Funzione free() nella libreria C con esempi
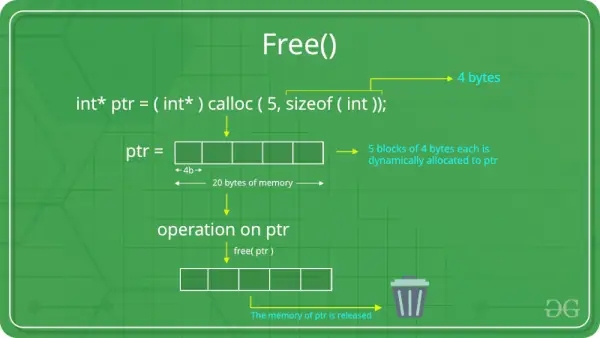
IL funzione free() in C viene utilizzato per liberare o deallocare la memoria allocata dinamicamente e aiuta a ridurre lo spreco di memoria. IL C libero() La funzione non può essere utilizzata per liberare la memoria allocata staticamente (ad esempio, variabili locali) o la memoria allocata sullo stack. Può essere utilizzato solo per deallocare la memoria heap precedentemente allocata utilizzando le funzioni malloc(), calloc() e realloc().
La funzione free() è definita all'interno file di intestazione.

Funzione C libera()
Sintassi della funzione free() in C
void free (void * ptr );
Parametri
- ptr è il puntatore al blocco di memoria che deve essere liberato o deallocato.
Valore di ritorno
- La funzione free() non restituisce alcun valore.
Esempi di free()
Esempio 1:
Il seguente programma C illustra l'uso di calloc() funzione per allocare la memoria in modo dinamico e gratuito() funzione per liberare quella memoria.
C
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using calloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> > // This pointer ptr will hold the> > // base address of the block created> > int> * ptr;> > int> n = 5;> > // Get the number of elements for the array> > printf> (> 'Enter number of Elements: %d
'> , n);> > scanf> (> '%d'> , &n);> > // Dynamically allocate memory using calloc()> > ptr = (> int> *)> calloc> (n,> sizeof> (> int> ));> > // Check if the memory has been successfully> > // allocated by calloc() or not> > if> (ptr == NULL) {> > printf> (> 'Memory not allocated
'> );> > exit> (0);> > }> > // Memory has been Successfully allocated using calloc()> > printf> (> 'Successfully allocated the memory using '> > 'calloc().
'> );> > // Free the memory> > free> (ptr);> > printf> (> 'Calloc Memory Successfully freed.'> );> > return> 0;> }> |
Produzione
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using calloc(). Calloc Memory Successfully freed.
Esempio 2:
Il seguente programma C illustra l'uso di malloc() funzione per allocare la memoria in modo dinamico e gratuito() funzione per liberare quella memoria.
C
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using malloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> > // This pointer ptr will hold the> > // base address of the block created> > int> * ptr;> > int> n = 5;> > // Get the number of elements for the array> > printf> (> 'Enter number of Elements: %d
'> , n);> > scanf> (> '%d'> , &n);> > // Dynamically allocate memory using malloc()> > ptr = (> int> *)> malloc> (n *> sizeof> (> int> ));> > // Check if the memory has been successfully> > // allocated by malloc() or not> > if> (ptr == NULL) {> > printf> (> 'Memory not allocated
'> );> > exit> (0);> > }> > // Memory has been Successfully allocated using malloc()> > printf> (> 'Successfully allocated the memory using '> > 'malloc().
'> );> > // Free the memory> > free> (ptr);> > printf> (> 'Malloc Memory Successfully freed.'> );> > return> 0;> }> |
Produzione
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using malloc(). Malloc Memory Successfully freed.







![Metodo Java main() – public static void main(String[] args)](https://techcodeview.com/img/java-basics/92/java-main-method-public-static-void-main.webp)