Python의 해시 맵
해시 맵은 색인화된 데이터 구조입니다. 해시 맵은 다음을 사용합니다. 해시 함수 버킷 또는 슬롯 배열에 대한 키를 사용하여 인덱스를 계산합니다. 해당 값은 해당 인덱스가 있는 버킷에 매핑됩니다. 키는 고유하고 변경할 수 없습니다. 해시 맵을 서랍에 저장된 항목에 대한 레이블이 있는 캐비닛으로 생각하세요. 예를 들어 사용자 정보를 저장하는 경우 이메일을 키로 간주하면 이름, 성 등 해당 사용자에 해당하는 값을 버킷에 매핑할 수 있습니다.
해시 함수는 해시 맵 구현의 핵심입니다. 키를 가져와 버킷 목록에 있는 버킷의 인덱스로 변환합니다. 이상적인 해싱은 각 키에 대해 서로 다른 인덱스를 생성해야 합니다. 그러나 충돌이 발생할 수 있습니다. 해싱이 기존 인덱스를 제공하는 경우 목록을 추가하거나 다시 해싱하여 여러 값에 대해 버킷을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Python에서 사전은 해시 맵의 예입니다. 검색 최적화를 위해 이러한 데이터 구조를 구축하고 사용자 정의하는 방법을 배우기 위해 처음부터 해시 맵 구현을 살펴보겠습니다.
해시 맵 디자인에는 다음 기능이 포함됩니다.
- set_val(키, 값): 해시 맵에 키-값 쌍을 삽입합니다. 값이 해시 맵에 이미 존재하는 경우 값을 업데이트합니다.
- get_val(키): 지정된 키가 매핑된 값을 반환하거나, 이 맵에 키에 대한 매핑이 포함되어 있지 않으면 레코드를 찾을 수 없습니다.
- delete_val(키): 해시 맵에 키에 대한 매핑이 포함된 경우 특정 키에 대한 매핑을 제거합니다.
아래는 구현입니다.
파이썬3
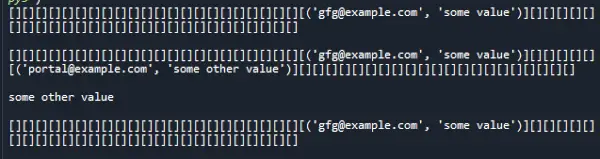
class> HashTable:> > # Create empty bucket list of given size> > def> __init__(> self> , size):> > self> .size> => size> > self> .hash_table> => self> .create_buckets()> > def> create_buckets(> self> ):> > return> [[]> for> _> in> range> (> self> .size)]> > # Insert values into hash map> > def> set_val(> self> , key, val):> > > # Get the index from the key> > # using hash function> > hashed_key> => hash> (key)> %> self> .size> > > # Get the bucket corresponding to index> > bucket> => self> .hash_table[hashed_key]> > found_key> => False> > for> index, record> in> enumerate> (bucket):> > record_key, record_val> => record> > > # check if the bucket has same key as> > # the key to be inserted> > if> record_key> => => key:> > found_key> => True> > break> > # If the bucket has same key as the key to be inserted,> > # Update the key value> > # Otherwise append the new key-value pair to the bucket> > if> found_key:> > bucket[index]> => (key, val)> > else> :> > bucket.append((key, val))> > # Return searched value with specific key> > def> get_val(> self> , key):> > > # Get the index from the key using> > # hash function> > hashed_key> => hash> (key)> %> self> .size> > > # Get the bucket corresponding to index> > bucket> => self> .hash_table[hashed_key]> > found_key> => False> > for> index, record> in> enumerate> (bucket):> > record_key, record_val> => record> > > # check if the bucket has same key as> > # the key being searched> > if> record_key> => => key:> > found_key> => True> > break> > # If the bucket has same key as the key being searched,> > # Return the value found> > # Otherwise indicate there was no record found> > if> found_key:> > return> record_val> > else> :> > return> 'No record found'> > # Remove a value with specific key> > def> delete_val(> self> , key):> > > # Get the index from the key using> > # hash function> > hashed_key> => hash> (key)> %> self> .size> > > # Get the bucket corresponding to index> > bucket> => self> .hash_table[hashed_key]> > found_key> => False> > for> index, record> in> enumerate> (bucket):> > record_key, record_val> => record> > > # check if the bucket has same key as> > # the key to be deleted> > if> record_key> => => key:> > found_key> => True> > break> > if> found_key:> > bucket.pop(index)> > return> > # To print the items of hash map> > def> __str__(> self> ):> > return> ''.join(> str> (item)> for> item> in> self> .hash_table)> hash_table> => HashTable(> 50> )> # insert some values> hash_table.set_val(> '[email protected]'> ,> 'some value'> )> print> (hash_table)> print> ()> hash_table.set_val(> '[email protected]'> ,> 'some other value'> )> print> (hash_table)> print> ()> # search/access a record with key> print> (hash_table.get_val(> '[email protected]'> ))> print> ()> # delete or remove a value> hash_table.delete_val(> '[email protected]'> )> print> (hash_table)> |
산출:

시간 복잡도:
메모리 인덱스 액세스에는 일정한 시간이 걸리고 해싱에는 일정한 시간이 걸립니다. 따라서 해시 맵의 검색 복잡도도 일정한 시간, 즉 O(1)입니다.
HashMap의 장점
● 해시 함수를 통한 빠른 랜덤 메모리 액세스
● 음수 및 비정수 값을 사용하여 값에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
● 키는 정렬된 순서로 저장될 수 있으므로 맵에서 쉽게 반복할 수 있습니다.
HashMap의 단점
● 충돌은 큰 페널티를 초래할 수 있으며 시간 복잡도를 선형으로 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
● 키 개수가 많은 경우 단일 해시 함수로 인해 충돌이 발생하는 경우가 많습니다.
HashMap의 응용
● 이는 메모리 위치가 작은 세트에 매핑되는 캐시 구현에 적용됩니다.
● 데이터베이스 관리 시스템에서 튜플을 색인화하는 데 사용됩니다.
● Rabin Karp 패턴 매칭과 같은 알고리즘에도 사용됩니다.