N-Queen 문제의 모든 솔루션 인쇄
정수가 주어지면 N 임무는 모든 것을 찾는 것입니다 차별화된 솔루션 에 n-퀸 문제 어디 N 여왕은에 배치됩니다 엔 * 엔 두 명의 퀸이 서로 공격할 수 없도록 체스판을 만듭니다.
메모: 각 솔루션은 다음의 고유한 구성을 갖습니다. N 순열로 표현되는 여왕 [123....n] . 전화번호는 나 일 위치는 여왕의 행을 나타냅니다. 나 일 열. 예를 들어 [3142] 그러한 레이아웃 중 하나를 보여줍니다.
예:
입력: n = 4
산출: [2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]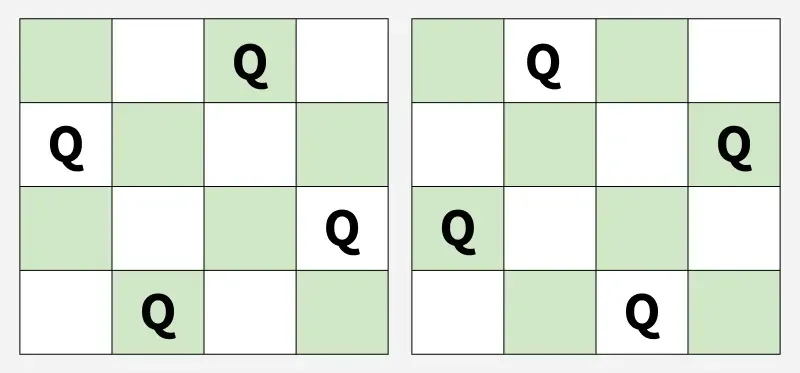
설명 : 가능한 해결책은 2가지입니다.입력: n = 2
산출: []
설명: 여왕은 가능한 모든 구성에서 서로를 공격할 수 있으므로 해결책은 없습니다.
목차
[순진한 접근 방식] - 재귀 사용 - O(n! * n) 시간 및 O(n) 공간
문제를 해결하는 간단한 아이디어 N-퀸즈 문제 가능한 모든 순열을 생성하는 것입니다. [1 2 3 ... 엔] 그런 다음 유효한 N-Queens 구성을 나타내는지 확인합니다. 각 퀸은 서로 다른 행과 열에 있어야 하므로 순열을 자동으로 사용 그 규칙을 처리합니다. 하지만 우리는 여전히 두 명의 퀸이 없는지 확인해야 합니다. 같은 대각선.
아래에는 구현:
C++ //C++ program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion #include #include #include using namespace std ; // Function to check if the current placement is safe bool isSafe ( vector < int >& board int currRow int currCol ) { // Check all previously placed queens for ( int i = 0 ; i < board . size (); ++ i ) { int placedRow = board [ i ]; // Columns are 1-based int placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check if the queen is on the same diagonal if ( abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } // Safe to place the queen return true ; } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations void nQueenUtil ( int col int n vector < int >& board vector < vector < int >>& res vector < bool >& visited ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . push_back ( board ); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if the row is already used if ( ! visited [ row ]) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark the row as used visited [ row ] = true ; // Place the queen board . push_back ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop_back (); // Unmark row visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle vector < vector < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { vector < vector < int >> res ; // Current board configuration vector < int > board ; // Track used rows vector < bool > visited ( n + 1 false ); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } int main () { int n = 4 ; vector < vector < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < res . size (); i ++ ) { cout < < '[' ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { cout < < res [ i ][ j ]; if ( j != n - 1 ) cout < < ' ' ; } cout < < '] n ' ; } return 0 ; }
Java //Java program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion import java.util.ArrayList ; class GfG { // Check if placement is safe static boolean isSafe ( ArrayList < Integer > board int currRow int currCol ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < board . size (); i ++ ) { int placedRow = board . get ( i ); int placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check diagonals if ( Math . abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == Math . abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } return true ; // Safe to place } // Recursive utility to solve static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n ArrayList < Integer > board ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res boolean [] visited ) { // If all queens placed add to res if ( col > n ) { res . add ( new ArrayList <> ( board )); return ; } // Try each row in column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; row ++ ) { // If row not used if ( ! visited [ row ] ) { // Check safety if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark row visited [ row ] = true ; // Place queen board . add ( row ); // Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack board . remove ( board . size () - 1 ); visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Function to solve N-Queen static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nQueen ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = new ArrayList <> (); ArrayList < Integer > board = new ArrayList <> (); boolean [] visited = new boolean [ n + 1 ] ; nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 4 ; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > row : res ) { System . out . print ( '[' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < row . size (); i ++ ) { System . out . print ( row . get ( i )); if ( i != row . size () - 1 ) System . out . print ( ' ' ); } System . out . println ( ']' ); } } }
Python #Python program to find all solution of N queen problem #using recursion # Function to check if placement is safe def isSafe ( board currRow currCol ): for i in range ( len ( board )): placedRow = board [ i ] placedCol = i + 1 # Check diagonals if abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == abs ( placedCol - currCol ): return False # Not safe return True # Safe to place # Recursive utility to solve N-Queens def nQueenUtil ( col n board res visited ): # If all queens placed add to res if col > n : res . append ( board . copy ()) return # Try each row in column for row in range ( 1 n + 1 ): # If row not used if not visited [ row ]: # Check safety if isSafe ( board row col ): # Mark row visited [ row ] = True # Place queen board . append ( row ) # Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ) # Backtrack board . pop () visited [ row ] = False # Main N-Queen solver def nQueen ( n ): res = [] board = [] visited = [ False ] * ( n + 1 ) nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ) return res if __name__ == '__main__' : n = 4 res = nQueen ( n ) for row in res : print ( row )
C# //C# program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Check if placement is safe static bool isSafe ( List < int > board int currRow int currCol ){ for ( int i = 0 ; i < board . Count ; i ++ ) { int placedRow = board [ i ]; int placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check diagonals if ( Math . Abs ( placedRow - currRow ) == Math . Abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } return true ; // Safe to place } // Recursive utility to solve static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n List < int > board List < List < int > > res bool [] visited ){ // If all queens placed add to res if ( col > n ) { res . Add ( new List < int > ( board )); return ; } // Try each row in column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; row ++ ) { // If row not used if ( ! visited [ row ]) { // Check safety if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark row visited [ row ] = true ; // Place queen board . Add ( row ); // Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack board . RemoveAt ( board . Count - 1 ); visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Main N-Queen solver static List < List < int >> nQueen ( int n ){ List < List < int > > res = new List < List < int > > (); List < int > board = new List < int > (); bool [] visited = new bool [ n + 1 ]; nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int n = 4 ; List < List < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); foreach ( var temp in res ) { Console . WriteLine ( '[' + String . Join ( ' ' temp ) + ']' ); } } }
JavaScript //JavaScript program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion // Function to check if placement is safe function isSafe ( board currRow currCol ){ for ( let i = 0 ; i < board . length ; i ++ ) { let placedRow = board [ i ]; let placedCol = i + 1 ; // Check diagonals if ( Math . abs ( placedRow - currRow ) === Math . abs ( placedCol - currCol )) { return false ; // Not safe } } return true ; // Safe to place } // Recursive utility to solve N-Queens function nQueenUtil ( col n board res visited ){ // If all queens placed add to res if ( col > n ) { res . push ([... board ]); return ; } // Try each row in column for ( let row = 1 ; row <= n ; row ++ ) { // If row not used if ( ! visited [ row ]) { // Check safety if ( isSafe ( board row col )) { // Mark row visited [ row ] = true ; // Place queen board . push ( row ); // Recur for next column nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res visited ); // Backtrack board . pop (); visited [ row ] = false ; } } } } // Main N-Queen solver function nQueen ( n ){ let res = []; let board = []; let visited = Array ( n + 1 ). fill ( false ); nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res visited ); return res ; } // Driver code let n = 4 ; let res = nQueen ( n ); res . forEach ( row => console . log ( row ));
산출
[2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]
시간 복잡도: 오(n!*n) n! 모두 생성하기 위해 순열 그리고 각 순열의 검증을 위한 O(n)입니다.
보조 공간: 에)
[예상 접근 방식] - 가지치기와 함께 역추적 사용 - O(n!) 시간과 O(n) 공간
위의 접근 방식을 최적화하기 위해 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다. 가지치기로 역추적 . 가능한 모든 순열을 생성하는 대신 점진적으로 솔루션을 구축하는 동시에 각 단계에서 부분 솔루션이 유효한지 확인할 수 있습니다. 충돌이 발생하면 즉시 역추적하여 도움이 됩니다. 회피 불필요한 계산 .
단계별 구현 :
- 첫 번째 열부터 시작하여 각 행에 여왕을 배치해 보세요.
- 배열을 유지하여 추적 행 이미 점유되어 있습니다. 추적에도 마찬가지로 주요한 그리고 작은 대각선 이미 점유되어 있습니다.
- 여왕이라면 놓기 기존 여왕과의 갈등 건너뛰다 저것 열 그리고 역추적하다 여왕은 다음을 시도합니다 가능한 행(충돌 중 정리 및 역추적).
// C++ program to find all solution of N queen problem by // using backtracking and pruning #include #include #include using namespace std ; // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. void nQueenUtil ( int j int n vector < int > & board vector < bool > & rows vector < bool > & diag1 vector < bool > & diag2 vector < vector < int >> & res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . push_back ( board ); return ; } for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ]) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . push_back ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . pop_back (); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. vector < vector < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { vector < vector < int >> res ; vector < int > board ; // Rows occupied vector < bool > rows ( n + 1 false ); // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) vector < bool > diag1 ( 2 * n + 1 false ); vector < bool > diag2 ( 2 * n + 1 false ); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } int main () { int n = 4 ; vector < vector < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < res . size (); i ++ ) { cout < < '[' ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { cout < < res [ i ][ j ]; if ( j != n - 1 ) cout < < ' ' ; } cout < < '] n ' ; } return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem // using backtracking and pruning import java.util.ArrayList ; import java.util.List ; class GfG { // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. static void nQueenUtil ( int j int n ArrayList < Integer > board boolean [] rows boolean [] diag1 boolean [] diag2 ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . add ( new ArrayList <> ( board )); return ; } for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ] ) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . add ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . remove ( board . size () - 1 ); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nQueen ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = new ArrayList <> (); ArrayList < Integer > board = new ArrayList <> (); // Rows occupied boolean [] rows = new boolean [ n + 1 ] ; // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) boolean [] diag1 = new boolean [ 2 * n + 1 ] ; boolean [] diag2 = new boolean [ 2 * n + 1 ] ; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 4 ; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > solution : res ) { System . out . print ( '[' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < solution . size (); i ++ ) { System . out . print ( solution . get ( i )); if ( i != solution . size () - 1 ) { System . out . print ( ' ' ); } } System . out . println ( ']' ); } } }
Python # Python program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem # using backtracking and pruning def nQueenUtil ( j n board rows diag1 diag2 res ): if j > n : # A solution is found res . append ( board [:]) return for i in range ( 1 n + 1 ): if not rows [ i ] and not diag1 [ i + j ] and not diag2 [ i - j + n ]: # Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = True board . append ( i ) # Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ) # Remove queen (backtrack) board . pop () rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = False def nQueen ( n ): res = [] board = [] # Rows occupied rows = [ False ] * ( n + 1 ) # Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) diag1 = [ False ] * ( 2 * n + 1 ) diag2 = [ False ] * ( 2 * n + 1 ) # Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ) return res if __name__ == '__main__' : n = 4 res = nQueen ( n ) for temp in res : print ( temp )
C# // C# program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem // using backtracking and pruning using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. static void nQueenUtil ( int j int n List < int > board bool [] rows bool [] diag1 bool [] diag2 List < List < int >> res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . Add ( new List < int > ( board )); return ; } for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ]) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . Add ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . RemoveAt ( board . Count - 1 ); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. static List < List < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { List < List < int >> res = new List < List < int >> (); List < int > board = new List < int > (); // Rows occupied bool [] rows = new bool [ n + 1 ]; // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) bool [] diag1 = new bool [ 2 * n + 1 ]; bool [] diag2 = new bool [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { int n = 4 ; List < List < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); foreach ( var temp in res ) { Console . WriteLine ( '[' + String . Join ( ' ' temp ) + ']' ); } } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find all solutions of the N-Queens problem // using backtracking and pruning // Utility function for solving the N-Queens // problem using backtracking. function nQueenUtil ( j n board rows diag1 diag2 res ) { if ( j > n ) { // A solution is found res . push ([... board ]); return ; } for ( let i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i ) { if ( ! rows [ i ] && ! diag1 [ i + j ] && ! diag2 [ i - j + n ]) { // Place queen rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = true ; board . push ( i ); // Recurse to the next column nQueenUtil ( j + 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); // Remove queen (backtrack) board . pop (); rows [ i ] = diag1 [ i + j ] = diag2 [ i - j + n ] = false ; } } } // Solves the N-Queens problem and returns // all valid configurations. function nQueen ( n ) { const res = []; const board = []; // Rows occupied const rows = Array ( n + 1 ). fill ( false ); // Major diagonals (row + j) and Minor diagonals (row - col + n) const diag1 = Array ( 2 * n + 1 ). fill ( false ); const diag2 = Array ( 2 * n + 1 ). fill ( false ); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board rows diag1 diag2 res ); return res ; } // Driver Code const n = 4 ; const res = nQueen ( n ); res . forEach ( temp => console . log ( temp ));
산출
[2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]
시간 복잡도: O(n!) 모두 생성하려면 순열 .
보조 공간: 에)
[대체 접근 방식] - 비트 마스킹을 사용한 역추적
더욱 최적화하려면 역추적 특히 더 큰 값에 대한 접근 방식 N 우리는 사용할 수 있습니다 비트마스킹 효율적으로 추적하기 가득차 있는 행과 대각선. 비트 마스킹 정수를 사용할 수 있습니다( 행 ld rd ) 빠른 속도를 사용하여 어떤 행과 대각선이 점유되어 있는지 추적합니다. 비트 연산 더 빨리 계산. 접근 방식은 위와 동일합니다.
아래에는 구현:
C++ //C++ program to find all solution of N queen problem //using recursion #include #include using namespace std ; // Function to check if the current placement is safe bool isSafe ( int row int col int rows int ld int rd int n ) { return ! (( rows >> row ) & 1 ) && ! (( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) && ! (( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations void nQueenUtil ( int col int n vector < int >& board vector < vector < int >>& res int rows int ld int rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . push_back ( board ); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . push_back ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop_back (); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle vector < vector < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { vector < vector < int >> res ; // Current board configuration vector < int > board ; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } int main () { int n = 4 ; vector < vector < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < res . size (); i ++ ) { cout < < '[' ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { cout < < res [ i ][ j ]; if ( j != n - 1 ) cout < < ' ' ; } cout < < '] n ' ; } return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find all solution of N queen problem // using recursion import java.util.* ; class GfG { // Function to check if the current placement is safe static boolean isSafe ( int row int col int rows int ld int rd int n ) { return ! ((( rows >> row ) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ) == 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n ArrayList < Integer > board ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res int rows int ld int rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . add ( new ArrayList <> ( board )); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . add ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . remove ( board . size () - 1 ); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle static ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> nQueen ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = new ArrayList <> (); // Current board configuration ArrayList < Integer > board = new ArrayList <> (); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int n = 4 ; ArrayList < ArrayList < Integer >> res = nQueen ( n ); for ( ArrayList < Integer > solution : res ) { System . out . print ( '[' ); for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { System . out . print ( solution . get ( j )); if ( j != n - 1 ) System . out . print ( ' ' ); } System . out . println ( ']' ); } } }
Python # Python program to find all solution of N queen problem # using recursion # Function to check if the current placement is safe def isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n ): return not (( rows >> row ) & 1 ) and not (( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) and not (( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ) # Recursive function to generate all possible permutations def nQueenUtil ( col n board res rows ld rd ): # If all queens are placed add into res if col > n : res . append ( board [:]) return # Try placing a queen in each row # of the current column for row in range ( 1 n + 1 ): # Check if it's safe to place the queen if isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n ): # Place the queen board . append ( row ) # Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))) # Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop () # Main function to find all distinct # res to the n-queens puzzle def nQueen ( n ): res = [] # Current board configuration board = [] # Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ) return res if __name__ == '__main__' : n = 4 res = nQueen ( n ) for solution in res : print ( '[' end = '' ) for j in range ( n ): print ( solution [ j ] end = '' ) if j != n - 1 : print ( ' ' end = '' ) print ( ']' )
C# // C# program to find all solution of N queen problem // using recursion using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Function to check if the current placement is safe static bool isSafe ( int row int col int rows int ld int rd int n ) { return ! ((( rows >> row ) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) == 1 ) && ! ((( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ) == 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations static void nQueenUtil ( int col int n List < int > board List < List < int >> res int rows int ld int rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . Add ( new List < int > ( board )); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( int row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . Add ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . RemoveAt ( board . Count - 1 ); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle static List < List < int >> nQueen ( int n ) { List < List < int >> res = new List < List < int >> (); // Current board configuration List < int > board = new List < int > (); // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } static void Main () { int n = 4 ; List < List < int >> res = nQueen ( n ); foreach ( var solution in res ) { Console . Write ( '[' ); for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { Console . Write ( solution [ j ]); if ( j != n - 1 ) Console . Write ( ' ' ); } Console . WriteLine ( ']' ); } } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find all solution of N queen problem // using recursion // Function to check if the current placement is safe function isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n ) { return ! (( rows >> row ) & 1 ) && ! (( ld >> ( row + col )) & 1 ) && ! (( rd >> ( row - col + n )) & 1 ); } // Recursive function to generate all possible permutations function nQueenUtil ( col n board res rows ld rd ) { // If all queens are placed add into res if ( col > n ) { res . push ([... board ]); return ; } // Try placing a queen in each row // of the current column for ( let row = 1 ; row <= n ; ++ row ) { // Check if it's safe to place the queen if ( isSafe ( row col rows ld rd n )) { // Place the queen board . push ( row ); // Recur to place the next queen nQueenUtil ( col + 1 n board res rows | ( 1 < < row ) ( ld | ( 1 < < ( row + col ))) ( rd | ( 1 < < ( row - col + n )))); // Backtrack: remove the queen board . pop (); } } } // Main function to find all distinct // res to the n-queens puzzle function nQueen ( n ) { let res = []; // Current board configuration let board = []; // Start solving from the first column nQueenUtil ( 1 n board res 0 0 0 ); return res ; } // Driver Code let n = 4 ; let res = nQueen ( n ); for ( let i = 0 ; i < res . length ; i ++ ) { process . stdout . write ( '[' ); for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; ++ j ) { process . stdout . write ( res [ i ][ j ]. toString ()); if ( j !== n - 1 ) process . stdout . write ( ' ' ); } console . log ( ']' ); }
산출
[2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]
시간 복잡도: O(n!) 모든 순열을 생성합니다.
공간 복잡도: 에)