Petersons Algorithmus für gegenseitigen Ausschluss | Set 2 (CPU-Zyklen und Speicherbegrenzung)
Problem: Bei 2 Prozessen i und j müssen Sie ein Programm schreiben, das den gegenseitigen Ausschluss zwischen den beiden ohne zusätzliche Hardwareunterstützung gewährleisten kann.
Verschwendung von CPU-Taktzyklen
Laienhaft ausgedrückt endete ein Thread, der darauf wartete, an die Reihe zu kommen, in einer langen While-Schleife, die die Bedingung millionenfach pro Sekunde testete und so unnötige Berechnungen durchführte. Es gibt eine bessere Art zu warten und sie heißt 'Ertrag' .
Um zu verstehen, was es tut, müssen wir uns eingehend mit der Funktionsweise des Prozessplaners unter Linux befassen. Die hier erwähnte Idee ist eine vereinfachte Version des Schedulers, die tatsächliche Implementierung weist viele Komplikationen auf.
Betrachten Sie das folgende Beispiel
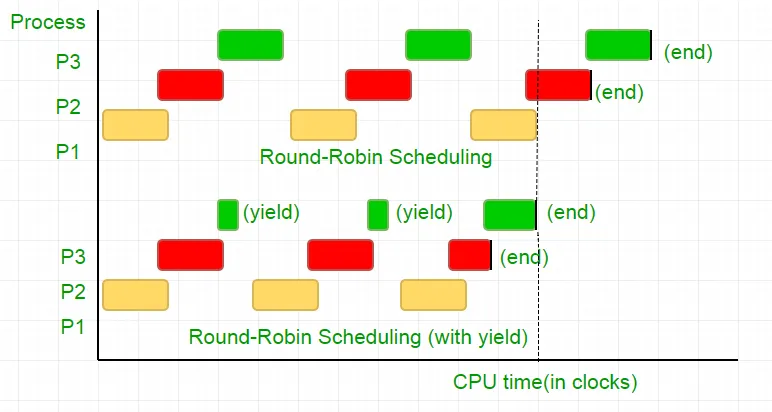
Es gibt drei Prozesse P1, P2 und P3. Der Prozess P3 verfügt über eine While-Schleife, die der in unserem Code ähnelt und nicht so nützliche Berechnungen durchführt, und er existiert nur dann aus der Schleife, wenn P2 seine Ausführung beendet hat. Der Scheduler stellt sie alle in eine Round-Robin-Warteschlange. Angenommen, die Taktrate des Prozessors beträgt 1.000.000/s und er weist jedem Prozess in jeder Iteration 100 Takte zu. Dann wird zuerst P1 für 100 Takte (0,0001 Sekunden) ausgeführt, dann P2 (0,0001 Sekunden), gefolgt von P3 (0,0001 Sekunden). Da es keine weiteren Prozesse mehr gibt, wiederholt sich dieser Zyklus, bis P2 endet, gefolgt von der Ausführung von P3 und schließlich seiner Beendigung.
Dies ist eine völlige Verschwendung der 100 CPU-Taktzyklen. Um dies zu vermeiden, geben wir gegenseitig die CPU-Zeitscheibe auf, d. h. Yield, wodurch diese Zeitscheibe im Wesentlichen endet und der Scheduler den nächsten auszuführenden Prozess aufnimmt. Jetzt testen wir einmal unseren Zustand und geben dann die CPU ab. Wenn man bedenkt, dass unser Test 25 Taktzyklen dauert, sparen wir 75 % unserer Berechnungen in einem Zeitabschnitt. Um es grafisch auszudrücken

Wenn man bedenkt, dass die Prozessortaktrate 1 MHz beträgt, ist das eine Menge Ersparnis!
Verschiedene Distributionen bieten unterschiedliche Funktionen, um diese Funktionalität zu erreichen. Linux bietet sched_yield() .
void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] = 1 ; turn = 1 - self ; while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Only change is the addition of // sched_yield() call sched_yield (); }
Erinnerungszaun.
Der Code im früheren Tutorial hat möglicherweise auf den meisten Systemen funktioniert, war jedoch nicht 100 % korrekt. Die Logik war perfekt, aber die meisten modernen CPUs verwenden Leistungsoptimierungen, die zu einer Ausführung außerhalb der Reihenfolge führen können. Diese Neuordnung von Speicheroperationen (Laden und Speichern) bleibt innerhalb eines einzelnen Ausführungsthreads normalerweise unbemerkt, kann jedoch zu unvorhersehbarem Verhalten in gleichzeitigen Programmen führen.
Betrachten Sie dieses Beispiel
while ( f == 0 ); // Memory fence required here print x ;
Im obigen Beispiel betrachtet der Compiler die beiden Anweisungen als unabhängig voneinander und versucht daher, die Codeeffizienz zu erhöhen, indem er sie neu anordnet, was bei gleichzeitigen Programmen zu Problemen führen kann. Um dies zu vermeiden, platzieren wir einen Speicherzaun, um dem Compiler einen Hinweis auf die mögliche Beziehung zwischen den Anweisungen über die Barriere hinweg zu geben.
Also die Reihenfolge der Aussagen
flag[self] = 1;
turn = 1-selbst;
while (Prüfung der Turn-Bedingung)
Ertrag();
muss genau gleich sein, damit die Sperre funktioniert, andernfalls kommt es zu einem Deadlock-Zustand.
Um dies sicherzustellen, stellen Compiler eine Anweisung bereit, die die Reihenfolge von Anweisungen über diese Barriere hinweg verhindert. Im Falle von gcc ist es __sync_synchronize() .
So wird der geänderte Code
Vollständige Implementierung in C:
// Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp // Use below command to compile: // g++ -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include std :: atomic < int > flag [ 2 ]; std :: atomic < int > turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. std :: atomic_thread_fence ( std :: memory_order_seq_cst ); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. std :: this_thread :: yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; std :: cout < < 'Thread Entered: ' < < self < < std :: endl ; lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) std :: thread t1 ( func 0 ); std :: thread t2 ( func 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); std :: cout < < 'Actual Count: ' < < ans < < ' | Expected Count: ' < < MAX * 2 < < std :: endl ; return 0 ; }
C // Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c // Use below command to compile: // gcc -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include 'mythreads.h' int flag [ 2 ]; int turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. __sync_synchronize (); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. sched_yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void * func ( void * s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = ( int * ) s ; printf ( 'Thread Entered: %d n ' self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { pthread_t p1 p2 ; // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) Pthread_create ( & p1 NULL func ( void * ) 0 ); Pthread_create ( & p2 NULL func ( void * ) 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. Pthread_join ( p1 NULL ); Pthread_join ( p2 NULL ); printf ( 'Actual Count: %d | Expected Count:' ' %d n ' ans MAX * 2 ); return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger ; public class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static AtomicInteger [] flag = new AtomicInteger [ 2 ] ; static AtomicInteger turn = new AtomicInteger (); static final int MAX = 1000000000 ; static int ans = 0 ; static void lockInit () { flag [ 0 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 1 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 0 ] . set ( 0 ); flag [ 1 ] . set ( 0 ); turn . set ( 0 ); } static void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 1 ); turn . set ( 1 - self ); // Memory fence to prevent the reordering of instructions beyond this barrier. // In Java volatile variables provide this guarantee implicitly. // No direct equivalent to atomic_thread_fence is needed. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] . get () == 1 && turn . get () == 1 - self ) Thread . yield (); } static void unlock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 0 ); } static void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; System . out . println ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Initialize the lock lockInit (); // Create two threads (both run func) Thread t1 = new Thread (() -> func ( 0 )); Thread t2 = new Thread (() -> func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); try { // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } System . out . println ( 'Actual Count: ' + ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + MAX * 2 ); } }
Python import threading flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 MAX = 10 ** 9 ans = 0 def lock_init (): # This function initializes the lock by resetting the flags and turn. global flag turn flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 def lock ( self ): # This function is executed before entering the critical section. It sets the flag for the current thread and gives the turn to the other thread. global flag turn flag [ self ] = 1 turn = 1 - self while flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 and turn == 1 - self : pass def unlock ( self ): # This function is executed after leaving the critical section. It resets the flag for the current thread. global flag flag [ self ] = 0 def func ( s ): # This function is executed by each thread. It locks the critical section increments the shared variable and then unlocks the critical section. global ans self = s print ( f 'Thread Entered: { self } ' ) lock ( self ) for _ in range ( MAX ): ans += 1 unlock ( self ) def main (): # This is the main function where the threads are created and started. lock_init () t1 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 0 )) t2 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 1 )) t1 . start () t2 . start () t1 . join () t2 . join () print ( f 'Actual Count: { ans } | Expected Count: { MAX * 2 } ' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static flag = [ 0 0 ]; static turn = 0 ; static MAX = 1000000000 ; static ans = 0 ; // Function to acquire the lock static async lock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 1 ; PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn = 1 - self ; // Asynchronous loop with a small delay to yield while ( PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn == 1 - self ) { await new Promise ( resolve => setTimeout ( resolve 0 )); } } // Function to release the lock static unlock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // Function representing the critical section static func ( s ) { let i = 0 ; let self = s ; console . log ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); // Lock the critical section PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . lock ( self ). then (() => { // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX ; i ++ ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans ++ ; } // Release the lock PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . unlock ( self ); }); } // Main function static main () { // Create two threads (both run func) const t1 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 0 )); const t2 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); // Wait for the threads to end. setTimeout (() => { console . log ( 'Actual Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX * 2 ); } 1000 ); // Delay for a while to ensure threads finish } } // Define a simple Thread class for simulation class Thread { constructor ( func ) { this . func = func ; } start () { this . func (); } } // Run the main function PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . main ();
C++ // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include // Function to lock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was locked successfully } // Function to unlock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was unlocked successfully } // Function to create a pthread void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was created successfully } // Function to join a pthread void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was joined successfully } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
C // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert // statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
Python import threading import ctypes # Function to lock a thread lock def Thread_lock ( lock ): lock . acquire () # Acquire the lock # No need for assert in Python acquire will raise an exception if it fails # Function to unlock a thread lock def Thread_unlock ( lock ): lock . release () # Release the lock # No need for assert in Python release will raise an exception if it fails # Function to create a thread def Thread_create ( target args = ()): thread = threading . Thread ( target = target args = args ) thread . start () # Start the thread # No need for assert in Python thread.start() will raise an exception if it fails # Function to join a thread def Thread_join ( thread ): thread . join () # Wait for the thread to finish # No need for assert in Python thread.join() will raise an exception if it fails
Ausgabe:
Thread Entered: 1
Thread Entered: 0
Actual Count: 2000000000 | Expected Count: 2000000000