Reverse-Delete-Algorithmus für Minimum Spanning Tree
 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; } Der Reverse-Delete-Algorithmus ist eng damit verbunden Kruskals Algorithmus . Was wir im Kruskal-Algorithmus tun, ist: Kanten nach aufsteigender Reihenfolge ihrer Gewichte sortieren. Nach dem Sortieren wählen wir die Kanten nacheinander in aufsteigender Reihenfolge aus. Wir beziehen die aktuell ausgewählte Kante mit ein, wenn wir diese in den Spanning Tree aufnehmen und keinen Zyklus bilden, bis es V-1 Kanten im Spanning Tree gibt, wobei V = Anzahl der Scheitelpunkte ist.
Im Reverse-Delete-Algorithmus sortieren wir alle Kanten ein abnehmend Reihenfolge ihrer Gewichte. Nach dem Sortieren wählen wir die Kanten nacheinander in absteigender Reihenfolge aus. Wir Aktuelle ausgewählte Kante einbeziehen, wenn das Ausschließen der aktuellen Kante zu einer Verbindungsunterbrechung im aktuellen Diagramm führt . Die Hauptidee besteht darin, die Kante zu löschen, wenn ihre Löschung nicht zur Trennung des Diagramms führt.
Der Algorithmus:
- Sortieren Sie alle Kanten des Diagramms in nicht aufsteigender Reihenfolge der Kantengewichte.
- Initialisieren Sie MST als Originaldiagramm und entfernen Sie zusätzliche Kanten mit Schritt 3.
- Wählen Sie die Kante mit dem höchsten Gewicht aus den verbleibenden Kanten aus und Überprüfen Sie, ob durch das Löschen der Kante die Verbindung zum Diagramm unterbrochen wird oder nicht .
Bei Verbindungsabbrüchen löschen wir die Kante nicht.
Andernfalls löschen wir die Kante und fahren fort.
Illustration:
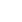
Lassen Sie es uns anhand des folgenden Beispiels verstehen:
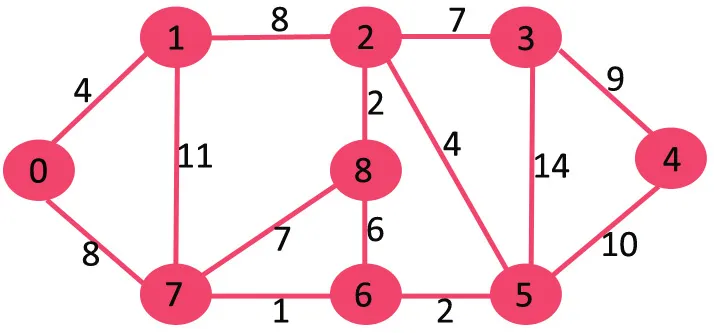
Wenn wir die höchste Gewichtungskante der Gewichtung 14 löschen, wird die Verbindung nicht getrennt, also entfernen wir sie.
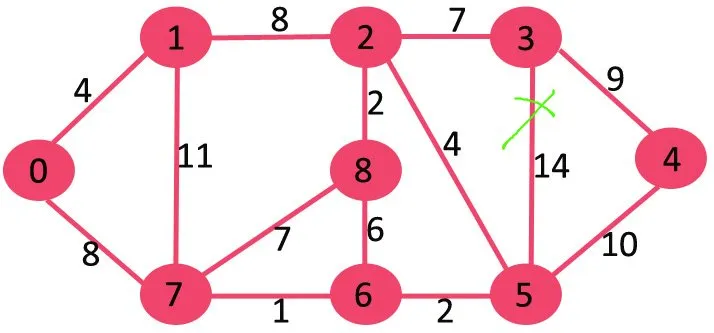
Als nächstes löschen wir 11, da durch das Löschen die Verbindung zum Diagramm nicht unterbrochen wird.
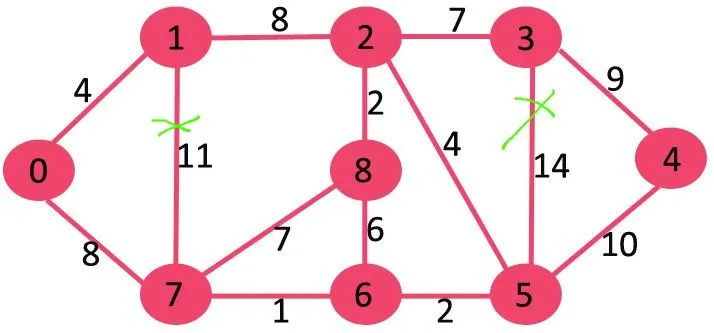
Als nächstes löschen wir 10, da durch das Löschen die Verbindung zum Diagramm nicht unterbrochen wird.

Als nächstes kommt 9. Wir können 9 nicht löschen, da das Löschen zu einer Verbindungsunterbrechung führt.

Wir machen auf diese Weise weiter und die folgenden Kanten bleiben im endgültigen MST.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
Notiz : Bei gleichgewichtigen Kanten können wir jede beliebige Kante mit gleichgewichtigen Kanten auswählen.
Empfohlene Praxis Reverse-Delete-Algorithmus für Minimum Spanning Tree Probieren Sie es aus!Durchführung:
C++Java// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #includeusing namespace std ; // Creating shortcut for an integer pair typedef pair < int int > iPair ; // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { int V ; // No. of vertices list < int > * adj ; vector < pair < int iPair > > edges ; void DFS ( int v bool visited []); public : Graph ( int V ); // Constructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge ( int u int v int w ); // Returns true if graph is connected bool isConnected (); void reverseDeleteMST (); }; Graph :: Graph ( int V ) { this -> V = V ; adj = new list < int > [ V ]; } void Graph :: addEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ]. push_back ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ]. push_back ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . push_back ({ w { u v }}); } void Graph :: DFS ( int v bool visited []) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex list < int >:: iterator i ; for ( i = adj [ v ]. begin (); i != adj [ v ]. end (); ++ i ) if ( ! visited [ * i ]) DFS ( * i visited ); } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false bool Graph :: isConnected () { bool visited [ V ]; memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not void Graph :: reverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost sort ( edges . begin () edges . end ()); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST cout < < 'Edges in MST n ' ; // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . size () -1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges [ i ]. second . first ; int v = edges [ i ]. second . second ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ]. remove ( v ); adj [ v ]. remove ( u ); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( isConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ]. push_back ( v ); adj [ v ]. push_back ( u ); // This edge is part of MST cout < < '(' < < u < < ' ' < < v < < ') n ' ; mst_wt += edges [ i ]. first ; } } cout < < 'Total weight of MST is ' < < mst_wt ; } // Driver code int main () { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; Graph g ( V ); // making above shown graph g . addEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . addEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . addEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . addEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . addEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . addEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . addEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . addEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . addEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . addEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . addEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . addEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . addEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . addEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . reverseDeleteMST (); return 0 ; } Python3// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.* ; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable < Edge > { int u v w ; Edge ( int u int v int w ) { this . u = u ; this . w = w ; this . v = v ; } public int compareTo ( Edge other ) { return ( this . w - other . w ); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V ; // No. of vertices private List < Integer >[] adj ; private List < Edge > edges ; @SuppressWarnings ({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG ( int v ) // Constructor { V = v ; adj = new ArrayList [ v ] ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < v ; i ++ ) adj [ i ] = new ArrayList < Integer > (); edges = new ArrayList < Edge > (); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ] . add ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ] . add ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . add ( new Edge ( u v w )); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS ( int v boolean [] visited ) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for ( int i : adj [ v ] ) { if ( ! visited [ i ] ) DFS ( i visited ); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected () { boolean [] visited = new boolean [ V ] ; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) { if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; } return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections . sort ( edges ); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST System . out . println ( 'Edges in MST' ); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . size () - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges . get ( i ). u ; int v = edges . get ( i ). v ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ] . remove ( adj [ u ] . indexOf ( v )); adj [ v ] . remove ( adj [ v ] . indexOf ( u )); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( IsConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ] . add ( v ); adj [ v ] . add ( u ); // This edge is part of MST System . out . println ( '(' + u + ' ' + v + ')' ); mst_wt += edges . get ( i ). w ; } } System . out . println ( 'Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; GFG g = new GFG ( V ); // making above shown graph g . AddEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . AddEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . AddEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . AddEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . ReverseDeleteMST (); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_DeyC## Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph : def __init__ ( self v ): # No. of vertices self . v = v self . adj = [ 0 ] * v self . edges = [] for i in range ( v ): self . adj [ i ] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge ( self u : int v : int w : int ): self . adj [ u ] . append ( v ) # Add w to v’s list. self . adj [ v ] . append ( u ) # Add w to v’s list. self . edges . append (( w ( u v ))) def dfs ( self v : int visited : list ): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self . adj [ v ]: if not visited [ i ]: self . dfs ( i visited ) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected ( self ): visited = [ False ] * self . v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self . dfs ( 0 visited ) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range ( 1 self . v ): if not visited [ i ]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST ( self ): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self . edges . sort ( key = lambda a : a [ 0 ]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print ( 'Edges in MST' ) # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range ( len ( self . edges ) - 1 - 1 - 1 ): u = self . edges [ i ][ 1 ][ 0 ] v = self . edges [ i ][ 1 ][ 1 ] # Remove edge from undirected graph self . adj [ u ] . remove ( v ) self . adj [ v ] . remove ( u ) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self . connected () == False : self . adj [ u ] . append ( v ) self . adj [ v ] . append ( u ) # This edge is part of MST print ( '( %d %d )' % ( u v )) mst_wt += self . edges [ i ][ 0 ] print ( 'Total weight of MST is' mst_wt ) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph ( V ) # making above shown graph g . addEdge ( 0 1 4 ) g . addEdge ( 0 7 8 ) g . addEdge ( 1 2 8 ) g . addEdge ( 1 7 11 ) g . addEdge ( 2 3 7 ) g . addEdge ( 2 8 2 ) g . addEdge ( 2 5 4 ) g . addEdge ( 3 4 9 ) g . addEdge ( 3 5 14 ) g . addEdge ( 4 5 10 ) g . addEdge ( 5 6 2 ) g . addEdge ( 6 7 1 ) g . addEdge ( 6 8 6 ) g . addEdge ( 7 8 7 ) g . reverseDeleteMST () # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552JavaScript// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable < Edge > { public int u v w ; public Edge ( int u int v int w ) { this . u = u ; this . v = v ; this . w = w ; } public int CompareTo ( Edge other ) { return this . w . CompareTo ( other . w ); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V ; // No. of vertices private List < int > [] adj ; private List < Edge > edges ; public Graph ( int v ) // Constructor { V = v ; adj = new List < int > [ v ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < v ; i ++ ) adj [ i ] = new List < int > (); edges = new List < Edge > (); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge ( int u int v int w ) { adj [ u ]. Add ( v ); // Add w to v’s list. adj [ v ]. Add ( u ); // Add w to v’s list. edges . Add ( new Edge ( u v w )); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS ( int v bool [] visited ) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited [ v ] = true ; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach ( int i in adj [ v ]) { if ( ! visited [ i ]) DFS ( i visited ); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected () { bool [] visited = new bool [ V ]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS ( 0 visited ); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for ( int i = 1 ; i < V ; i ++ ) { if ( visited [ i ] == false ) return false ; } return true ; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST () { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges . Sort (); int mst_wt = 0 ; // Initialize weight of MST Console . WriteLine ( 'Edges in MST' ); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for ( int i = edges . Count - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i -- ) { int u = edges [ i ]. u ; int v = edges [ i ]. v ; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj [ u ]. Remove ( v ); adj [ v ]. Remove ( u ); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if ( IsConnected () == false ) { adj [ u ]. Add ( v ); adj [ v ]. Add ( u ); // This edge is part of MST Console . WriteLine ( '({0} {1})' u v ); mst_wt += edges [ i ]. w ; } } Console . WriteLine ( 'Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt ); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main ( string [] args ) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9 ; Graph g = new Graph ( V ); // making above shown graph g . AddEdge ( 0 1 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 0 7 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 2 8 ); g . AddEdge ( 1 7 11 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 3 7 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 8 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 2 5 4 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 4 9 ); g . AddEdge ( 3 5 14 ); g . AddEdge ( 4 5 10 ); g . AddEdge ( 5 6 2 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 7 1 ); g . AddEdge ( 6 8 6 ); g . AddEdge ( 7 8 7 ); g . ReverseDeleteMST (); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
AusgabeEdges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37Zeitkomplexität: O((E*(V+E)) + E log E) wobei E die Anzahl der Kanten ist.
Raumkomplexität: O(V+E) Dabei ist V die Anzahl der Eckpunkte und E die Anzahl der Kanten. Wir verwenden die Adjazenzliste zum Speichern des Diagramms, daher benötigen wir Platz proportional zu O(V+E).
Hinweise:
- Die obige Implementierung ist eine einfache/naive Implementierung des Reverse-Delete-Algorithmus und kann auf O(E log V (log log V) optimiert werden. 3 ) [Quelle : Eine Woche ]. Diese optimierte Zeitkomplexität ist jedoch immer noch geringer als Prim Und Kruskal Algorithmen für MST.
- Die obige Implementierung ändert das ursprüngliche Diagramm. Wir können eine Kopie des Diagramms erstellen, wenn das Originaldiagramm beibehalten werden muss.
Quiz erstellen