Più grande o '+' formato da tutti gli uno in una matrice quadrata binaria
Dato un n×n matrice binaria insieme a composto da 0s E 1 secondo . Il tuo compito è trovare la dimensione del più grande "+" forma che può essere formata utilizzando solo 1 secondo .

UN "+" forma è costituita da una cella centrale con quattro bracci che si estendono in tutte e quattro le direzioni ( su giù a destra e a sinistra ) pur rimanendo entro i confini della matrice. La dimensione di a "+" è definito come numero totale di celle formandolo compreso il centro e tutte le braccia.
Il compito è restituire il file dimensione massima di qualsiasi valido "+" In insieme a . Se no "+" può essere formato ritorno .
Esempi:
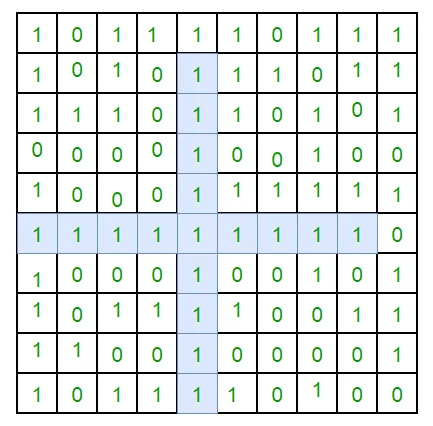
Ingresso: con = [ [0 1 1 0 1] [0 0 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 0 1] [0 1 1 1 0] ]
Produzione: 9
Spiegazione: Al centro del tappetino può essere formato un "+" con una lunghezza del braccio pari a 2 (2 celle in ciascuna direzione + 1 centro).
01 1 01
00 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 01
01 1 10
Dimensione totale = (2 × 4) + 1 = 9Ingresso: con = [ [0 1 1] [0 0 1] [1 1 1] ]
Produzione: 1
Spiegazione: Un "+" con una lunghezza del braccio pari a 0 (0 celle in ciascuna direzione + 1 centro) può essere formato con uno qualsiasi degli 1.Ingresso: con = [ [0] ]
Produzione:
Spiegazione: NO È possibile formare il segno "+".
[Approccio ingenuo] - Considera ogni punto come centro - Tempo O(n^4) e Spazio O(n^4)
Attraversa le celle della matrice una per una. Considera ogni punto attraversato come centro di un più e trova la dimensione del +. Per ogni elemento attraversiamo da sinistra a destra in basso e in alto. Il caso peggiore in questa soluzione si verifica quando abbiamo tutti 1.
[Approccio previsto] - Precalcolo 4 array - O(n^2) Tempo e O(n^2) Spazio
IL idea è mantenere quattro matrici ausiliarie sinistra[][] destra[][] in alto[][] in basso[][] per memorizzare 1 consecutivi in ogni direzione. Per ogni cella (ioj) nella matrice di input memorizziamo le seguenti informazioni in questi quattro matrici -
- sinistra(ij) memorizza il numero massimo di 1 consecutivi nel file Sinistra della cella (i j) inclusa la cella (i j).
- destra(ij) memorizza il numero massimo di 1 consecutivi nel file Giusto della cella (i j) inclusa la cella (i j).
- in alto(ij) memorizza il numero massimo di 1 consecutivi in superiore della cella (i j) inclusa la cella (i j).
- fondo(ij) memorizza il numero massimo di 1 consecutivi in metter il fondo a della cella (i j) inclusa la cella (i j).
Dopo aver calcolato il valore per ciascuna cella delle matrici precedenti, il più grande'+' sarebbe formato da una cella della matrice di input che ha valore massimo considerando il minimo di ( sinistra(i j) destra(i j) sopra(i j) sotto(i j) )
Possiamo usare Programmazione dinamica per calcolare il numero totale di 1 consecutivi in ogni direzione:
se mat(ij) == 1
sinistra(ij) = sinistra(ij - 1) + 1altrimenti sinistra(i j) = 0
se mat(ij) == 1
sopra(i j) = sopra(i - 1 j) + 1;altrimenti top(ij) = 0;
se mat(ij) == 1
fondo(i j) = fondo(i + 1 j) + 1;altrimenti bottom(i j) = 0;
se mat(ij) == 1
destra(i j) = destra(i j + 1) + 1;altrimenti destra(i j) = 0;
Di seguito è riportata l'implementazione dell'approccio di cui sopra:
C++ // C++ program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming #include using namespace std ; int findLargestPlus ( vector < vector < int >> & mat ) { int n = mat . size (); vector < vector < int >> left ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); vector < vector < int >> right ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); vector < vector < int >> top ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); vector < vector < int >> bottom ( n vector < int > ( n 0 )); // Fill left and top matrices for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { left [ i ][ j ] = ( j == 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i ][ j ] = ( i == 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { right [ i ][ j ] = ( j == n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i ][ j ] = ( i == n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } int maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { int armLength = min ({ left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ]}); maxPlusSize = max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } int main () { // Hardcoded input matrix vector < vector < int >> mat = { { 0 1 1 0 1 } { 0 0 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 0 1 } { 0 1 1 1 0 } }; cout < < findLargestPlus ( mat ) < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming class GfG { static int findLargestPlus ( int [][] mat ) { int n = mat . length ; int [][] left = new int [ n ][ n ] ; int [][] right = new int [ n ][ n ] ; int [][] top = new int [ n ][ n ] ; int [][] bottom = new int [ n ][ n ] ; // Fill left and top matrices for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { left [ i ][ j ] = ( j == 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i ][ j ] = ( i == 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { right [ i ][ j ] = ( j == n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i ][ j ] = ( i == n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } int maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 ) { int armLength = Math . min ( Math . min ( left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] ) Math . min ( top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ] )); maxPlusSize = Math . max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Hardcoded input matrix int [][] mat = { { 0 1 1 0 1 } { 0 0 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 0 1 } { 0 1 1 1 0 } }; System . out . println ( findLargestPlus ( mat )); } }
Python # Python program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix # using Dynamic Programming def findLargestPlus ( mat ): n = len ( mat ) left = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] right = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] top = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] bottom = [[ 0 ] * n for i in range ( n )] # Fill left and top matrices for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( n ): if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 : left [ i ][ j ] = 1 if j == 0 else left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 top [ i ][ j ] = 1 if i == 0 else top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 # Fill right and bottom matrices for i in range ( n - 1 - 1 - 1 ): for j in range ( n - 1 - 1 - 1 ): if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 : right [ i ][ j ] = 1 if j == n - 1 else right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 bottom [ i ][ j ] = 1 if i == n - 1 else bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 maxPlusSize = 0 # Compute the maximum '+' size for i in range ( n ): for j in range ( n ): if mat [ i ][ j ] == 1 : armLength = min ( left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ]) maxPlusSize = max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ) return maxPlusSize if __name__ == '__main__' : # Hardcoded input matrix mat = [ [ 0 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 0 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 1 1 1 0 ] ] print ( findLargestPlus ( mat ))
C# // C# program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming using System ; class GfG { static int FindLargestPlus ( int [] mat ) { int n = mat . GetLength ( 0 ); int [] left = new int [ n n ]; int [] right = new int [ n n ]; int [] top = new int [ n n ]; int [] bottom = new int [ n n ]; // Fill left and top matrices for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i j ] == 1 ) { left [ i j ] = ( j == 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i j ] = ( i == 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i j ] == 1 ) { right [ i j ] = ( j == n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i j ] = ( i == n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 j ] + 1 ; } } } int maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i j ] == 1 ) { int armLength = Math . Min ( Math . Min ( left [ i j ] right [ i j ]) Math . Min ( top [ i j ] bottom [ i j ])); maxPlusSize = Math . Max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } public static void Main () { // Hardcoded input matrix int [] mat = { { 0 1 1 0 1 } { 0 0 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 1 1 } { 1 1 1 0 1 } { 0 1 1 1 0 } }; Console . WriteLine ( FindLargestPlus ( mat )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to find the largest '+' in a binary matrix // using Dynamic Programming function findLargestPlus ( mat ) { let n = mat . length ; let left = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); let right = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); let top = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); let bottom = Array . from ({ length : n } () => Array ( n ). fill ( 0 )); // Fill left and top matrices for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { left [ i ][ j ] = ( j === 0 ) ? 1 : left [ i ][ j - 1 ] + 1 ; top [ i ][ j ] = ( i === 0 ) ? 1 : top [ i - 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } // Fill right and bottom matrices for ( let i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { for ( let j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j -- ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { right [ i ][ j ] = ( j === n - 1 ) ? 1 : right [ i ][ j + 1 ] + 1 ; bottom [ i ][ j ] = ( i === n - 1 ) ? 1 : bottom [ i + 1 ][ j ] + 1 ; } } } let maxPlusSize = 0 ; // Compute the maximum '+' size for ( let i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { for ( let j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++ ) { if ( mat [ i ][ j ] === 1 ) { let armLength = Math . min ( left [ i ][ j ] right [ i ][ j ] top [ i ][ j ] bottom [ i ][ j ]); maxPlusSize = Math . max ( maxPlusSize ( 4 * ( armLength - 1 )) + 1 ); } } } return maxPlusSize ; } // Hardcoded input matrix let mat = [ [ 0 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 0 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 1 1 ] [ 1 1 1 0 1 ] [ 0 1 1 1 0 ] ]; console . log ( findLargestPlus ( mat ));
Produzione
9
Complessità temporale: O(n²) dovuto a quattro passaggi per calcolare le matrici direzionali e un passaggio finale per determinare il "+" più grande. Ogni passaggio richiede un tempo O(n²) che porta ad una complessità complessiva di O(n²).
Complessità spaziale: O(n²) a causa di quattro matrici ausiliarie (sinistra destra in alto in basso) che consumano O(n²) spazio extra.