Hierholzers algoritme for rettet graf

Givet en rettet Eulersk graf er opgaven at udskrive en Euler kredsløb . Et Euler-kredsløb er en sti, der krydser hver kant af en graf nøjagtig én gang, og stien ender på startpunktet.
Note: Den givne graf indeholder et Euler-kredsløb.
Eksempel:
Input : Styret graf

Produktion: 0 3 4 0 2 1 0
Forudsætninger:
- Vi har diskuteret problem med at finde ud af, om en given graf er Eulersk eller ej for en udirigeret graf
- Betingelser for Eulersk kredsløb i en rettet Grpag: (1) Alle toppunkter tilhører en enkelt stærkt forbundet komponent. (2) Alle hjørner har samme in-grad og ud-grad. Bemærk, at for en urettet graf er betingelsen anderledes (alle hjørner har lige grad)
Nærme sig:
- Vælg et hvilket som helst startpunkt v og følg et spor af kanter fra det toppunkt, indtil du vender tilbage til v. Det er ikke muligt at sidde fast ved noget andet toppunkt end v, fordi indegrad og udgrad af hvert toppunkt skal være ens, når sporet går ind i et andet toppunkt w der skal være en ubrugt kant, der forlader w. Turen dannet på denne måde er en lukket tur, men dækker muligvis ikke alle toppunkter og kanter på den indledende graf.
- Så længe der eksisterer et toppunkt u, der hører til den aktuelle tur, men som har tilstødende kanter, som ikke er en del af turen, skal du starte et andet spor fra u følger ubrugte kanter, indtil du vender tilbage til u, og forener turen dannet på denne måde til den forrige tur.
Illustration:
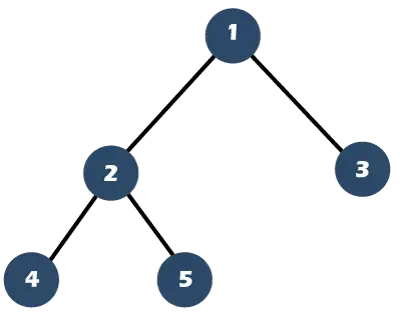
Tag et eksempel på ovenstående graf med 5 noder: adj = {{2 3} {0} {1} {4} {0}}.
- Start ved toppunkt 0 :
- Nuværende sti: [0]
- Kredsløb: []
- Toppunkt 0 → 3 :
- Nuværende sti: [0 3]
- Kredsløb: []
- Toppunkt 3 → 4 :
- Nuværende sti: [0 3 4]
- Kredsløb: []
- Toppunkt 4 → 0 :
- Nuværende sti: [0 3 4 0]
- Kredsløb: []
- Toppunkt 0 → 2 :
- Nuværende sti: [0 3 4 0 2]
- Kredsløb: []
- Toppunkt 2 → 1 :
- Aktuel sti: [0 3 4 0 2 1]
- Kredsløb: []
- Toppunkt 1 → 0 :
- Aktuel sti: [0 3 4 0 2 1 0]
- Kredsløb: []
- Gå tilbage til toppunkt 0 : Tilføj 0 til kredsløb.
- Aktuel sti: [0 3 4 0 2 1]
- Kredsløb: [0]
- Tilbage til toppunkt 1 : Tilføj 1 til kredsløb.
- Nuværende sti: [0 3 4 0 2]
- Kredsløb: [0 1]
- Tilbage til toppunkt 2 : Tilføj 2 til kredsløb.
- Nuværende sti: [0 3 4 0]
- Kredsløb: [0 1 2]
- Gå tilbage til toppunkt 0 : Tilføj 0 til kredsløb.
- Nuværende sti: [0 3 4]
- Kredsløb: [0 1 2 0]
- Tilbage til toppunkt 4 : Tilføj 4 til kredsløb.
- Nuværende sti: [0 3]
- Kredsløb: [0 1 2 0 4]
- Tilbage til toppunkt 3 : Tilføj 3 til kredsløb.
- Nuværende sti: [0]
- Kredsløb: [0 1 2 0 4 3]
- Gå tilbage til toppunkt 0 : Tilføj 0 til kredsløb.
- Nuværende sti: []
- Kredsløb: [0 1 2 0 4 3 0]
Nedenfor er implementeringen af ovenstående tilgang:
C++ // C++ program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm #include using namespace std ; // Function to print Eulerian circuit vector < int > printCircuit ( vector < vector < int >> & adj ) { int n = adj . size (); if ( n == 0 ) return {}; // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 vector < int > currPath ; currPath . push_back ( 0 ); // list to store final circuit vector < int > circuit ; while ( currPath . size () > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath [ currPath . size () - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. size () > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj [ currNode ]. back (); adj [ currNode ]. pop_back (); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . push_back ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . push_back ( currPath . back ()); currPath . pop_back (); } } // reverse the result vector reverse ( circuit . begin () circuit . end ()); return circuit ; } int main () { vector < vector < int >> adj = {{ 2 3 } { 0 } { 1 } { 4 } { 0 }}; vector < int > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( auto v : ans ) cout < < v < < ' ' ; cout < < endl ; return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm import java.util.* ; class GfG { // Function to print Eulerian circuit static List < Integer > printCircuit ( List < List < Integer >> adj ) { int n = adj . size (); if ( n == 0 ) return new ArrayList <> (); // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 List < Integer > currPath = new ArrayList <> (); currPath . add ( 0 ); // list to store final circuit List < Integer > circuit = new ArrayList <> (); while ( currPath . size () > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath . get ( currPath . size () - 1 ); // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj . get ( currNode ). get ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () - 1 ); adj . get ( currNode ). remove ( adj . get ( currNode ). size () - 1 ); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . add ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . add ( currPath . get ( currPath . size () - 1 )); currPath . remove ( currPath . size () - 1 ); } } // reverse the result vector Collections . reverse ( circuit ); return circuit ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { List < List < Integer >> adj = new ArrayList <> (); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 2 3 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 0 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 1 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 4 ))); adj . add ( new ArrayList <> ( Arrays . asList ( 0 ))); List < Integer > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( int v : ans ) System . out . print ( v + ' ' ); System . out . println (); } }
Python # Python program to print Eulerian circuit in given # directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm # Function to print Eulerian circuit def printCircuit ( adj ): n = len ( adj ) if n == 0 : return [] # Maintain a stack to keep vertices # We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 currPath = [ 0 ] # list to store final circuit circuit = [] while len ( currPath ) > 0 : currNode = currPath [ - 1 ] # If there's remaining edge in adjacency list # of the current vertex if len ( adj [ currNode ]) > 0 : # Find and remove the next vertex that is # adjacent to the current vertex nextNode = adj [ currNode ] . pop () # Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . append ( nextNode ) # back-track to find remaining circuit else : # Remove the current vertex and # put it in the circuit circuit . append ( currPath . pop ()) # reverse the result vector circuit . reverse () return circuit if __name__ == '__main__' : adj = [[ 2 3 ] [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 4 ] [ 0 ]] ans = printCircuit ( adj ) for v in ans : print ( v end = ' ' ) print ()
C# // C# program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GfG { // Function to print Eulerian circuit static List < int > printCircuit ( List < List < int >> adj ) { int n = adj . Count ; if ( n == 0 ) return new List < int > (); // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 List < int > currPath = new List < int > { 0 }; // list to store final circuit List < int > circuit = new List < int > (); while ( currPath . Count > 0 ) { int currNode = currPath [ currPath . Count - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. Count > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex int nextNode = adj [ currNode ][ adj [ currNode ]. Count - 1 ]; adj [ currNode ]. RemoveAt ( adj [ currNode ]. Count - 1 ); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . Add ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . Add ( currPath [ currPath . Count - 1 ]); currPath . RemoveAt ( currPath . Count - 1 ); } } // reverse the result vector circuit . Reverse (); return circuit ; } static void Main ( string [] args ) { List < List < int >> adj = new List < List < int >> { new List < int > { 2 3 } new List < int > { 0 } new List < int > { 1 } new List < int > { 4 } new List < int > { 0 } }; List < int > ans = printCircuit ( adj ); foreach ( int v in ans ) { Console . Write ( v + ' ' ); } Console . WriteLine (); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript program to print Eulerian circuit in given // directed graph using Hierholzer algorithm // Function to print Eulerian circuit function printCircuit ( adj ) { let n = adj . length ; if ( n === 0 ) return []; // Maintain a stack to keep vertices // We can start from any vertex here we start with 0 let currPath = [ 0 ]; // list to store final circuit let circuit = []; while ( currPath . length > 0 ) { let currNode = currPath [ currPath . length - 1 ]; // If there's remaining edge in adjacency list // of the current vertex if ( adj [ currNode ]. length > 0 ) { // Find and remove the next vertex that is // adjacent to the current vertex let nextNode = adj [ currNode ]. pop (); // Push the new vertex to the stack currPath . push ( nextNode ); } // back-track to find remaining circuit else { // Remove the current vertex and // put it in the circuit circuit . push ( currPath . pop ()); } } // reverse the result vector circuit . reverse (); return circuit ; } let adj = [[ 2 3 ] [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 4 ] [ 0 ]]; let ans = printCircuit ( adj ); for ( let v of ans ) { console . log ( v ' ' ); }
Produktion
0 3 4 0 2 1 0
Tidskompleksitet: O(V + E) hvor V er antallet af hjørner og E er antallet af kanter i grafen. Årsagen til dette er, at algoritmen udfører en dybde-først-søgning (DFS) og besøger hvert vertex og hver kant nøjagtigt én gang. Så for hvert hjørne tager det O(1) tid at besøge det, og for hver kant tager det O(1) tid at krydse det.
Rumkompleksitet: O(V + E), da algoritmen bruger en stak til at gemme den aktuelle sti og en liste til at gemme det endelige kredsløb. Den maksimale størrelse af stakken kan i værste fald være V + E, så pladskompleksiteten er O(V + E).
Opret Quiz