켜 실패를 나타냅니다. 단, new 연산자와 함께 nothrow를 사용하지 않는 한 NULL 포인터를 반환합니다(예외 섹션으로 스크롤). 새로운 운영자 처리 이것 기사). 따라서 프로그램을 사용하기 전에 new가 생성한 포인터 변수를 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
int *p = new(nothrow) int; if (!p) { cout < < 'Memory allocation failed
'; } 삭제 연산자
동적으로 할당된 메모리를 해제하는 것은 프로그래머의 책임이므로 프로그래머에게는 C++ 언어로 삭제 연산자가 제공됩니다.
통사론:
// Release memory pointed by pointer-variable delete pointer-variable;
여기서 포인터 변수는 생성된 데이터 객체를 가리키는 포인터이다. 새로운 .
예:
delete p; delete q;
포인터 변수가 가리키는 동적으로 할당된 배열을 해제하려면 다음 형식을 사용합니다. 삭제 :
// Release block of memory // pointed by pointer-variable delete[] pointer-variable; Example: // It will free the entire array // pointed by p. delete[] p;CPP
// C++ program to illustrate dynamic allocation // and deallocation of memory using new and delete #include using namespace std; int main() { // Pointer initialization to null int* p = NULL; // Request memory for the variable // using new operator p = new (nothrow) int; if (!p) cout < < 'allocation of memory failed
'; else { // Store value at allocated address *p = 29; cout < < 'Value of p: ' < < *p < < endl; } // Request block of memory // using new operator float* r = new float(75.25); cout < < 'Value of r: ' < < *r < < endl; // Request block of memory of size n int n = 5; int* q = new (nothrow) int[n]; if (!q) cout < < 'allocation of memory failed
'; else { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) q[i] = i + 1; cout < < 'Value store in block of memory: '; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout < < q[i] < < ' '; } // freed the allocated memory delete p; delete r; // freed the block of allocated memory delete[] q; return 0; } 산출
Value of p: 29 Value of r: 75.25 Value store in block of memory: 1 2 3 4 5
시간 복잡도: O(n), 여기서 n은 주어진 메모리 크기입니다.
관련 기사:
- 신규 및 삭제에 대한 퀴즈
- 삭제 vs 무료