Trova la profondità o l'altezza massima di un determinato albero binario

Dato un albero binario, il compito è trovare l'altezza dell'albero. L'altezza dell'albero è il numero di vertici dell'albero dalla radice al nodo più profondo.
Nota: L'altezza di un albero vuoto è 0 e l'altezza di un albero con nodo singolo è 1 .

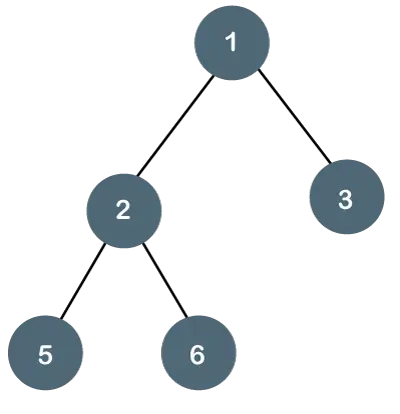
Esempio di albero binario
Altezza pratica consigliata dell'albero binario Provalo!Calcolare ricorsivamente l'altezza di Sinistra e il Giusto sottoalberi di un nodo e assegnare l'altezza al nodo come altezza massima di due bambini più 1 . Vedi sotto lo pseudo codice e il programma per i dettagli.
Illustrazione:
Consideriamo il seguente albero:

Esempio di albero
maxProfondità('1') = max(maxProfondità('2'), maxProfondità('3')) + 1 = 2 + 1
perché ricorsivamente
maxDepth('2') = max (maxDepth('4'), maxDepth('5')) + 1 = 1 + 1 e (poiché l'altezza di '4' e '5' è 1)
profonditàmax('3') = 1
Segui i passaggi seguenti per implementare l'idea:
- Esegui ricorsivamente una ricerca approfondita.
- Se l'albero è vuoto restituisce 0
- Altrimenti, procedi come segue
- Ottieni ricorsivamente la profondità massima del sottoalbero sinistro, ovvero chiama maxDepth( tree->left-subtree)
- Ottieni ricorsivamente la profondità massima del sottoalbero destro, ovvero chiama maxDepth( tree->right-subtree)
- Ottieni il massimo della profondità massima di Sinistra E Giusto sottoalberi e aggiungi 1 ad esso per il nodo corrente.
-
- Restituisce profondità_massima.
Di seguito è riportata l’implementazione dell’approccio di cui sopra:
C++
// C++ program to find height of tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> /* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child> and a pointer to right child */> class> node {> public> :> > int> data;> > node* left;> > node* right;> };> /* Compute the 'maxDepth' of a tree -- the number of> > nodes along the longest path from the root node> > down to the farthest leaf node.*/> int> maxDepth(node* node)> {> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> 0;> > else> {> > /* compute the depth of each subtree */> > int> lDepth = maxDepth(node->sinistra);> > int> rDepth = maxDepth(node->destra);> > /* use the larger one */> > if> (lDepth>rProfondità)> > return> (lDepth + 1);> > else> > return> (rDepth + 1);> > }> }> /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the> given data and NULL left and right pointers. */> node* newNode(> int> data)> {> > node* Node => new> node();> > Node->dati = dati;> > Node->sinistra = NULL;> > Node->destra = NULL;> > return> (Node);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> > node* root = newNode(1);> > root->sinistra = nuovoNodo(2);> > root->destra = nuovoNodo(3);> > root->sinistra->sinistra = nuovoNodo(4);> > root->sinistra->destra = nuovoNodo(5);> > cout < <> 'Height of tree is '> < < maxDepth(root);> > return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Amit Srivastav> |
C
#include> #include> /* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child> > and a pointer to right child */> struct> node {> > int> data;> > struct> node* left;> > struct> node* right;> };> /* Compute the 'maxDepth' of a tree -- the number of> > nodes along the longest path from the root node> > down to the farthest leaf node.*/> int> maxDepth(> struct> node* node)> {> > if> (node == NULL)> > return> 0;> > else> {> > /* compute the depth of each subtree */> > int> lDepth = maxDepth(node->sinistra);> > int> rDepth = maxDepth(node->destra);> > /* use the larger one */> > if> (lDepth>rProfondità)> > return> (lDepth + 1);> > else> > return> (rDepth + 1);> > }> }> /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the> > given data and NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> node* newNode(> int> data)> {> > struct> node* node> > = (> struct> node*)> malloc> (> sizeof> (> struct> node));> > node->dati = dati;> > node->sinistra = NULL;> > node->destra = NULL;> > return> (node);> }> int> main()> {> > struct> node* root = newNode(1);> > root->sinistra = nuovoNodo(2);> > root->destra = nuovoNodo(3);> > root->sinistra->sinistra = nuovoNodo(4);> > root->sinistra->destra = nuovoNodo(5);> > printf> (> 'Height of tree is %d'> , maxDepth(root));> > getchar> ();> > return> 0;> }> |
Giava
// Java program to find height of tree> // A binary tree node> class> Node {> > int> data;> > Node left, right;> > Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> class> BinaryTree {> > Node root;> > /* Compute the 'maxDepth' of a tree -- the number of> > nodes along the longest path from the root node> > down to the farthest leaf node.*/> > int> maxDepth(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> 0> ;> > else> {> > /* compute the depth of each subtree */> > int> lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);> > int> rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);> > /* use the larger one */> > if> (lDepth>rProfondità)> > return> (lDepth +> 1> );> > else> > return> (rDepth +> 1> );> > }> > }> > /* Driver program to test above functions */> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > BinaryTree tree => new> BinaryTree();> > tree.root => new> Node(> 1> );> > tree.root.left => new> Node(> 2> );> > tree.root.right => new> Node(> 3> );> > tree.root.left.left => new> Node(> 4> );> > tree.root.left.right => new> Node(> 5> );> > System.out.println(> 'Height of tree is '> > + tree.maxDepth(tree.root));> > }> }> // This code has been contributed by Amit Srivastav> |
Python3
# Python3 program to find the maximum depth of tree> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> > # Constructor to create a new node> > def> __init__(> self> , data):> > self> .data> => data> > self> .left> => None> > self> .right> => None> # Compute the 'maxDepth' of a tree -- the number of nodes> # along the longest path from the root node down to the> # farthest leaf node> def> maxDepth(node):> > if> node> is> None> :> > return> 0> > else> :> > # Compute the depth of each subtree> > lDepth> => maxDepth(node.left)> > rDepth> => maxDepth(node.right)> > # Use the larger one> > if> (lDepth>rProfondità):> > return> lDepth> +> 1> > else> :> > return> rDepth> +> 1> # Driver program to test above function> root> => Node(> 1> )> root.left> => Node(> 2> )> root.right> => Node(> 3> )> root.left.left> => Node(> 4> )> root.left.right> => Node(> 5> )> print> (> 'Height of tree is %d'> %> (maxDepth(root)))> # This code is contributed by Amit Srivastav> |
C#
// C# program to find height of tree> using> System;> // A binary tree node> public> class> Node {> > public> int> data;> > public> Node left, right;> > public> Node(> int> item)> > {> > data = item;> > left = right => null> ;> > }> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> > Node root;> > /* Compute the 'maxDepth' of a tree -- the number of> > nodes along the longest path from the root node> > down to the farthest leaf node.*/> > int> maxDepth(Node node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> 0;> > else> {> > /* compute the depth of each subtree */> > int> lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);> > int> rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);> > /* use the larger one */> > if> (lDepth>rProfondità)> > return> (lDepth + 1);> > else> > return> (rDepth + 1);> > }> > }> > /* Driver code */> > public> static> void> Main(String[] args)> > {> > BinaryTree tree => new> BinaryTree();> > tree.root => new> Node(1);> > tree.root.left => new> Node(2);> > tree.root.right => new> Node(3);> > tree.root.left.left => new> Node(4);> > tree.root.left.right => new> Node(5);> > Console.WriteLine(> 'Height of tree is '> > + tree.maxDepth(tree.root));> > }> }> // This code has been contributed by> // Correction done by Amit Srivastav> |
Javascript
> // JavaScript program to find height of tree> // A binary tree node> class Node> {> > constructor(item)> > {> > this> .data=item;> > this> .left=> this> .right=> null> ;> > }> }> > let root;> > > /* Compute the 'maxDepth' of a tree -- the number of> > nodes along the longest path from the root node> > down to the farthest leaf node.*/> > function> maxDepth(node)> > {> > if> (node ==> null> )> > return> 0;> > else> > {> > /* compute the depth of each subtree */> > let lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);> > let rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);> > > /* use the larger one */> > if> (lDepth>rProfondità)> > return> (lDepth + 1);> > else> > return> (rDepth + 1);> > }> > }> > > /* Driver program to test above functions */> > > root => new> Node(1);> > root.left => new> Node(2);> > root.right => new> Node(3);> > root.left.left => new> Node(4);> > root.left.right => new> Node(5);> > > document.write(> 'Height of tree is : '> +> > maxDepth(root));> // This code is contributed by rag2127> //Correction done by Amit Srivastav> > |
Produzione
Height of tree is 3
Complessità temporale: O(N) (Vedi il post su Attraversamento degli alberi per dettagli)
Spazio ausiliario: O(N) a causa dello stack ricorsivo.
Trova la profondità o l'altezza massima di un albero utilizzando Attraversamento dell'ordine di livello :
Fare Attraversamento dell'ordine di livello , aggiungendo nodi ad ogni livello a Segui i passaggi seguenti per implementare l'idea:
- Attraversare l'albero in ordine di livello partendo da radice .
- Inizializza una coda vuota Q , una variabile profondità e spingere radice , quindi spingere nullo dentro Q .
- Esegui un ciclo while fino a Q non è vuoto.
- Conservare l'elemento anteriore di Q ed estrarre l'elemento anteriore.
- Se la parte anteriore di Q È NULLO quindi incrementare profondità per uno e se la coda non è vuota, premere NULLO dentro Q .
- Altrimenti se l'elemento non lo è NULLO quindi controllalo Sinistra E Giusto bambini e se non lo sono NULLO spingerli dentro Q .
- Ritorno profondità .
Di seguito è riportata l’implementazione dell’approccio di cui sopra:
C++
#include>#include>using>namespace>std;>// A Tree node>struct>Node {>>int>key;>>struct>Node *left, *right;>};>// Utility function to create a new node>Node* newNode(>int>key)>{>>Node* temp =>new>Node;>>temp->chiave = chiave;>>temp->sinistra = temp->destra = NULL;>>return>(temp);>}>/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/>int>height(>struct>Node* root)>{>>// Initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>int>depth = 0;>>queue q;>>// Pushing first level element along with NULL>>q.push(root);>>q.push(NULL);>>while>(!q.empty()) {>>Node* temp = q.front();>>q.pop();>>// When NULL encountered, increment the value>>if>(temp == NULL) {>>depth++;>>}>>// If NULL not encountered, keep moving>>if>(temp != NULL) {>>if>(temp->sinistra) {>>q.push(temp->sinistra);>>}>>if>(temp->destra) {>>q.push(temp->destra);>>}>>}>>// If queue still have elements left,>>// push NULL again to the queue.>>else>if>(!q.empty()) {>>q.push(NULL);>>}>>}>>return>depth;>}>// Driver program>int>main()>{>>// Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example>>Node* root = newNode(1);>>root->sinistra = nuovoNodo(2);>>root->destra = nuovoNodo(3);>>root->sinistra->sinistra = nuovoNodo(4);>>root->sinistra->destra = nuovoNodo(5);>>cout < <>'Height(Depth) of tree is: '>< < height(root);>}>Giava
// Java program for above approach>import>java.util.LinkedList;>import>java.util.Queue;>class>GFG {>>// A tree node structure>>static>class>Node {>>int>key;>>Node left;>>Node right;>>}>>// Utility function to create>>// a new node>>static>Node newNode(>int>key)>>{>>Node temp =>new>Node();>>temp.key = key;>>temp.left = temp.right =>null>;>>return>temp;>>}>>/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/>>public>static>int>height(Node root)>>{>>// Initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>int>depth =>0>;>>Queue q =>new>LinkedList();>>// Pushing first level element along with null>>q.add(root);>>q.add(>null>);>>while>(!q.isEmpty()) {>>Node temp = q.peek();>>q.remove();>>// When null encountered, increment the value>>if>(temp ==>null>) {>>depth++;>>}>>// If null not encountered, keep moving>>if>(temp !=>null>) {>>if>(temp.left !=>null>) {>>q.add(temp.left);>>}>>if>(temp.right !=>null>) {>>q.add(temp.right);>>}>>}>>// If queue still have elements left,>>// push null again to the queue.>>else>if>(!q.isEmpty()) {>>q.add(>null>);>>}>>}>>return>depth;>>}>>// Driver Code>>public>static>void>main(String args[])>>{>>Node root = newNode(>1>);>>root.left = newNode(>2>);>>root.right = newNode(>3>);>>root.left.left = newNode(>4>);>>root.left.right = newNode(>5>);>>System.out.println(>'Height(Depth) of tree is: '>>+ height(root));>>}>}>// This code is contributed by jana_sayantan.>Python3
# Python code to implement the approach># A Tree node>class>Node:>>def>__init__(>self>):>>self>.key>=>0>>self>.left,>self>.right>=>None>,>None># Utility function to create a new node>def>newNode(key):>>temp>=>Node()>>temp.key>=>key>>temp.left, temp.right>=>None>,>None>>return>temp># Function to find the height(depth) of the tree>def>height(root):>># Initialising a variable to count the>># height of tree>>depth>=>0>>q>=>[]>># appending first level element along with None>>q.append(root)>>q.append(>None>)>>while>(>len>(q)>>0>):>>temp>=>q[>0>]>>q>=>q[>1>:]>># When None encountered, increment the value>>if>(temp>=>=>None>):>>depth>+>=>1>># If None not encountered, keep moving>>if>(temp !>=>None>):>>if>(temp.left):>>q.append(temp.left)>>if>(temp.right):>>q.append(temp.right)>># If queue still have elements left,>># append None again to the queue.>>elif>(>len>(q)>>0>):>>q.append(>None>)>>return>depth># Driver program># Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example>root>=>newNode(>1>)>root.left>=>newNode(>2>)>root.right>=>newNode(>3>)>root.left.left>=>newNode(>4>)>root.left.right>=>newNode(>5>)>print>(f>'Height(Depth) of tree is: {height(root)}'>)># This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>C#
// C# Program to find the Maximum Depth or Height of Binary Tree>using>System;>using>System.Collections.Generic;>// A Tree node>public>class>Node {>>public>int>data;>>public>Node left, right;>>public>Node(>int>item)>>{>>data = item;>>left =>null>;>>right =>null>;>>}>}>public>class>BinaryTree {>>Node root;>>// Function to find the height(depth) of the tree>>int>height()>>{>>// Initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>int>depth = 0;>>Queue q =>new>Queue();>>// Pushing first level element along with NULL>>q.Enqueue(root);>>q.Enqueue(>null>);>>while>(q.Count != 0) {>>Node temp = q.Dequeue();>>// When NULL encountered, increment the value>>if>(temp ==>null>)>>depth++;>>// If NULL not encountered, keep moving>>if>(temp !=>null>) {>>if>(temp.left !=>null>) {>>q.Enqueue(temp.left);>>}>>if>(temp.right !=>null>) {>>q.Enqueue(temp.right);>>}>>}>>// If queue still have elements left,>>// push NULL again to the queue>>else>if>(q.Count != 0) {>>q.Enqueue(>null>);>>}>>}>>return>depth;>>}>>// Driver program>>public>static>void>Main()>>{>>// Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example>>BinaryTree tree =>new>BinaryTree();>>tree.root =>new>Node(1);>>tree.root.left =>new>Node(2);>>tree.root.right =>new>Node(3);>>tree.root.left.left =>new>Node(4);>>tree.root.left.right =>new>Node(5);>>Console.WriteLine(>'Height(Depth) of tree is: '>>+ tree.height());>>}>}>// This code is contributed by Yash Agarwal(yashagarwal2852002)>Javascript
>// JavaScript code to implement the approach>// A Tree node>class Node{>>constructor(){>>this>.key = 0>>this>.left =>null>>this>.right =>null>>}>}>// Utility function to create a new node>function>newNode(key){>>let temp =>new>Node()>>temp.key = key>>temp.left =>null>>temp.right =>null>>return>temp>}>// Function to find the height(depth) of the tree>function>height(root){>>// Initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>let depth = 0>>let q = []>>>// pushing first level element along with null>>q.push(root)>>q.push(>null>)>>while>(q.length>0){>>let temp = q.shift()>>>// When null encountered, increment the value>>if>(temp ==>null>)>>depth += 1>>>// If null not encountered, keep moving>>if>(temp !=>null>){>>if>(temp.left)>>q.push(temp.left)>>>if>(temp.right)>>q.push(temp.right)>>}>>>// If queue still have elements left,>>// push null again to the queue.>>else>if>(q.length>0)>>q.push(>null>)>>}>>return>depth>}>// Driver program>// Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example>let root = newNode(1)>root.left = newNode(2)>root.right = newNode(3)>root.left.left = newNode(4)>root.left.right = newNode(5)>document.write(`Height(Depth) of tree is: ${height(root)}`,>''>)>// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>>
ProduzioneHeight(Depth) of tree is: 3Complessità temporale: SU)
Spazio ausiliario: SU)Un altro metodo per trovare l'altezza utilizzando Attraversamento dell'ordine di livello :
C++
// C++ program for above approach>#include>using>namespace>std;>// A Tree node>struct>Node {>>int>key;>>struct>Node *left, *right;>};>// Utility function to create a new node>Node* newNode(>int>key)>{>>Node* temp =>new>Node;>>temp->chiave = chiave;>>temp->sinistra = temp->destra = NULL;>>return>(temp);>}>/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/>int>height(Node* root)>{>>// Initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>queue q;>>q.push(root);>>int>height = 0;>>while>(!q.empty()) {>>int>size = q.size();>>for>(>int>i = 0; i Node* temp = q.front(); q.pop(); if (temp->sinistra!= NULL) { q.push(temp->sinistra); } if (temp->right != NULL) { q.push(temp->right); } } altezza++; } restituisce l'altezza; } // Programma driver int main() { // Creiamo l'albero binario mostrato nell'esempio sopra Node* root = newNode(1); radice->sinistra = nuovoNodo(2); radice->destra = nuovoNodo(3); radice->sinistra->sinistra = nuovoNodo(4); radice->sinistra->destra = nuovoNodo(5); cout < < 'Height(Depth) of tree is: ' < < height(root); } // This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)>Giava
// Java program for above approach>import>java.util.LinkedList;>import>java.util.Queue;>class>GFG {>>// A tree node structure>>static>class>Node {>>int>key;>>Node left;>>Node right;>>}>>// Utility function to create>>// a new node>>static>Node newNode(>int>key)>>{>>Node temp =>new>Node();>>temp.key = key;>>temp.left = temp.right =>null>;>>return>temp;>>}>>/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/>>public>static>int>height(Node root)>>{>>// Initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>Queue q =>new>LinkedList();>>q.add(root);>>int>height =>0>;>>while>(!q.isEmpty()) {>>int>size = q.size();>>for>(>int>i =>0>; i Node temp = q.poll(); if (temp.left != null) { q.add(temp.left); } if (temp.right != null) { q.add(temp.right); } } height++; } return height; } // Driver Code public static void main(String args[]) { Node root = newNode(1); root.left = newNode(2); root.right = newNode(3); root.left.left = newNode(4); root.left.right = newNode(5); System.out.println('Height(Depth) of tree is: ' + height(root)); } }>Python3
# Python3 program to find the height of a tree>># A binary tree node>class>Node:>>># Constructor to create a new node>>def>__init__(>self>, data):>>self>.key>=>data>>self>.left>=>None>>self>.right>=>None>># Function to find height of tree>def>height(root):>># Base Case>>if>root>is>None>:>>return>0>>># Create an empty queue for level order traversal>>q>=>[]>>># Enqueue Root and initialize height>>q.append(root)>>height>=>0>>># Loop while queue is not empty>>while>q:>>># nodeCount (queue size) indicates number of nodes>># at current level>>nodeCount>=>len>(q)>>># Dequeue all nodes of current level and Enqueue all>># nodes of next level>>while>nodeCount>>0>:>>node>=>q.pop(>0>)>>if>node.left>is>not>None>:>>q.append(node.left)>>if>node.right>is>not>None>:>>q.append(node.right)>>nodeCount>->=>1>>height>+>=>1>>>return>height>># Driver Code>root>=>Node(>1>)>root.left>=>Node(>2>)>root.right>=>Node(>3>)>root.left.left>=>Node(>4>)>root.left.right>=>Node(>5>)>>print>(>'Height(Depth) of tree is'>, height(root))>C#
using>System;>using>System.Collections.Generic;>class>GFG {>>// A Tree node>>class>Node {>>public>int>key;>>public>Node left, right;>>public>Node(>int>key)>>{>>this>.key=key;>>this>.left=>this>.right=>null>;>>}>>}>>// Utility function to create a new node>>/*Node newNode(int key)>>{>>Node* temp = new Node;>>temp.key = key;>>temp.left = temp.right = NULL;>>return (temp);>>}*/>>/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/>>static>int>height(Node root)>>{>>// Initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>Queue q=>new>Queue();>>q.Enqueue(root);>>int>height = 0;>>while>(q.Count>0) {>>int>size = q.Count;>>for>(>int>i = 0; i Node temp = q.Peek(); q.Dequeue(); if (temp.left != null) { q.Enqueue(temp.left); } if (temp.right != null) { q.Enqueue(temp.right); } } height++; } return height; } // Driver program public static void Main() { // Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); Console.Write('Height(Depth) of tree is: ' + height(root)); } } // This code is contributed by poojaagarwal2.>Javascript
// JavaScript program for above approach>// a tree node>class Node{>>constructor(key){>>this>.key = key;>>this>.left =>this>.right =>null>;>>}>}>// utility function to create a new node>function>newNode(key){>>return>new>Node(key);>}>// function to find the height of the tree>function>height(root){>>// initialising a variable to count the>>// height of tree>>let q = [];>>q.push(root);>>let height = 0;>>while>(q.length>0){>>let size = q.length;>>for>(let i = 0; i let temp = q.shift(); if(temp.left != null){ q.push(temp.left); } if(temp.right != null){ q.push(temp.right); } } height++; } return height; } // driver code let root = newNode(1); root.left = newNode(2); root.right = newNode(3); root.left.left = newNode(4); root.left.right = newNode(5); document.write('Height(Depth) of tree is: ' + height(root)); // this code is contributed by Kirti Agarwal(kirtiagarwal23121999)>
ProduzioneHeight(Depth) of tree is: 3Complessità temporale: SU)
Spazio ausiliario: SU)