BFSとDFSの違い
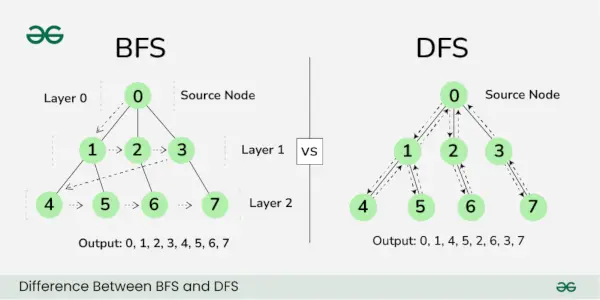
幅優先検索 (BFS) そして 深さ優先検索 (DFS) は、グラフやツリーの走査または検索に使用される 2 つの基本的なアルゴリズムです。この記事では、幅優先検索と深さ優先検索の基本的な違いについて説明します。

BFSとDFSの違い
幅優先検索 (BFS) :
BFS、幅優先検索、 は、グラフ内の最短パスを見つけるための頂点ベースの手法です。それは、 出力:
A, B, C, D, E, F
コード:
C++ #include #include using namespace std; // This class represents a directed graph using adjacency // list representation class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices // Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists list * 形容詞;パブリック: グラフ(int V); // コンストラクター // グラフにエッジを追加する関数 void addEdge(int v, int w); // 指定されたソースからの BFS トラバーサルを出力します。 s void BFS(int s); }; Graph::Graph(int V) { this->V = V; adj = 新しいリスト [V]; void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); // w を v のリストに追加します。 } void Graph::BFS(int s) { // すべての頂点を未訪問としてマークする bool* Visited = new bool[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) visited[i] = false; // Create a queue for BFS list 列; // 現在のノードを訪問済みとしてマークし、訪問済みとしてキューに入れます[s] = true; キュー.プッシュバック; // 'i' は、頂点リストの隣接する頂点をすべて取得するために使用されます // ::反復子 i; // 整数から文字へのマッピングを作成します char map[6] = { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F ' }; while (!queue.empty()) { // キューから頂点をデキューして出力します s = queue.front(); コート < < map[s] < < ' '; // Use the mapping to print // the original label queue.pop_front(); // Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex // s If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark // it visited and enqueue it for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i) { if (!visited[*i]) { queue.push_back(*i); visited[*i] = true; } } } } int main() { // Create a graph given in the diagram /* A / B C / / D E F */ Graph g(6); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(0, 2); g.addEdge(1, 3); g.addEdge(2, 4); g.addEdge(2, 5); cout < < 'Breadth First Traversal is: '; g.BFS(0); // Start BFS from A (0) return 0; } パイソン from collections import deque # This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__(self, V): self.V = V # No. of vertices self.adj = [[] for _ in range(V)] # Adjacency lists # Function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self, v, w): self.adj[v].append(w) # Add w to v’s list # Prints BFS traversal from a given source s def BFS(self, s): # Mark all the vertices as not visited visited = [False] * self.V # Create a queue for BFS queue = deque() # Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it visited[s] = True queue.append(s) # Create a mapping from integers to characters mapping = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'] while queue: # Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it s = queue.popleft() # Use the mapping to print the original label print(mapping[s], end=' ') # Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex s # If an adjacent has not been visited, then mark it visited # and enqueue it for i in self.adj[s]: if not visited[i]: queue.append(i) visited[i] = True if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a graph given in the diagram # A # / # B C # / / # D E F g = Graph(6) g.addEdge(0, 1) g.addEdge(0, 2) g.addEdge(1, 3) g.addEdge(2, 4) g.addEdge(2, 5) print('Breadth First Traversal is: ', end='') g.BFS(0) # Start BFS from A (0) JavaScript // This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list representation class Graph { constructor(V) { this.V = V; // No. of vertices this.adj = new Array(V).fill(null).map(() =>[]); // 隣接リストの配列 } // グラフにエッジを追加する関数 addEdge(v, w) { this.adj[v].push(w); // w を v のリストに追加します。 } // 指定されたソースから BFS トラバーサルを実行する関数 s BFS(s) { // すべての頂点を未訪問としてマーク let Visited = new Array(this.V).fill(false); // BFS のキューを作成 let queue = []; // 現在のノードを訪問済みとしてマークし、訪問済みとしてキューに入れます[s] = true; キュー.プッシュ; // 整数から文字へのマッピング let map = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F']; while (queue.length> 0) { // キューから頂点をデキューして出力します s = queue.shift(); console.log(マップ[s] + ' '); // マッピングを使用して元のラベルを印刷します // デキューされた頂点のすべての隣接する頂点を取得します s // 隣接する頂点が訪問されていない場合は、訪問済みとしてマークします // そしてそれをキューに入れます (let i of this.adj[s ]) { if (!visited[i]) { queue.push(i); 訪問[i] = true; } } } } } // メイン関数 function main() { // 図に示すグラフを作成します /* A / B C / / D E F */ let g = new Graph(6); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(0, 2); g.addEdge(1, 3); g.addEdge(2, 4); g.addEdge(2, 5); console.log('幅優先トラバーサルは: '); g.BFS(0); // A (0) から BFS を開始します } // メイン関数 main() を実行します。> 出力
Breadth First Traversal is: A B C D E F
深さ優先検索 (DFS) :
DFS、 深さ優先検索 、エッジベースのテクニックです。それは、 出力:
A, B, C, D, E, F
BFS と DFS の違い:
| パラメーター | BFS | DFS |
|---|---|---|
| を意味する | BFS は幅優先検索の略です。 | DFS は深さ優先検索の略です。 |
| データ構造 | BFS(Breadth First Search)は、Queueデータ構造を使用して最短パスを検索します。 | DFS(Depth First Search)はスタックデータ構造を使用します。 |
| 意味 | BFS は、次のレベルに進む前に、最初に同じレベルのすべてのノードをウォークスルーするトラバーサル アプローチです。 | DFS は、ルート ノードからトラバースを開始し、近くに未訪問のノードがないノードに到達するまで、可能な限りノードを通過するトラバーサル アプローチでもあります。 |
| 概念的な違い | BFS はツリーをレベルごとに構築します。 | DFS は、サブツリーごとにツリーのサブツリーを構築します。 |
| 使用されるアプローチ | FIFO (First In First Out) の概念に基づいて動作します。 | LIFO (Last In First Out) の概念に基づいて動作します。 |
| に適し | BFS は、指定されたソースに近い頂点を検索する場合により適しています。 | DFS は、ソースから離れたソリューションがある場合に適しています。 |
| アプリケーション | BFS は、2 部グラフ、最短パスなどのさまざまなアプリケーションで使用されます。 | DFS は、非巡回グラフや強く接続されたコンポーネントの検索など、さまざまなアプリケーションで使用されます。 |
こちらもご覧ください バイナリ ツリーの BFS と DFS バイナリ ツリー トラバーサルの違いについては、