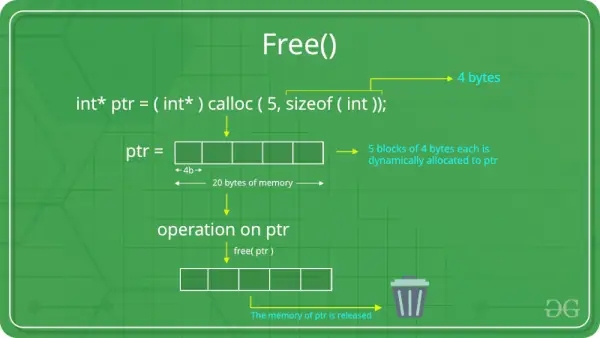
Trabajar con archivos zip en Python

Este artículo explica cómo se pueden realizar varias operaciones en un archivo zip usando un programa Python simple. ¿Qué es un archivo zip? ZIP es un formato de archivo que admite la compresión de datos sin pérdidas. Por compresión sin pérdidas queremos decir que el algoritmo de compresión permite reconstruir perfectamente los datos originales a partir de los datos comprimidos. Por lo tanto, un archivo ZIP es un archivo único que contiene uno o más archivos comprimidos y ofrece una forma ideal de reducir el tamaño de archivos grandes y mantener juntos los archivos relacionados. ¿Por qué necesitamos archivos zip?  Intentemos comprender el código anterior en partes:
Intentemos comprender el código anterior en partes:  Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python
Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python  Intentemos comprender el código anterior dividiéndolo en fragmentos:
Intentemos comprender el código anterior dividiéndolo en fragmentos: 
- Para reducir los requisitos de almacenamiento.
1. Extraer un archivo zip
Python # importing required modules from zipfile import ZipFile # specifying the zip file name file_name = 'my_python_files.zip' # opening the zip file in READ mode with ZipFile ( file_name 'r' ) as zip : # printing all the contents of the zip file zip . printdir () # extracting all the files print ( 'Extracting all the files now...' ) zip . extractall () print ( 'Done!' )
The above program extracts a zip file named 'my_python_files.zip' in the same directory as of this python script. The output of above program may look like this:  Intentemos comprender el código anterior en partes:
Intentemos comprender el código anterior en partes: -
from zipfile import ZipFile
ZipFile is a class of zipfile module for reading and writing zip files. Here we import only class ZipFile from zipfile module. -
with ZipFile(file_name 'r') as zip:
Here a ZipFile object is made by calling ZipFile constructor which accepts zip file name and mode parameters. We create a ZipFile object in LEER modo y nombrarlo como cremallera . -
zip.printdir()
imprimirdir() El método imprime una tabla de contenido para el archivo. -
zip.extractall()
extraer todo() El método extraerá todo el contenido del archivo zip al directorio de trabajo actual. También puedes llamar extracto() method to extract any file by specifying its path in the zip file. For example:zip.extract('python_files/python_wiki.txt')This will extract only the specified file. If you want to read some specific file you can go like this:data = zip.read(name_of_file_to_read)
2. Escribir en un archivo zip
Considere un directorio (carpeta) con el siguiente formato: Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python
Here we will need to crawl the whole directory and its sub-directories in order to get a list of all file paths before writing them to a zip file. The following program does this by crawling the directory to be zipped: Python # importing required modules from zipfile import ZipFile import os def get_all_file_paths ( directory ): # initializing empty file paths list file_paths = [] # crawling through directory and subdirectories for root directories files in os . walk ( directory ): for filename in files : # join the two strings in order to form the full filepath. filepath = os . path . join ( root filename ) file_paths . append ( filepath ) # returning all file paths return file_paths def main (): # path to folder which needs to be zipped directory = './python_files' # calling function to get all file paths in the directory file_paths = get_all_file_paths ( directory ) # printing the list of all files to be zipped print ( 'Following files will be zipped:' ) for file_name in file_paths : print ( file_name ) # writing files to a zipfile with ZipFile ( 'my_python_files.zip' 'w' ) as zip : # writing each file one by one for file in file_paths : zip . write ( file ) print ( 'All files zipped successfully!' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
The output of above program looks like this:  Intentemos comprender el código anterior dividiéndolo en fragmentos:
Intentemos comprender el código anterior dividiéndolo en fragmentos: -
def get_all_file_paths(directory): file_paths = [] for root directories files in os.walk(directory): for filename in files: filepath = os.path.join(root filename) file_paths.append(filepath) return file_paths
First of all to get all file paths in our directory we have created this function which uses the os.walk() rutas_archivo . Al final devolvemos todas las rutas de los archivos. -
file_paths = get_all_file_paths(directory)
Here we pass the directory to be zipped to the función y obtener una lista que contiene todas las rutas de archivos. -
with ZipFile('my_python_files.zip''w') as zip:Here we create a ZipFile object in WRITE mode this time. -
for file in file_paths: zip.write(file)
Here we write all the files to the zip file one by one using escribir método.
3. Obtener toda la información sobre un archivo zip
Python # importing required modules from zipfile import ZipFile import datetime # specifying the zip file name file_name = 'example.zip' # opening the zip file in READ mode with ZipFile ( file_name 'r' ) as zip : for info in zip . infolist (): print ( info . filename ) print ( ' t Modified: t ' + str ( datetime . datetime ( * info . date_time ))) print ( ' t System: tt ' + str ( info . create_system ) + '(0 = Windows 3 = Unix)' ) print ( ' t ZIP version: t ' + str ( info . create_version )) print ( ' t Compressed: t ' + str ( info . compress_size ) + ' bytes' ) print ( ' t Uncompressed: t ' + str ( info . file_size ) + ' bytes' )
The output of above program may look like this: 
for info in zip.infolist():Here infolista() El método crea una instancia de Información postal clase que contiene toda la información sobre el archivo zip. Podemos acceder a toda la información, como la fecha de la última modificación de los archivos, los nombres de los archivos, el sistema en el que se crearon los archivos, la versión zip, el tamaño de los archivos en forma comprimida y sin comprimir, etc. Este artículo es una contribución de Nikhil Kumar . Crear cuestionario