Putket
Putket IO tarjoaa linkin kahden JVM:ssä samanaikaisesti käynnissä olevan säikeen välillä. Joten putkia käytetään sekä lähteenä että määränpäänä.
- PipedInputStream liitetään myös PipedOutputStreamin kanssa. Joten dataa voidaan kirjoittaa käyttämällä PipedOutputStreamia ja PipedInputStreamia. Mutta molempien säikeiden käyttäminen samanaikaisesti luo umpikujan säikeille.
- Putken sanotaan katkenneeksi, jos lanka, joka toimitti datatavuja yhdistetylle liukuhihnalähtövirralle, ei ole enää elossa.
Ilmoitus: public class PipedInputStream extends InputStream
Rakentaja: | PipedInputStream() : | luo PipedInputStreamin, jota ei ole yhdistetty.
| PipedInputStream(int pSize) : | luo PipedInputStreamin, jota ei ole yhdistetty määritettyyn putken kokoon.
| PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream outStream) : | luo PipedInputStreamin, joka on yhdistetty PipedOutputStreamiin - "outStream".
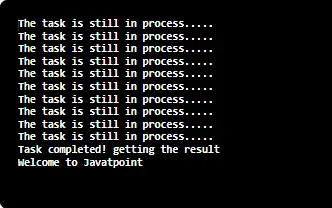
| PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream outStream int pSize) : | luo putken syöttövirran, joka on yhdistetty putkettuun lähtövirtaan määritetyn putken kokoisena. Menetelmät: | int read(): | Reads the next byte of data from this piped input stream.The value byte is returned as an int in the range 0 to 255. This method blocks until input data is available the end of the stream is detected or an exception is thrown. Java // Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { PipedInputStream geek_input = new PipedInputStream (); PipedOutputStream geek_output = new PipedOutputStream (); try { // Use of connect() : connecting geek_input with geek_output geek_input . connect ( geek_output ); // Use of read() method : geek_output . write ( 71 ); System . out . println ( 'using read() : ' + ( char ) geek_input . read ()); geek_output . write ( 69 ); System . out . println ( 'using read() : ' + ( char ) geek_input . read ()); geek_output . write ( 75 ); System . out . println ( 'using read() : ' + ( char ) geek_input . read ()); } catch ( IOException except ) { except . printStackTrace (); } } } Lähtö: using read() : G using read() : E using read() : K
| read(byte[] puskuri int offset int maxlen): | java.io.PipedInputStream.read(tavu[] puskuri int offset int maxlen) lukee enintään tavua dataa Piped Input Streamista puskureihin. Menetelmä estää, jos virran loppu saavutetaan tai tehdään poikkeus. Syntaksi: public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : the destination buffer into which the data is to be read offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'. maxlen : maximum length of array to be read Return : next 'maxlen' bytes of the data as an integer value return -1 is end of stream is reached Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. -> NullPointerException : if buffer is null. -> IndexOutOfBoundsException : if offset is -ve or maxlen is -ve or maxlen > buffer.length - offset.
| vastaanottaa (int tavu): | java.io.PipedInputStream.receive(int byte) vastaanottaa datatavun. Jos tuloa ei ole saatavilla, menetelmä estää. Syntaksi: protected void receive(int byte) Parameters : byte : the bytes of the data received Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs or pipe is broken.
| sulje() : | java.io.PipedInputStream.close() sulkee Piped Input Streamin ja vapauttaa allokoidut resurssit. Syntaksi: public void close() Parameters : -------------- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
| yhdistä (PipedOutputStream-lähde): | java.io.PipedInputStream.connect(PipedOutputStream-lähde) yhdistää Piped Input Streamin 'lähteeseen' Piped Output Streamiin ja jos 'lähde' on putkia, joissa on jokin muu stream IO -poikkeus heitetään Syntaksi: public void connect(PipedOutputStream source) Parameters : source : the Piped Output Stream to be connected to Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
| saatavilla () : | java.io.PipedInputStream.available() palautus nro. tavuja, jotka voidaan lukea Input Streamista ilman, että niitä varsinaisesti estetään. Syntaksi: public int available() Parameters : ------------- Return : no. of bytes that can be read from Input Stream without actually being blocked. 0 if the stream is already closed but by invoking close() method Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.
Java-ohjelma, joka selittää PipedInputStream-luokkamenetelmien toiminnan: Java // Java program illustrating the working of PipedInputStream // connect() read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) // close() available() import java.io.* ; public class NewClass { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException { PipedInputStream geek_input = new PipedInputStream (); PipedOutputStream geek_output = new PipedOutputStream (); try { // Use of connect() : connecting geek_input with geek_output geek_input . connect ( geek_output ); geek_output . write ( 71 ); geek_output . write ( 69 ); geek_output . write ( 69 ); geek_output . write ( 75 ); geek_output . write ( 83 ); // Use of available() : System . out . println ( 'Use of available() : ' + geek_input . available ()); // Use of read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) : byte [] buffer = new byte [ 5 ] ; // destination 'buffer' geek_input . read ( buffer 0 5 ); String str = new String ( buffer ); System . out . println ( 'Using read(buffer offset maxlen) : ' + str ); // USe of close() method : System . out . println ( 'Closing the stream' ); geek_input . close (); } catch ( IOException except ) { except . printStackTrace (); } } } Lähtö: Use of available() : 5 Using read(buffer offset maxlen) : GEEKS Closing the stream
Next Article: Java.io.PipedOutputStream-luokka Javassa Luo tietokilpailu
Top Artikkelit
Luokka
Mielenkiintoisia Artikkeleita

 Putket IO tarjoaa linkin kahden JVM:ssä samanaikaisesti käynnissä olevan säikeen välillä. Joten putkia käytetään sekä lähteenä että määränpäänä.
Putket IO tarjoaa linkin kahden JVM:ssä samanaikaisesti käynnissä olevan säikeen välillä. Joten putkia käytetään sekä lähteenä että määränpäänä.