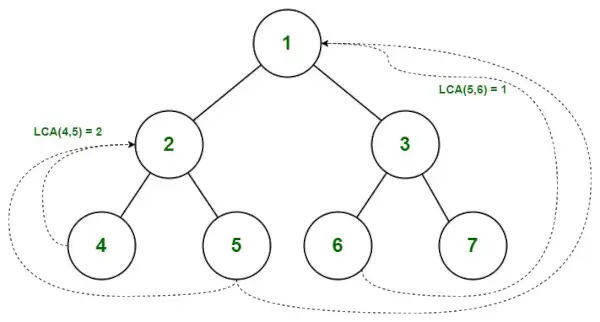
/* C++ Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal> > * of Binary Tree */> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree Node> struct> Node {> > struct> Node *left, *right;> > int> key;> };> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(> int> key)> {> > Node* temp => new> Node;> > temp->キー = キー;>> > temp->左 = 温度->右 = NULL;>> > return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given values> // n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2 are> // present in Binary Tree> struct> Node* findLCA(> struct> Node* root,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > > // Base case> > if> (root == NULL)> > return> NULL;> > // If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> > // the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> > // ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> > if> (root->キー == n1>>' C
// C Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversalof> // Binary Tree> #include> #include> // A Binary Tree Node> typedef> struct> Node {> > struct> Node *left, *right;> > int> key;> } Node;> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(> int> key)> {> > Node* temp = (Node*)> malloc> (> sizeof> (Node));> > temp->キー = キー;>> > temp->左 = 温度->右 = NULL;>> > return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given values> // n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2 are> // present in Binary Tree> Node* findLCA(Node* root,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > > // Base case> > if> (root == NULL)> > return> NULL;> > // If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> > // the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> > // ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> > if> (root->キー == n1>> , findLCA(root, 4, 5)->キー);>> , findLCA(root, 4, 6)->キー);>> , findLCA(root, 3, 4)->キー);>> , findLCA(root, 2, 4)->キー);>> ジャワ
// Java implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current> > node and key value*/> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> > // Root of the Binary Tree> > Node root;> > Node findLCA(> int> n1,> int> n2)> > {> > return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> > }> > // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> > // values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and> > // n2 are present in Binary Tree> > Node findLCA(Node node,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > > > // Base case> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> null> ;> > // If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> > // report the presence by returning root (Note that> > // if a key is ancestor of other, then the ancestor> > // key becomes LCA> > if> (node.data == n1> > /* Driver program to test above functions */> > public> static> void> main(String args[])> > {> > BinaryTree tree => new> BinaryTree();> > tree.root => new> Node(> 1> );> > tree.root.left => new> Node(> 2> );> > tree.root.right => new> Node(> 3> );> > tree.root.left.left => new> Node(> 4> );> > tree.root.left.right => new> Node(> 5> );> > tree.root.right.left => new> Node(> 6> );> > tree.root.right.right => new> Node(> 7> );> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> > + tree.findLCA(> 4> ,> 5> ).data);> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> > + tree.findLCA(> 4> ,> 6> ).data);> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> > + tree.findLCA(> 3> ,> 4> ).data);> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> > + tree.findLCA(> 2> ,> 4> ).data);> > }> }> | Python3
# Python program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one> # traversal of Binary tree> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> > # Constructor to create a new tree node> > def> __init__(> self> , key):> > self> .key> => key> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> # values n1 and n2> # This function assumes that n1 and n2 are present in> # Binary Tree> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> > # Base Case> > if> root> is> None> :> > return> None> > # If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> > # the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> > # ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> > if> root.key> => => n1> or> root.key> => => n2:> > return> root> > # Look for keys in left and right subtrees> > left_lca> => findLCA(root.left, n1, n2)> > right_lca> => findLCA(root.right, n1, n2)> > # If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key> > # is present in once subtree and other is present in other,> > # So this node is the LCA> > if> left_lca> and> right_lca:> > return> root> > # Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA> > return> left_lca> if> left_lca> is> not> None> else> right_lca> # Driver code> if> __name__> => => '__main__'> :> > > # Let us create a binary tree given in the above example> > root> => Node(> 1> )> > root.left> => Node(> 2> )> > root.right> => Node(> 3> )> > root.left.left> => Node(> 4> )> > root.left.right> => Node(> 5> )> > root.right.left> => Node(> 6> )> > root.right.right> => Node(> 7> )> > print> (> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> , findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 5> ).key)> > print> (> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> , findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 6> ).key)> > print> (> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> , findLCA(root,> 3> ,> 4> ).key)> > print> (> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> , findLCA(root,> 2> ,> 4> ).key)> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> | C#
// C# implementation to find lowest common> // ancestor of n1 and n2 using one traversal> // of binary tree> using> System;> // Class containing left and right> // child of current node and key value> public> class> Node {> > public> int> data;> > public> Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> class> BinaryTree {> > // Root of the Binary Tree> > Node root;> > Node findLCA(> int> n1,> int> n2)> > {> > return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> > }> > // This function returns pointer to LCA> > // of two given values n1 and n2. This> > // function assumes that n1 and n2 are> > // present in Binary Tree> > Node findLCA(Node node,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > node.data == n2)> > return> node;> > // Look for keys in left and right subtrees> > Node left_lca = findLCA(node.left, n1, n2);> > Node right_lca = findLCA(node.right, n1, n2);> > // If both of the above calls return Non-NULL,> > // then one key is present in once subtree> > // and other is present in other, So this> > // node is the LCA> > if> (left_lca !=> null> && right_lca !=> null> )> > return> node;> > // Otherwise check if left subtree or> > // right subtree is LCA> > return> (left_lca !=> null> ) ? left_lca : right_lca;> > > > // Driver code> > public> static> void> Main(> string> [] args)> > {> > BinaryTree tree => new> BinaryTree();> > tree.root => new> Node(1);> > tree.root.left => new> Node(2);> > tree.root.right => new> Node(3);> > tree.root.left.left => new> Node(4);> > tree.root.left.right => new> Node(5);> > tree.root.right.left => new> Node(6);> > tree.root.right.right => new> Node(7);> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> > + tree.findLCA(4, 5).data);> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> > + tree.findLCA(4, 6).data);> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> > + tree.findLCA(3, 4).data);> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> > + tree.findLCA(2, 4).data);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by pratham76> | JavaScript
> > // JavaScript implementation to find> > // lowest common ancestor of> > // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> > > class Node> > {> > constructor(item) {> > this> .left => null> ;> > this> .right => null> ;> > this> .data = item;> > }> > }> > > //Root of the Binary Tree> > let root;> > > function> findlCA(n1, n2)> > {> > return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> > }> > > // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> > // values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and> > // n2 are present in Binary Tree> > function> findLCA(node, n1, n2)> > > > > root => new> Node(1);> > root.left => new> Node(2);> > root.right => new> Node(3);> > root.left.left => new> Node(4);> > root.left.right => new> Node(5);> > root.right.left => new> Node(6);> > root.right.right => new> Node(7);> > document.write(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> +> > findlCA(4, 5).data +> ''> );> > document.write(> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> +> > findlCA(4, 6).data +> ''> );> > document.write(> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> +> > findlCA(3, 4).data +> ''> );> > document.write(> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> +> > findlCA(2, 4).data +> ''> );> > > | 出力 LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3, 4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2 時間計算量 : O(N) は、メソッドがボトムアップ方式で単純なツリー走査を実行するためです。
補助スペース: O(H)、H は木の高さです。 注記: 上記の方法は次のことを前提としています キーはバイナリ ツリーに存在します 。一方のキーが存在し、もう一方のキーが存在しない場合は、現在のキーを LCA として返します (理想的には NULL を返す必要があります)。最初に n1 と n2 がツリー内に存在するかどうかを確認し、次に n1 と n2 の LCA を見つけることにより、このメソッドを拡張してすべてのケースを処理できます。ノードがバイナリ ツリーに存在するかどうかを確認するには、n1 ノードと n2 ノードの両方についてツリーを個別に走査します。 C++
/* C++ program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal> > of Binary Tree. It handles all cases even when n1 or n2> > is not there in Binary Tree */> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree Node> struct> Node {> > struct> Node *left, *right;> > int> key;> };> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(> int> key)> {> > Node* temp => new> Node;> > temp->キー = キー;>> > temp->左 = 温度->右 = NULL;>> > return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> // valuesn1 and n2.> struct> Node* findLCAUtil(> struct> Node* root,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > // Returns true if key k is present in tree rooted with root> bool> find(Node* root,> int> k)> find(root->そうですね、k))>> | ジャワ
// Java implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> // It also handles cases even when n1 and n2 are not there> // in Tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current node and> > * key */> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> > // Root of the Binary Tree> > Node root;> > static> boolean> v1 => false> , v2 => false> ;> > // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> > // values n1 and n2.> > // v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> > // v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> > Node findLCAUtil(Node node,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > {> > // Base case> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> null> ;> > // Store result in temp, in case of key match so> > // that we can search for other key also.> > Node temp => null> ;> > // If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> > // report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true> > // and return root (Note that if a key is ancestor> > // of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA)> > if> (node.data == n1) {> > v1 => true> ;> > temp = node;> > }> > if> (node.data == n2) {> > v2 => true> ;> > temp = node;> > }> > // Look for keys in left and right subtrees> > Node left_lca = findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> > Node right_lca = findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> > if> (temp !=> null> )> > return> temp;> > // If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then> > // one key is present in once subtree and other is> > // present in other, So this node is the LCA> > if> (left_lca !=> null> && right_lca !=> null> )> > return> node;> > // Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree> > // is LCA> > return> (left_lca !=> null> ) ? left_lca : right_lca;> > }> > // Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the subtree rooted with> > // 'node'> > Node findLCA(> int> n1,> int> n2)> > {> > // Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> > v1 => false> ;> > v2 => false> ;> > // Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique> > // discussed above> > Node lca = findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> > // Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in> > // tree> > if> (v1 && v2)> > return> lca;> > // Else return NULL> > return> null> ;> > }> > /* Driver program to test above functions */> > public> static> void> main(String args[])> > {> > BinaryTree tree => new> BinaryTree();> > tree.root => new> Node(> 1> );> > tree.root.left => new> Node(> 2> );> > tree.root.right => new> Node(> 3> );> > tree.root.left.left => new> Node(> 4> );> > tree.root.left.right => new> Node(> 5> );> > tree.root.right.left => new> Node(> 6> );> > tree.root.right.right => new> Node(> 7> );> > Node lca = tree.findLCA(> 4> ,> 5> );> > if> (lca !=> null> )> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> + lca.data);> > else> > System.out.println(> 'Keys are not present'> );> > lca = tree.findLCA(> 4> ,> 10> );> > if> (lca !=> null> )> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(4, 10) = '> + lca.data);> > else> > System.out.println(> 'Keys are not present'> );> > }> }> | Python3
''' Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal of> > Binary tree> It handles all cases even when n1 or n2 is not there in tree> '''> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> > # Constructor to create a new node> > def> __init__(> self> , key):> > self> .key> => key> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # This function return pointer to LCA of two given values> # n1 and n2> # v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> # v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> def> findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2, v):> > # Base Case> > if> root> is> None> :> > return> None> > # IF either n1 or n2 matches ith root's key, report> > # the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true and return> > # root (Note that if a key is ancestor of other, then> > # the ancestor key becomes LCA)> > if> root.key> => => n1:> > v[> 0> ]> => True> > return> root> > if> root.key> => => n2:> > v[> 1> ]> => True> > return> root> > # Look for keys in left and right subtree> > left_lca> => findLCAUtil(root.left, n1, n2, v)> > right_lca> => findLCAUtil(root.right, n1, n2, v)> > # If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key> > # is present in once subtree and other is present in other,> > # So this node is the LCA> > if> left_lca> and> right_lca:> > return> root> > # Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA> > return> left_lca> if> left_lca> is> not> None> else> right_lca> def> find(root, k):> > # Base Case> > if> root> is> None> :> > return> False> > # If key is present at root, or if left subtree or right> > # subtree , return true> > if> (root.key> => => k> or> find(root.left, k)> or> > find(root.right, k)):> > return> True> > # Else return false> > return> False> # This function returns LCA of n1 and n2 on value if both> # n1 and n2 are present in tree, otherwise returns None> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> > # Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> > v> => [> False> ,> False> ]> > # Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique discussed above> > lca> => findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2, v)> > # Returns LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in tree> > if> (v[> 0> ]> and> v[> 1> ]> or> v[> 0> ]> and> find(lca, n2)> or> v[> 1> ]> and> > find(lca, n1)):> > return> lca> > # Else return None> > return> None> # Driver program to test above function> root> => Node(> 1> )> root.left> => Node(> 2> )> root.right> => Node(> 3> )> root.left.left> => Node(> 4> )> root.left.right> => Node(> 5> )> root.right.left> => Node(> 6> )> root.right.right> => Node(> 7> )> lca> => findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 5> )> if> lca> is> not> None> :> > print> (> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> , lca.key)> else> :> > print> (> 'Keys are not present'> )> lca> => findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 10> )> if> lca> is> not> None> :> > print> (> 'LCA(4,10) = '> , lca.key)> else> :> > print> (> 'Keys are not present'> )> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> | C#
using> System;> // c# implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> // It also handles cases even when n1 and n2 are not there> // in Tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current node and> > * key */> public> class> Node {> > public> int> data;> > public> Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> > // Root of the Binary Tree> > public> Node root;> > public> static> bool> v1 => false> , v2 => false> ;> > // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> > // values n1 and n2.> > // v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> > // v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> > public> virtual> Node findLCAUtil(Node node,> int> n1,> > int> n2)> > {> > // Base case> > if> (node ==> null> ) {> > return> null> ;> > }> > // Store result in temp, in case of key match so> > // that we can search for other key also.> > Node temp => null> ;> > // If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> > // report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true> > // and return root (Note that if a key is ancestor> > // of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA)> > if> (node.data == n1) {> > v1 => true> ;> > temp = node;> > }> > if> (node.data == n2) {> > v2 => true> ;> > temp = node;> > }> > // Look for keys in left and right subtrees> > Node left_lca = findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> > Node right_lca = findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> > if> (temp !=> null> ) {> > return> temp;> > }> > // If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then> > // one key is present in once subtree and other is> > // present in other, So this node is the LCA> > if> (left_lca !=> null> && right_lca !=> null> ) {> > return> node;> > }> > // Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree> > // is LCA> > return> (left_lca !=> null> ) ? left_lca : right_lca;> > }> > // Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the subtree rooted with> > // 'node'> > public> virtual> Node findLCA(> int> n1,> int> n2)> > {> > // Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> > v1 => false> ;> > v2 => false> ;> > // Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique> > // discussed above> > Node lca = findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> > // Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in> > // tree> > if> (v1 && v2) {> > return> lca;> > }> > // Else return NULL> > return> null> ;> > }> > /* Driver program to test above functions */> > public> static> void> Main(> string> [] args)> > {> > BinaryTree tree => new> BinaryTree();> > tree.root => new> Node(1);> > tree.root.left => new> Node(2);> > tree.root.right => new> Node(3);> > tree.root.left.left => new> Node(4);> > tree.root.left.right => new> Node(5);> > tree.root.right.left => new> Node(6);> > tree.root.right.right => new> Node(7);> > Node lca = tree.findLCA(4, 5);> > if> (lca !=> null> ) {> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> + lca.data);> > }> > else> {> > Console.WriteLine(> 'Keys are not present'> );> > }> > lca = tree.findLCA(4, 10);> > if> (lca !=> null> ) {> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(4, 10) = '> + lca.data);> > }> > else> {> > Console.WriteLine(> 'Keys are not present'> );> > }> > }> }> // This code is contributed by Shrikant13> | JavaScript
> // JavaScript implementation to find lowest> // common ancestor of n1 and n2 using one> // traversal of binary tree. It also handles> // cases even when n1 and n2 are not there in Tree> // Class containing left and right child> // of current node and key> class Node> {> > constructor(item)> > {> > this> .data = item;> > this> .left => null> ;> > this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> class BinaryTree{> > // Root of the Binary Tree> constructor()> {> > this> .root => null> ;> > this> .v1 => false> ;> > this> .v2 => false> ;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA> // of two given values n1 and n2.> // v1 is set as true by this function> // if n1 is found> // v2 is set as true by this function> // if n2 is found> findLCAUtil(node, n1, n2)> {> > > // Base case> > if> (node ==> null> )> > {> > return> null> ;> > }> > > // Store result in temp, in case of> > // key match so that we can search> > // for other key also.> > var> temp => null> ;> > > // If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> > // report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as> > // true and return root (Note that if a key> > // is ancestor of other, then the ancestor> > // key becomes LCA)> > if> (node.data == n1)> > {> > this> .v1 => true> ;> > temp = node;> > }> > if> (node.data == n2)> > {> > this> .v2 => true> ;> > temp = node;> > }> > > // Look for keys in left and right subtrees> > var> left_lca => this> .findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> > var> right_lca => this> .findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> > > if> (temp !=> null> )> > {> > return> temp;> > }> > > // If both of the above calls return Non-NULL,> > // then one key is present in once subtree and> > // other is present in other, So this node is the LCA> > if> (left_lca !=> null> && right_lca !=> null> )> > {> > return> node;> > }> > > // Otherwise check if left subtree or> > // right subtree is LCA> > return> left_lca !=> null> ? left_lca : right_lca;> }> // Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the> // subtree rooted with 'node'> findLCA(n1, n2)> {> > > // Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> > this> .v1 => false> ;> > this> .v2 => false> ;> > > // Find lca of n1 and n2 using the> > // technique discussed above> > var> lca => this> .findLCAUtil(> this> .root, n1, n2);> > > // Return LCA only if both n1 and n2> > // are present in tree> > if> (> this> .v1 &&> this> .v2)> > {> > return> lca;> > }> > > // Else return NULL> > return> null> ;> }> }> // Driver code> var> tree => new> BinaryTree();> tree.root => new> Node(1);> tree.root.left => new> Node(2);> tree.root.right => new> Node(3);> tree.root.left.left => new> Node(4);> tree.root.left.right => new> Node(5);> tree.root.right.left => new> Node(6);> tree.root.right.right => new> Node(7);> var> lca = tree.findLCA(4, 5);> if> (lca !=> null> )> {> > document.write(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> +> > lca.data +> ' '> );> }> else> {> > document.write(> 'Keys are not present'> +> ' '> );> }> lca = tree.findLCA(4, 10);> if> (lca !=> null> )> {> > document.write(> 'LCA(4, 10) = '> +> > lca.data +> ' '> );> }> else> {> > document.write(> 'Keys are not present'> +> ' '> );> }> // This code is contributed by rdtank> > | 出力 LCA(4, 5) = 2 Keys are not present 時間計算量 : O(N) は、メソッドがボトムアップ方式で単純なツリー走査を実行するためです。
補助スペース: O(H)、h は木の高さです。 補助データ構造 (ハッシュ テーブル) の使用: The basic idea behind the 'Using an auxiliary data structure' approach for finding the lowest common ancestor of two nodes in a binary tree is to use a hash table or a map to store the parent pointers of each node. Once we have the parent pointers, we can traverse up from the first node and add all its ancestors to a set or a list. Then we can traverse up from the second node and check if each ancestor is already in the set or the list. The first ancestor that is already in the set or the list is the lowest common ancestor. 上記のアプローチを実装するには、次の手順に従います。 - ハッシュ テーブルまたはマップを作成して、バイナリ ツリー内の各ノードの親ポインターを保存します。
- バイナリ ツリーを走査し、ハッシュ テーブルまたはマップに各ノードの親ポインタを設定します。
- 最初のノードから開始してツリーを上にたどり、各祖先をセットまたはリストに追加します。
- 2 番目のノードから開始してツリーを上にたどり、各祖先がすでにセットまたはリストに存在するかどうかを確認します。セットまたはリストに既に存在する最初の祖先が、最も低い共通祖先です。
- 共通の祖先が見つからない場合は、null または共通の祖先が存在しないことを示すその他の値を返します。
上記のアプローチの実装を以下に示します。 C++
// C++ code to implement above approach> #include> #include> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Definition of a binary tree node> struct> Node {> > int> data;> > Node* left;> > Node* right;> };> // Function to create a new binary tree node> Node* newNode(> int> data)> {> > Node* node => new> Node;> > node->データ = データ;>> > node->left = NULL;>>' }> > if> (node->右) {>> > parentMap[node->右] = ノード;>>' }> > }> > return> parentMap;> }> // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two nodes> // using an auxiliary data structure> int> findLCA(Node* root,> int> n1,> int> n2)> {> > // Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers for> > // each node in the tree> > unordered_map parentMap> > = buildParentMap(root);> > // Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> > Node* p = NULL;> > Node* q = NULL;> > vector queue = { root };> > while> (!queue.empty()) {> > Node* node = queue.front();> > queue.erase(queue.begin());> > if> (node->データ == n1) {> > p = node;> > }> > if> (node->データ == n2) {> > q = node;> > }> > if> (node->左) {>> > queue.push_back(node->左);>> }> > }> > // Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set or a> > // list> > set ancestors;> > while> (p) {> > ancestors.insert(p);> > p = parentMap[p];> > }> > // Traverse up from the second node and check if each> > // ancestor is already in the set or the list> > while> (q) {> > if> (ancestors.find(q) != ancestors.end()) {> > return> q> > ->データ;>> // The first ancestor that is> > // already in the set or the list is> > // the lowest common ancestor> > }> > q = parentMap[q];> > }> > return> -1;> // No common ancestor found> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> > Node* root = newNode(1);> > root->left = newNode(2);>> > root->right = newNode(3);>> > root->left->left = newNode(4);>> > root->left->right = newNode(5);>> > root->right->left = newNode(6);>> > root->right->right = newNode(7);>> > cout < <> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> < < findLCA(root, 4, 5) < < endl;> > cout < <> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> < < findLCA(root, 4, 6) < < endl;> > cout < <> 'LCA(3,4) = '> < < findLCA(root, 3, 4) < < endl;> > cout < <> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> < < findLCA(root, 2, 4) < < endl;> > return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Veerendra_Singh_Rajpoot> | ジャワ
import> java.util.*;> // Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> class> Main {> > // Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> > // pointers for each node in the tree> > static> Map buildParentMap(Node root)> > {> > Map parentMap => new> HashMap();> > parentMap.put(root,> null> );> > Queue queue => new> LinkedList();> > queue.add(root);> > while> (!queue.isEmpty()) {> > Node node = queue.poll();> > if> (node.left !=> null> ) {> > parentMap.put(node.left, node);> > queue.add(node.left);> > }> > if> (node.right !=> null> ) {> > parentMap.put(node.right, node);> > queue.add(node.right);> > }> > }> > return> parentMap;> > }> > // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> > // nodes using an auxiliary data structure> > static> int> findLCA(Node root,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > {> > // Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> > // for each node in the tree> > Map parentMap = buildParentMap(root);> > // Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> > Node p => null> , q => null> ;> > Queue queue => new> LinkedList();> > queue.add(root);> > while> (!queue.isEmpty()) {> > Node node = queue.poll();> > if> (node.data == n1) {> > p = node;> > }> > if> (node.data == n2) {> > q = node;> > }> > if> (node.left !=> null> ) {> > queue.add(node.left);> > }> > if> (node.right !=> null> ) {> > queue.add(node.right);> > }> > }> > // Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> > // or a list> > Set ancestors => new> HashSet();> > while> (p !=> null> ) {> > ancestors.add(p);> > p = parentMap.get(p);> > }> > // Traverse up from the second node and check if> > // each ancestor is already in the set or the list> > while> (q !=> null> ) {> > if> (ancestors.contains(q)) {> > return> q.data;> > }> > q = parentMap.get(q);> > }> > return> -> 1> ;> // No common ancestor found> > }> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > Node root => new> Node(> 1> );> > root.left => new> Node(> 2> );> > root.right => new> Node(> 3> );> > root.left.left => new> Node(> 4> );> > root.left.right => new> Node(> 5> );> > root.right.left => new> Node(> 6> );> > root.right.right => new> Node(> 7> );> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> > + findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 5> ));> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> > + findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 6> ));> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> > + findLCA(root,> 3> ,> 4> ));> > System.out.println(> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> > + findLCA(root,> 2> ,> 4> ));> > }> }> | Python3
from> collections> import> deque> # Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node:> > def> __init__(> self> , data):> > self> .data> => data> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> # pointers for each node in the tree> def> buildParentMap(root):> > parentMap> => {}> > parentMap[root]> => None> > queue> => deque([root])> > while> queue:> > node> => queue.popleft()> > if> node.left:> > parentMap[node.left]> => node> > queue.append(node.left)> > if> node.right:> > parentMap[node.right]> => node> > queue.append(node.right)> > return> parentMap> # Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two nodes> # using an auxiliary data structure> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> > # Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers for> > # each node in the tree> > parentMap> => buildParentMap(root)> > # Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> > p, q> => None> ,> None> > queue> => deque([root])> > while> queue:> > node> => queue.popleft()> > if> node.data> => => n1:> > p> => node> > if> node.data> => => n2:> > q> => node> > if> node.left:> > queue.append(node.left)> > if> node.right:> > queue.append(node.right)> > # Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set or a> > # list> > ancestors> => set> ()> > while> p:> > ancestors.add(p)> > p> => parentMap[p]> > # Traverse up from the second node and check if each> > # ancestor is already in the set or the list> > while> q:> > if> q> in> ancestors:> > return> q.data> > q> => parentMap[q]> > return> -> 1> # No common ancestor found> # Driver code> if> __name__> => => '__main__'> :> > root> => Node(> 1> )> > root.left> => Node(> 2> )> > root.right> => Node(> 3> )> > root.left.left> => Node(> 4> )> > root.left.right> => Node(> 5> )> > root.right.left> => Node(> 6> )> > root.right.right> => Node(> 7> )> > print> (> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> , findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 5> ))> > print> (> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> , findLCA(root,> 4> ,> 6> ))> > print> (> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> , findLCA(root,> 3> ,> 4> ))> > print> (> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> , findLCA(root,> 2> ,> 4> ))> | C#
using> System;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> // Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node> {> > public> int> data;> > public> Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> class> MainClass> {> > // Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> > // pointers for each node in the tree> > static> Dictionary BuildParentMap(Node root)> > {> > Dictionary parentMap => new> Dictionary();> > parentMap.Add(root,> null> );> > Queue queue => new> Queue();> > queue.Enqueue(root);> > while> (queue.Count != 0)> > {> > Node node = queue.Dequeue();> > if> (node.left !=> null> )> > {> > parentMap.Add(node.left, node);> > queue.Enqueue(node.left);> > }> > if> (node.right !=> null> )> > {> > parentMap.Add(node.right, node);> > queue.Enqueue(node.right);> > }> > }> > return> parentMap;> > }> > // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> > // nodes using an auxiliary data structure> > static> int> FindLCA(Node root,> int> n1,> int> n2)> > {> > // Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> > // for each node in the tree> > Dictionary parentMap = BuildParentMap(root);> > // Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> > Node p => null> , q => null> ;> > Queue queue => new> Queue();> > queue.Enqueue(root);> > while> (queue.Count != 0)> > {> > Node node = queue.Dequeue();> > if> (node.data == n1)> > {> > p = node;> > }> > if> (node.data == n2)> > {> > q = node;> > }> > if> (node.left !=> null> )> > {> > queue.Enqueue(node.left);> > }> > if> (node.right !=> null> )> > {> > queue.Enqueue(node.right);> > }> > }> > // Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> > // or a list> > HashSet ancestors => new> HashSet();> > while> (p !=> null> )> > {> > ancestors.Add(p);> > p = parentMap[p];> > }> > // Traverse up from the second node and check if> > // each ancestor is already in the set or the list> > while> (q !=> null> )> > {> > if> (ancestors.Contains(q))> > {> > return> q.data;> > }> > q = parentMap[q];> > }> > return> -1;> // No common ancestor found> > }> > public> static> void> Main()> > {> > Node root => new> Node(1);> > root.left => new> Node(2);> > root.right => new> Node(3);> > root.left.left => new> Node(4);> > root.left.right => new> Node(5);> > root.right.left => new> Node(6);> > root.right.right => new> Node(7);> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> + FindLCA(root, 4, 5));> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> + FindLCA(root, 4, 6));> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> + FindLCA(root, 3, 4));> > Console.WriteLine(> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> + FindLCA(root, 2, 4));> > }> }> // This code is contributed by akashish__> | JavaScript
// javascript code addition> // Definition of a binary tree node> class Node {> > constructor(item) {> > this> .data = item;> > this> .left => null> ;> > this> .right => null> ;> > }> }> // Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> // pointers for each node in the tree> function> buildParentMap(root) {> > const parentMap => new> Map();> > parentMap.set(root,> null> );> > const queue = [];> > queue.push(root);> > while> (queue.length>0) {>> > const node = queue.shift();> > if> (node.left !=> null> ) {> > parentMap.set(node.left, node);> > queue.push(node.left);> > }> > if> (node.right !=> null> ) {> > parentMap.set(node.right, node);> > queue.push(node.right);> > }> > }> > return> parentMap;> }> // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> // nodes using an auxiliary data structure> function> findLCA(root, n1, n2) {> > // Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> > // for each node in the tree> > const parentMap = buildParentMap(root);> > // Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> > let p => null> , q => null> ;> > const queue = [];> > queue.push(root);> > while> (queue.length>0) {>> > const node = queue.shift();> > if> (node.data === n1) {> > p = node;> > }> > if> (node.data === n2) {> > q = node;> > }> > if> (node.left !=> null> ) {> > queue.push(node.left);> > }> > if> (node.right !=> null> ) {> > queue.push(node.right);> > }> > }> > // Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> > // or a list> > const ancestors => new> Set();> > while> (p !=> null> ) {> > ancestors.add(p);> > p = parentMap.get(p);> > }> > // Traverse up from the second node and check if> > // each ancestor is already in the set or the list> > while> (q !=> null> ) {> > if> (ancestors.has(q)) {> > return> q.data;> > }> > q = parentMap.get(q);> > }> > return> -1;> // No common ancestor found> }> // Test the function> const root => new> Node(1);> root.left => new> Node(2);> root.right => new> Node(3);> root.left.left => new> Node(4);> root.left.right => new> Node(5);> root.right.left => new> Node(6);> root.right.right => new> Node(7);> console.log(> 'LCA(4, 5) = '> + findLCA(root, 4, 5));> console.log(> 'LCA(4, 6) = '> + findLCA(root, 4, 6));> console.log(> 'LCA(3, 4) = '> + findLCA(root, 3, 4));> console.log(> 'LCA(2, 4) = '> + findLCA(root, 2, 4));> // The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.> | 出力 LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3,4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2 時間計算量: O(n)、 指定されたコードの時間計算量は O(n) です。ここで、n はバイナリ ツリー内のノードの数です。 ツリー内の各ノードの親マップを構築するには、各ノードを 1 回訪問する必要があり、O(n) 時間がかかります。値 n1 と n2 を持つノードを見つけるには、各ノードを 1 回訪問する必要があり、これにも O(n) 時間がかかります。 2 番目のノードから上にたどって、各祖先がすでにセットまたはリストに含まれているかどうかを確認するには、O(h) 時間がかかります。ここで、h はバイナリ ツリーの高さです。 二分木が歪んでいる場合、最悪の場合、二分木の高さは O(n) になります。したがって、指定されたコードの全体的な時間計算量は O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n) となります。 空間の複雑さ: O(n)、 指定されたコードの空間複雑さは、最悪の場合でも O(n) です。これは、ツリー内の各ノードに対して構築される親マップのサイズが O(n) であるためです。さらに、最悪の場合、祖先のセットにはバイナリ ツリー内のすべてのノードが含まれる可能性があり、これも O(n) スペースを必要とします。最後に、バイナリ ツリーの走査に使用されるキューには O(n) スペースが必要です。したがって、指定されたコードの全体的な空間複雑さは、O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n) となります。 二分探索ツリーで LCA を見つけるための効率的なソリューションについて説明しました。二分探索木では、BST プロパティを使用して、O(h) 時間で LCA を見つけることができます。ここで、h は木の高さです。キーのバイナリ ツリー ノードは順序に従わないため、このような実装はバイナリ ツリーでは不可能です。 以下の記事もご覧ください。
親ポインタを使用した LCA
二分探索ツリー内の最下位共通祖先。
RMQ を使用してバイナリ ツリーで LCA を見つける
| |