Función free() en la biblioteca C con ejemplos
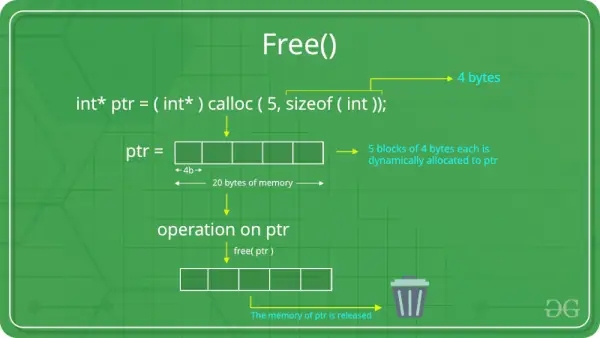
El función gratuita () en C se utiliza para liberar o desasignar la memoria asignada dinámicamente y ayuda a reducir el desperdicio de memoria. El C libre() La función no se puede utilizar para liberar la memoria asignada estáticamente (por ejemplo, variables locales) o la memoria asignada en la pila. Solo se puede utilizar para desasignar la memoria del montón previamente asignada mediante las funciones malloc(), calloc() y realloc().
La función free() está definida dentro archivo de cabecera.

Función C libre()
Sintaxis de la función free() en C
void free (void * ptr );
Parámetros
- ptr es el puntero al bloque de memoria que debe liberarse o desasignarse.
Valor de retorno
- La función free() no devuelve ningún valor.
Ejemplos de gratis()
Ejemplo 1:
El siguiente programa en C ilustra el uso de la calloc() función para asignar memoria dinámicamente y gratis() función para liberar esa memoria.
C
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using calloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> > // This pointer ptr will hold the> > // base address of the block created> > int> * ptr;> > int> n = 5;> > // Get the number of elements for the array> > printf> (> 'Enter number of Elements: %d
'> , n);> > scanf> (> '%d'> , &n);> > // Dynamically allocate memory using calloc()> > ptr = (> int> *)> calloc> (n,> sizeof> (> int> ));> > // Check if the memory has been successfully> > // allocated by calloc() or not> > if> (ptr == NULL) {> > printf> (> 'Memory not allocated
'> );> > exit> (0);> > }> > // Memory has been Successfully allocated using calloc()> > printf> (> 'Successfully allocated the memory using '> > 'calloc().
'> );> > // Free the memory> > free> (ptr);> > printf> (> 'Calloc Memory Successfully freed.'> );> > return> 0;> }> |
Producción
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using calloc(). Calloc Memory Successfully freed.
Ejemplo 2:
El siguiente programa en C ilustra el uso de la malloc() función para asignar memoria dinámicamente y gratis() función para liberar esa memoria.
C
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using malloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> > // This pointer ptr will hold the> > // base address of the block created> > int> * ptr;> > int> n = 5;> > // Get the number of elements for the array> > printf> (> 'Enter number of Elements: %d
'> , n);> > scanf> (> '%d'> , &n);> > // Dynamically allocate memory using malloc()> > ptr = (> int> *)> malloc> (n *> sizeof> (> int> ));> > // Check if the memory has been successfully> > // allocated by malloc() or not> > if> (ptr == NULL) {> > printf> (> 'Memory not allocated
'> );> > exit> (0);> > }> > // Memory has been Successfully allocated using malloc()> > printf> (> 'Successfully allocated the memory using '> > 'malloc().
'> );> > // Free the memory> > free> (ptr);> > printf> (> 'Malloc Memory Successfully freed.'> );> > return> 0;> }> |
Producción
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using malloc(). Malloc Memory Successfully freed.