Appiattire un elenco collegato a più livelli (in profondità)
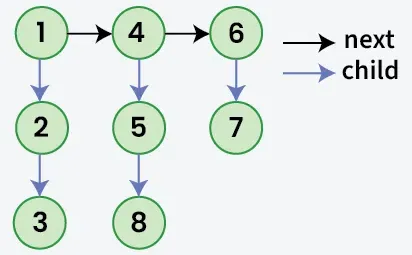
Dato un elenco collegato in cui oltre a Prossimo puntatore ogni nodo ha un bambino puntatore che può o meno puntare a un elenco separato. Questi elenchi secondari potrebbero avere uno o più figli propri per produrre a multilivello elenco collegato. dato che Testa del primo livello della lista. Il compito è quello appiattire l'elenco in modo che tutti i nodi appaiano in a unico livello elenco collegato. Appiattisci l'elenco in modo che tutti i nodi nella primo livello dovrebbe venire Primo quindi i nodi del secondo livello e così via.
Esempi:
Ingresso:

Produzione: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
Spiegazione: L'elenco collegato multilivello è appiattito poiché non ha puntatori secondari.
Abbiamo discusso appiattimento di un elenco collegato a più livelli dove i nodi hanno due puntatori verso il basso e verso il successivo. Nel post precedente noi appiattito l'elenco collegato a livello. Come appiattire un elenco collegato quando è sempre necessario elaborare il file puntatore verso il basso prima del prossimo in ogni nodo.
Sommario
- [Approccio previsto] Utilizzo della ricorsione - Tempo O(n) e Spazio O(n).
- [Approccio alternativo] Utilizzo dello Stack: O(n) Tempo e O(n) Spazio
[Approccio previsto] Utilizzo della ricorsione - Tempo O(n) e Spazio O(n).
C++L'approccio è quello di ricorsivamente appiattire a collegati a più livelli elenco attraversando ogni nodo e i suoi nodi figli. Primo appiattire l'elenco dei figli utilizzando la ricorsione. Una volta appiattito l'elenco dei figli, procedere al file nodo successivo nella sequenza. Durante l'attraversamento mantenere a riferimento al nodo precedentemente visitato e collegarlo al nodo corrente. Questo processo garantisce che tutti i nodi di diversi livelli siano collegati in a elenco lineare unico preservando il ordine in profondità.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * curr Node *& prev ) { if ( curr == nullptr ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node * next = curr -> next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr -> down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); Node * prev = nullptr ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node curr Node [] prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] != null ) prev [ 0 ] . next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node [] prev = new Node [ 1 ] ; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( curr prev ): if curr is None : return # Add the current element to the list. if prev [ 0 ] is not None : prev [ 0 ] . next = curr prev [ 0 ] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr . next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list ( curr . down prev ) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list ( next_node prev ) def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr is not None : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) prev = [ None ] flatten_list ( head prev ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node curr ref Node prev ) { if ( curr == null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList ( curr . down ref prev ); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList ( next ref prev ); } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); Node prev = null ; FlattenList ( head ref prev ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( curr prev ) { if ( curr === null ) return ; // Add the current element to the list. if ( prev [ 0 ] !== null ) prev [ 0 ]. next = curr ; prev [ 0 ] = curr ; // Store the next pointer let next = curr . next ; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList ( curr . down prev ); // Recursively add the next list flattenList ( next prev ); } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); let prev = [ null ]; flattenList ( head prev ); printList ( head );
Produzione
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[Approccio alternativo] Utilizzo dello Stack: O(n) Tempo e O(n) Spazio
C++L'approccio è quello di attraversare il elenco collegato a più livelli utilizzando a pila . Inizia da spingendo IL nodo della testa sulla pila. Poi mentre il lo stack non è vuoto pop il nodo superiore ed elaborarlo. Per ogni nodo spingere suo puntatori avanti e giù (se esistono) in pila. Durante questo processo collega il nodo corrente al nodo precedente mantenendo l'elenco in una forma appiattita. L'attraversamento garantisce che i nodi di tutti i livelli siano collegati in a elenco collegato a livello singolo preservando l’ordine in profondità.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * next ; Node * down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = nullptr ; } }; void flattenList ( Node * head ) { if ( head == nullptr ) return ; stack < Node *> st ; st . push ( head ); Node * prev = nullptr ; while ( ! st . empty ()) { Node * curr = st . top (); st . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr -> next != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr -> down != nullptr ) st . push ( curr -> down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != nullptr ) prev -> next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } void printList ( Node * head ) { Node * curr = head ; while ( curr != nullptr ) { cout < < curr -> data < < ' ' ; curr = curr -> next ; } cout < < endl ; } int main () { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node * head = new Node ( 5 ); head -> down = new Node ( 7 ); head -> down -> down = new Node ( 8 ); head -> down -> down -> down = new Node ( 30 ); head -> next = new Node ( 10 ); head -> next -> next = new Node ( 19 ); head -> next -> next -> down = new Node ( 22 ); head -> next -> next -> down -> down = new Node ( 50 ); head -> next -> next -> next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack ; class Node { int data ; Node next down ; Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void flattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack <> (); stack . push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( ! stack . isEmpty ()) { Node curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void printList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { System . out . print ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } System . out . println (); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head ); } }
Python # A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node : def __init__ ( self x ): self . data = x self . next = None self . down = None def flatten_list ( head ): if head is None : return stack = [ head ] prev = None while stack : curr = stack . pop () # Push the next node first if curr . next : stack . append ( curr . next ) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr . down : stack . append ( curr . down ) # Add the current element to the list if prev : prev . next = curr prev = curr def print_list ( head ): curr = head while curr : print ( curr . data end = ' ' ) curr = curr . next print () if __name__ == '__main__' : # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node ( 5 ) head . down = Node ( 7 ) head . down . down = Node ( 8 ) head . down . down . down = Node ( 30 ) head . next = Node ( 10 ) head . next . next = Node ( 19 ) head . next . next . down = Node ( 22 ) head . next . next . down . down = Node ( 50 ) head . next . next . next = Node ( 28 ) flatten_list ( head ) print_list ( head )
C# // A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class Node { public int data ; public Node next down ; public Node ( int x ) { data = x ; next = down = null ; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList ( Node head ) { if ( head == null ) return ; Stack < Node > stack = new Stack < Node > (); stack . Push ( head ); Node prev = null ; while ( stack . Count > 0 ) { Node curr = stack . Pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next != null ) stack . Push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down != null ) stack . Push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev != null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } static void PrintList ( Node head ) { Node curr = head ; while ( curr != null ) { Console . Write ( curr . data + ' ' ); curr = curr . next ; } Console . WriteLine (); } static void Main ( string [] args ) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); FlattenList ( head ); PrintList ( head ); } }
JavaScript // A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor ( x ) { this . data = x ; this . next = null ; this . down = null ; } } function flattenList ( head ) { if ( head === null ) return ; let stack = [ head ]; let prev = null ; while ( stack . length > 0 ) { let curr = stack . pop (); // Push the next node first if ( curr . next !== null ) stack . push ( curr . next ); // Push the bottom node into stack if ( curr . down !== null ) stack . push ( curr . down ); // Add the current element to the list if ( prev !== null ) prev . next = curr ; prev = curr ; } } function printList ( head ) { let curr = head ; while ( curr !== null ) { console . log ( curr . data ); curr = curr . next ; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node ( 5 ); head . down = new Node ( 7 ); head . down . down = new Node ( 8 ); head . down . down . down = new Node ( 30 ); head . next = new Node ( 10 ); head . next . next = new Node ( 19 ); head . next . next . down = new Node ( 22 ); head . next . next . down . down = new Node ( 50 ); head . next . next . next = new Node ( 28 ); flattenList ( head ); printList ( head );
Produzione
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28