Iteratori in C++ STL
Prerequisito: Introduzione agli iteratori
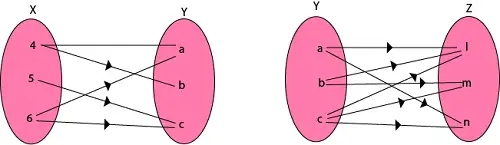
Gli iteratori vengono utilizzati per puntare agli indirizzi di memoria di STL contenitori. Vengono utilizzati principalmente in sequenze di numeri, caratteri, ecc. Riducono la complessità e il tempo di esecuzione del programma.
Operazioni degli iteratori :-
1. iniziare() :- Questa funzione viene utilizzata per restituire il file posizione iniziale del contenitore.
2. fine() :- Questa funzione viene utilizzata per restituire il file Dopo posizione finale del contenitore.
// C++ code to demonstrate the working of> // iterator, begin() and end()> #include> #include // for iterators> #include // for vectors> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> > vector <> int> >con = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };> > > // Declaring iterator to a vector> > vector <> int> >::iteratore ptr;> > > // Displaying vector elements using begin() and end()> > cout < <> 'The vector elements are : '> ;> > for> (ptr = ar.begin(); ptr cout < < *ptr < < ' '; return 0; }> |
Produzione:
The vector elements are : 1 2 3 4 5
3. anticipo() :- Questa funzione viene utilizzata per incrementare la posizione dell'iteratore fino al numero specificato menzionato nei suoi argomenti.
// C++ code to demonstrate the working of> // advance()> #include> #include // for iterators> #include // for vectors> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> > vector <> int> >con = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };> > > // Declaring iterator to a vector> > vector <> int> >::iteratore ptr = ar.begin();> > > // Using advance() to increment iterator position> > // points to 4> > advance(ptr, 3);> > > // Displaying iterator position> > cout < <> 'The position of iterator after advancing is : '> ;> > cout < < *ptr < <> ' '> ;> > > return> 0;> > }> |
Produzione:
The position of iterator after advancing is : 4
4. successivo() :- Questa funzione restituisce il nuovo iteratore a cui l'iteratore indicherebbe avanzando le posizioni citato nelle sue argomentazioni.
5. precedente() :- Questa funzione restituisce il nuovo iteratore che l'iteratore indicherebbe dopo aver decrementato le posizioni citato nelle sue argomentazioni.
// C++ code to demonstrate the working of> // next() and prev()> #include> #include // for iterators> #include // for vectors> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> > vector <> int> >con = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };> > > // Declaring iterators to a vector> > vector <> int> >::iteratore ptr = ar.begin();> > vector <> int> >::iteratore ftr = ar.end();> > > > // Using next() to return new iterator> > // points to 4> > auto> it = next(ptr, 3);> > > // Using prev() to return new iterator> > // points to 3> > auto> it1 = prev(ftr, 3);> > > // Displaying iterator position> > cout < <> 'The position of new iterator using next() is : '> ;> > cout < < *it < <> ' '> ;> > cout < < endl;> > > // Displaying iterator position> > cout < <> 'The position of new iterator using prev() is : '> ;> > cout < < *it1 < <> ' '> ;> > cout < < endl;> > > return> 0;> }> |
Produzione:
The position of new iterator using next() is : 4 The position of new iterator using prev() is : 3
6. inserisci() :- Questa funzione viene utilizzata per inserire gli elementi in qualsiasi posizione nel contenitore. Accetta 2 argomenti, il contenitore e l'iteratore per posizionarsi dove devono essere inseriti gli elementi .
// C++ code to demonstrate the working of> // inserter()> #include> #include // for iterators> #include // for vectors> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> > vector <> int> >con = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };> > vector <> int> >ar1 = {10, 20, 30};> > > // Declaring iterator to a vector> > vector <> int> >::iteratore ptr = ar.begin();> > > // Using advance to set position> > advance(ptr, 3);> > > // copying 1 vector elements in other using inserter()> > // inserts ar1 after 3rd position in ar> > copy(ar1.begin(), ar1.end(), inserter(ar,ptr));> > > // Displaying new vector elements> > cout < <> 'The new vector after inserting elements is : '> ;> > for> (> int> &x : ar)> > cout < < x < <> ' '> ;> > > return> 0;> }> |
Produzione:
The new vector after inserting elements is : 1 2 3 10 20 30 4 5
Tipi di iteratori:
- Iteratori di input
- Iteratori di output
- Iteratore in avanti
- Iteratori bidirezionali
- Iteratori ad accesso casuale