Unrolled Linked List | Sada 1 (úvod)
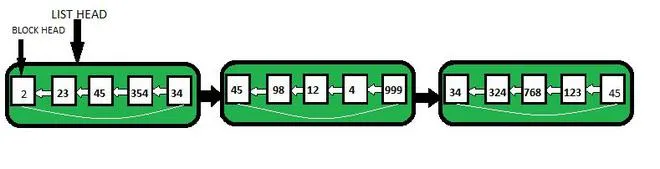
Stejně jako pole a propojený seznam je i rozbalený Linked List lineární datovou strukturou a je variantou propojeného seznamu.
Proč potřebujeme rozbalený propojený seznam?
Jednou z největších výhod spojených seznamů oproti polím je to, že vložení prvku na libovolné místo trvá pouze O(1). Háček je však v tom, že vyhledání prvku v propojeném seznamu trvá O(n). Aby se vyřešil problém vyhledávání, tj. zkrácení času pro vyhledávání prvku, byl navržen koncept rozbalených propojených seznamů. Rozbalený propojený seznam pokrývá výhody pole i propojeného seznamu, protože ve srovnání s jednoduchými propojenými seznamy snižuje nároky na paměť tím, že ukládá více prvků v každém uzlu, a má také výhodu rychlého vkládání a mazání jako u propojeného seznamu.


výhody:
- Kvůli chování mezipaměti je lineární vyhledávání mnohem rychlejší v rozbalených propojených seznamech.
- Ve srovnání s běžným propojeným seznamem vyžaduje méně úložného prostoru pro ukazatele/odkazy.
- Operace, jako je vkládání, mazání a procházení, provádí rychleji než běžné propojené seznamy (protože vyhledávání je rychlejší).
Nevýhody:
- Režie na uzel je poměrně vysoká než u samostatně propojených seznamů. Podívejte se na ukázkový uzel v níže uvedeném kódu
Příklad: Řekněme, že máme 8 prvků, takže sqrt(8)=2,82, což se zaokrouhlí na 3. Každý blok tedy uloží 3 prvky. Pro uložení 8 prvků se tedy vytvoří 3 bloky, z nichž do prvních dvou bloků budou uloženy 3 prvky a do posledního bloku budou uloženy 2 prvky.
Jak se vyhledávání zlepší v rozbalených propojených seznamech?
Vezmeme-li tedy výše uvedený příklad, chceme-li hledat 7. prvek v seznamu, projdeme seznamem bloků k tomu, který obsahuje 7. prvek. Trvá to pouze O(sqrt(n)), protože jsme to našli přes bloky nepřesahující sqrt(n).
Jednoduchá implementace:
Níže uvedený program vytvoří jednoduchý rozbalený propojený seznam se 3 uzly obsahujícími proměnný počet prvků v každém. Prochází také vytvořený seznam.
C++ // C++ program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include using namespace std ; #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public : int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) cout < < n -> array [ i ] < < ' ' ; // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { Node * head = NULL ; Node * second = NULL ; Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; } // This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C // C program to implement unrolled linked list // and traversing it. #include #include #define maxElements 4 // Unrolled Linked List Node struct Node { int numElements ; int array [ maxElements ]; struct Node * next ; }; /* Function to traverse an unrolled linked list and print all the elements*/ void printUnrolledList ( struct Node * n ) { while ( n != NULL ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n -> numElements ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' n -> array [ i ]); // Move to next node n = n -> next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes int main () { struct Node * head = NULL ; struct Node * second = NULL ; struct Node * third = NULL ; // allocate 3 Nodes head = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); second = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); third = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node )); // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) head -> numElements = 3 ; head -> array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head -> array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head -> array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the second Node head -> next = second ; // Let us put some values in second node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second -> numElements = 3 ; second -> array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second -> array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second -> array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second -> next = third ; // Let us put some values in third node (Number // of values must be less than or equal to // maxElement) third -> numElements = 3 ; third -> array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third -> array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third -> array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third -> next = NULL ; printUnrolledList ( head ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static final int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node static class Node { int numElements ; int [] array = new int [ maxElements ] ; Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) System . out . print ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Python3 # Python3 program to implement unrolled # linked list and traversing it. maxElements = 4 # Unrolled Linked List Node class Node : def __init__ ( self ): self . numElements = 0 self . array = [ 0 for i in range ( maxElements )] self . next = None # Function to traverse an unrolled linked list # and print all the elements def printUnrolledList ( n ): while ( n != None ): # Print elements in current node for i in range ( n . numElements ): print ( n . array [ i ] end = ' ' ) # Move to next node n = n . next # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__' : head = None second = None third = None # Allocate 3 Nodes head = Node () second = Node () third = Node () # Let us put some values in second # node (Number of values must be # less than or equal to # maxElement) head . numElements = 3 head . array [ 0 ] = 1 head . array [ 1 ] = 2 head . array [ 2 ] = 3 # Link first Node with the second Node head . next = second # Let us put some values in second node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) second . numElements = 3 second . array [ 0 ] = 4 second . array [ 1 ] = 5 second . array [ 2 ] = 6 # Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third # Let us put some values in third node # (Number of values must be less than # or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 third . array [ 0 ] = 7 third . array [ 1 ] = 8 third . array [ 2 ] = 9 third . next = None printUnrolledList ( head ) # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C# // C# program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. using System ; class GFG { static readonly int maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { public int numElements ; public int [] array = new int [ maxElements ]; public Node next ; }; // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements static void printUnrolledList ( Node n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( int i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) Console . Write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes public static void Main ( String [] args ) { Node head = null ; Node second = null ; Node third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to implement unrolled // linked list and traversing it. const maxElements = 4 ; // Unrolled Linked List Node class Node { constructor () { this . numElements = 0 ; this . array = new Array ( maxElements ); this . next = null ; } } // Function to traverse an unrolled // linked list and print all the elements function printUnrolledList ( n ) { while ( n != null ) { // Print elements in current node for ( var i = 0 ; i < n . numElements ; i ++ ) document . write ( n . array [ i ] + ' ' ); // Move to next node n = n . next ; } } // Program to create an unrolled linked list // with 3 Nodes var head = null ; var second = null ; var third = null ; // Allocate 3 Nodes head = new Node (); second = new Node (); third = new Node (); // Let us put some values in second // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) head . numElements = 3 ; head . array [ 0 ] = 1 ; head . array [ 1 ] = 2 ; head . array [ 2 ] = 3 ; // Link first Node with the // second Node head . next = second ; // Let us put some values in // second node (Number of values // must be less than or equal to // maxElement) second . numElements = 3 ; second . array [ 0 ] = 4 ; second . array [ 1 ] = 5 ; second . array [ 2 ] = 6 ; // Link second Node with the third Node second . next = third ; // Let us put some values in third // node (Number of values must be // less than or equal to maxElement) third . numElements = 3 ; third . array [ 0 ] = 7 ; third . array [ 1 ] = 8 ; third . array [ 2 ] = 9 ; third . next = null ; printUnrolledList ( head ); < /script>
Výstup
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Analýza složitosti:
V tomto článku jsme představili rozbalený seznam a jeho výhody. Také jsme si ukázali, jak seznam procházet. V příštím článku budeme podrobně diskutovat o mazání vložení a hodnotách maxElements/numElements.
Vložení do Unrolled Linked List
Vytvořit kvíz