Java의 배열 복사
배열이 주어지면 해당 요소를 다른 배열에 복사해야 합니다. 아래의 순진한 사용자에게는 아래에 설명된 것처럼 올바르지 않은 방법이 있습니다.
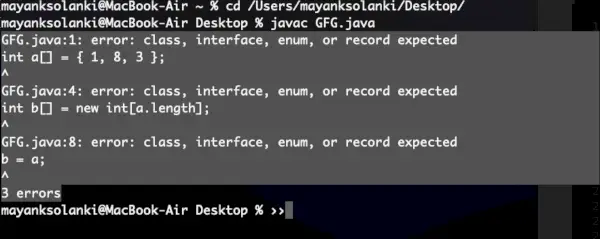
// Java Program to Illustrate Wrong Way Of Copying an Array // Input array int a[] = { 1, 8, 3 }; // Creating an array b[] of same size as a[] int b[] = new int[a.length]; // Doesn't copy elements of a[] to b[], only makes // b refer to same location b = a; 산출:

출력 설명: b = a를 수행하면 실제로 배열에 대한 참조를 할당하는 것입니다. 따라서 한 배열을 변경하면 a와 b가 모두 동일한 위치를 참조하기 때문에 다른 배열에도 반영됩니다. 아래와 같이 코드로 확인할 수도 있습니다.
예:
자바
// A Java program to demonstrate that simply> // assigning one array reference is incorrect> public> class> Test {> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > int> a[] = {> 1> ,> 8> ,> 3> };> > > // Create an array b[] of same size as a[]> > int> b[] => new> int> [a.length];> > > // Doesn't copy elements of a[] to b[],> > // only makes b refer to same location> > b = a;> > > // Change to b[] will also reflect in a[]> > // as 'a' and 'b' refer to same location.> > b[> 0> ]++;> > > System.out.println(> 'Contents of a[] '> );> > for> (> int> i => 0> ; i System.out.print(a[i] + ' '); System.out.println('
Contents of b[] '); for (int i = 0; i System.out.print(b[i] + ' '); } }> |
산출
Contents of a[] 2 8 3 Contents of b[] 2 8 3
행동 양식:
위에서 생성된 오류를 해결한 후 고려해야 할 요소 및 엣지 케이스를 복사하는 동안 내부 작업을 보았으므로 이제 다음과 같이 배열을 복사하는 올바른 방법을 제안할 수 있습니다.
- 주어진 원본 배열의 각 요소를 반복하고 한 번에 하나의 요소를 복사합니다.
- clone() 메소드 사용
- arraycopy() 메소드 사용
- Arrays 클래스의 copyOf() 메소드 사용
- Arrays 클래스의 copyOfRange() 메소드 사용
방법 1: 주어진 원본 배열의 각 요소를 반복하고 한 번에 하나의 요소를 복사합니다. 이 방법을 사용하면 아래 예제와 같이 b에 대한 수정으로 인해 원래 배열 a가 변경되지 않음이 보장됩니다.
예:
자바
// Java program to demonstrate copying by> // one by one assigning elements between arrays> > // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Input array a[]> > int> a[] = {> 1> ,> 8> ,> 3> };> > > // Create an array b[] of same size as a[]> > int> b[] => new> int> [a.length];> > > // Copying elements of a[] to b[]> > for> (> int> i => 0> ; i b[i] = a[i]; // Changing b[] to verify that // b[] is different from a[] b[0]++; // Display message only System.out.println('Contents of a[] '); for (int i = 0; i System.out.print(a[i] + ' '); // Display message only System.out.println('
Contents of b[] '); for (int i = 0; i System.out.print(b[i] + ' '); } }> |
산출
Contents of a[] 1 8 3 Contents of b[] 2 8 3
방법 2: Clone() 메소드 사용
이전 방법에서는 복사본을 만들기 위해 전체 배열을 반복해야 했습니다. 더 잘할 수 있을까요? 예, Java에서는 clone 메소드를 사용할 수 있습니다.
예:
자바
// Java program to demonstrate Copying of Array> // using clone() method> > // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Input array a[]> > int> a[] = {> 1> ,> 8> ,> 3> };> > > // Copying elements of a[] to b[]> > int> b[] = a.clone();> > > // Changing b[] to verify that> > // b[] is different from a[]> > b[> 0> ]++;> > > // Display message for better readability> > System.out.println(> 'Contents of a[] '> );> > > for> (> int> i => 0> ; i System.out.print(a[i] + ' '); // Display message for better readability System.out.println('
Contents of b[] '); for (int i = 0; i System.out.print(b[i] + ' '); } }> |
산출
Contents of a[] 1 8 3 Contents of b[] 2 8 3
방법 3: arraycopy() 메소드 사용
우리는 또한 사용할 수 있습니다 시스템.어레이복사() 방법. 시스템은 java.lang 패키지에 있습니다. 그 서명은 다음과 같습니다:
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
매개변수:
- 소스 소스 배열을 나타냅니다.
- srcPos 복사가 시작되는 인덱스입니다.
- 시작 대상 배열을 나타냅니다.
- 대상 위치 복사된 요소가 대상 배열에 배치되는 인덱스입니다.
- 길이 복사할 하위 배열의 길이입니다.
예:
자바
// Java program to demonstrate array> // copy using System.arraycopy()> > // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Custom input array> > int> a[] = {> 1> ,> 8> ,> 3> };> > > // Creating an array b[] of same size as a[]> > int> b[] => new> int> [a.length];> > > // Copying elements of a[] to b[]> > System.arraycopy(a,> 0> , b,> 0> ,> 3> );> > > // Changing b[] to verify that> > // b[] is different from a[]> > b[> 0> ]++;> > > // Display message only> > System.out.println(> 'Contents of a[] '> );> > > for> (> int> i => 0> ; i System.out.print(a[i] + ' '); // Display message only System.out.println('
Contents of b[] '); for (int i = 0; i System.out.print(b[i] + ' '); } }> |
산출
Contents of a[] 1 8 3 Contents of b[] 2 8 3
방법 4: Arrays 클래스의 copyOf() 메소드 사용
배열의 처음 몇 요소를 복사하거나 배열의 전체 복사본을 복사하려면 이 방법을 사용할 수 있습니다.
통사론:
public static int[] copyOf?(int[] original, int newLength)
매개변수:
- 원본 배열
- 복사할 배열의 길이입니다.
예:
자바
// Java program to demonstrate array> // copy using Arrays.copyOf()> > // Importing Arrays class from utility class> import> java.util.Arrays;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Custom input array> > int> a[] = {> 1> ,> 8> ,> 3> };> > > // Create an array b[] of same size as a[]> > // Copy elements of a[] to b[]> > int> b[] = Arrays.copyOf(a,> 3> );> > > // Change b[] to verify that> > // b[] is different from a[]> > b[> 0> ]++;> > > System.out.println(> 'Contents of a[] '> );> > > // Iterating over array. a[]> > for> (> int> i => 0> ; i System.out.print(a[i] + ' '); System.out.println('
Contents of b[] '); // Iterating over array b[] for (int i = 0; i System.out.print(b[i] + ' '); } }> |
산출
Contents of a[] 1 8 3 Contents of b[] 2 8 3
방법 5: Arrays 클래스의 copyOfRange() 메소드 사용
이 메서드는 지정된 배열의 지정된 범위를 새 배열로 복사합니다.
public static int[] copyOfRange?(int[] original, int from, int to)
매개변수:
- 범위를 복사할 원본 배열
- 복사할 범위의 초기 인덱스
- 복사할 범위의 최종 인덱스(배타적)
예:
자바
// Java program to demonstrate array> // copy using Arrays.copyOfRange()> > // Importing Arrays class from utility package> import> java.util.Arrays;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Custom input array> > int> a[] = {> 1> ,> 8> ,> 3> ,> 5> ,> 9> ,> 10> };> > > // Creating an array b[] and> > // copying elements of a[] to b[]> > int> b[] = Arrays.copyOfRange(a,> 2> ,> 6> );> > > // Changing b[] to verify that> > // b[] is different from a[]> > > // Iterating over array a[]> > System.out.println(> 'Contents of a[] '> );> > for> (> int> i => 0> ; i System.out.print(a[i] + ' '); // Iterating over array b[] System.out.println('
Contents of b[] '); for (int i = 0; i System.out.print(b[i] + ' '); } }> |
산출
Contents of a[] 1 8 3 5 9 10 Contents of b[] 3 5 9 10
마지막으로, 우리가 논의하자 위 방법의 개요:
- 단순히 참조를 할당하는 것은 잘못된 것입니다.
- 배열을 반복하고 요소를 하나씩 할당하여 배열을 복사할 수 있습니다.
- 요소에 대한 반복을 피할 수 있습니다 clone() 또는 System.arraycopy() 사용
- clone()은 같은 크기의 새로운 배열을 생성하지만 시스템.어레이복사() 소스 범위에서 대상 범위로 복사하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
- System.arraycopy()는 Java 기본 인터페이스를 사용하므로 clone()보다 빠릅니다.
- 배열의 처음 몇 요소 또는 배열의 전체 복사본을 복사하려면 Arrays.copyOf() 메서드를 사용할 수 있습니다.
- Arrays.copyOfRange()는 배열의 지정된 범위를 복사하는 데 사용됩니다. 시작 인덱스가 0이 아닌 경우 이 방법을 사용하여 부분 배열을 복사할 수 있습니다.