Petersonův algoritmus pro vzájemné vyloučení | Sada 2 (CPU cykly a paměťový plot)
Problém: Vzhledem k 2 procesu I a J musíte napsat program, který může zaručit vzájemné vyloučení mezi nimi bez jakékoli další hardwarové podpory.
Plýtvání cyklům CPU hodin
V laickém pojmu, když vlákno čekalo na řadu, skončilo dlouhou smyčkou, která testovala stav milionykrát za sekundu, čímž se provedl zbytečný výpočet. Existuje lepší způsob, jak čekat a je to známé jako 'výtěžek' .
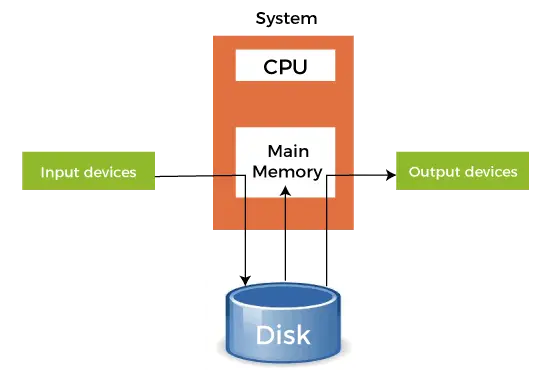
Abychom pochopili, co to dělá, musíme vykopat hluboko do toho, jak plánovač procesů funguje v Linuxu. Zde uvedená myšlenka je zjednodušená verze plánovače, která má skutečná implementace spoustu komplikací.
Zvažte následující příklad
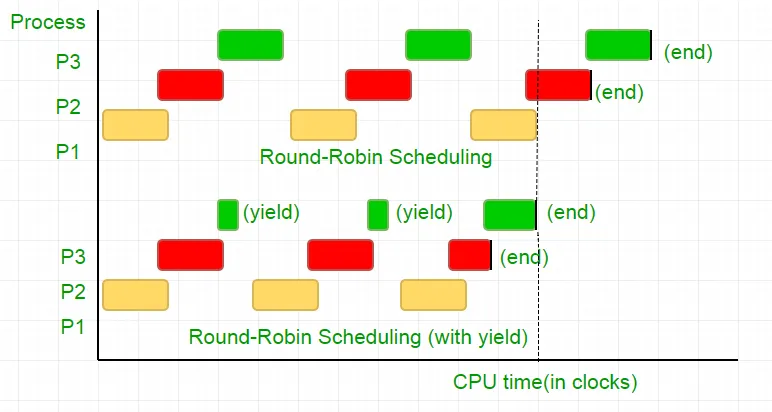
Existují tři procesy P1 P2 a P3. Proces P3 je takový, že má chvíli smyčku podobnou té v našem kódu, který není tak užitečný výpočet a existuje ze smyčky pouze tehdy, když P2 dokončí jeho provedení. Plánovač je staví všechny do kulaté fronty Robin. Nyní řekněte, že rychlost hodiny procesoru je 1000000/s a přiděluje na každý proces v každé iteraci 100 hodin. Poté bude první P1 spuštěn po dobu 100 hodin (0,0001 sekundy), pak P2 (0,0001 sekundy) následovaný P3 (0,0001 sekundy) nyní, protože už neexistují žádné další procesy, tento cyklus se opakuje, dokud nekončí P2 a poté následuje provedení P3 a nakonec jeho ukončení.
Toto je úplná plýtvání 100 cyklů hodin CPU. Abychom tomu zabránili, vzájemně se vzdáváme časového řezu CPU, tj. Výnos, který v podstatě končí tento časový řez a plánovač zvedne další proces spustit. Nyní testujeme náš stav jednou, pak se vzdáme CPU. Vzhledem k tomu, že náš test trvá 25 hodinových cyklů, ušetříme 75% našeho výpočtu v časovém řezu. Dát to graficky

Vzhledem k rychlosti hodin procesoru jako 1MHz je to hodně úspor!.
Různé rozdělení poskytují různé funkce k dosažení této funkce. Linux poskytuje SMERN_YIELD () .
void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] = 1 ; turn = 1 - self ; while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Only change is the addition of // sched_yield() call sched_yield (); }
Paměťový plot.
Kód v dřívějším tutoriálu mohl pracovat na většině systémů, ale nebyl 100% správný. Logika byla perfektní, ale většina moderních CPU využívá optimalizace výkonu, které mohou vést k provedení mimo řádek. Toto přehodnocení paměťových operací (načítání a obchody) obvykle bez povšimnutí v rámci jediného vlákna provádění však může způsobit nepředvídatelné chování v souběžných programech.
Zvažte tento příklad
while ( f == 0 ); // Memory fence required here print x ;
Ve výše uvedeném příkladu kompilátor považuje 2 příkazy za nezávislé na sobě, a proto se snaží zvýšit účinnost kódu jejich zařazením, což může vést k problémům pro souběžné programy. Abychom tomu zabránili, položíme paměťový plot, který kompilátoru náznak o možném vztahu mezi prohlášeními přes bariéru.
Pořadí prohlášení tedy
vlajka [self] = 1;
Turn = 1-self;
while (otočte se kontrolu podmínky)
výtěžek();
musí být úplně stejné, aby zámek fungoval, jinak to skončí ve stavu zablokování.
Aby se zajistilo, že tyto kompilátory poskytují instrukci, která zabrání uspořádání prohlášení v této bariéře. V případě GCC __sync_synchronize () .
Takže upravený kód se stává
Úplná implementace v C:
// Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp // Use below command to compile: // g++ -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.cpp -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include std :: atomic < int > flag [ 2 ]; std :: atomic < int > turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. std :: atomic_thread_fence ( std :: memory_order_seq_cst ); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. std :: this_thread :: yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; std :: cout < < 'Thread Entered: ' < < self < < std :: endl ; lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) std :: thread t1 ( func 0 ); std :: thread t2 ( func 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); std :: cout < < 'Actual Count: ' < < ans < < ' | Expected Count: ' < < MAX * 2 < < std :: endl ; return 0 ; }
C // Filename: peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c // Use below command to compile: // gcc -pthread peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence.c -o peterson_yieldlock_memoryfence #include #include #include 'mythreads.h' int flag [ 2 ]; int turn ; const int MAX = 1e9 ; int ans = 0 ; void lock_init () { // Initialize lock by resetting the desire of // both the threads to acquire the locks. // And giving turn to one of them. flag [ 0 ] = flag [ 1 ] = 0 ; turn = 0 ; } // Executed before entering critical section void lock ( int self ) { // Set flag[self] = 1 saying you want // to acquire lock flag [ self ] = 1 ; // But first give the other thread the // chance to acquire lock turn = 1 - self ; // Memory fence to prevent the reordering // of instructions beyond this barrier. __sync_synchronize (); // Wait until the other thread loses the // desire to acquire lock or it is your // turn to get the lock. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && turn == 1 - self ) // Yield to avoid wastage of resources. sched_yield (); } // Executed after leaving critical section void unlock ( int self ) { // You do not desire to acquire lock in future. // This will allow the other thread to acquire // the lock. flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // A Sample function run by two threads created // in main() void * func ( void * s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = ( int * ) s ; printf ( 'Thread Entered: %d n ' self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread // can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } // Driver code int main () { pthread_t p1 p2 ; // Initialize the lock lock_init (); // Create two threads (both run func) Pthread_create ( & p1 NULL func ( void * ) 0 ); Pthread_create ( & p2 NULL func ( void * ) 1 ); // Wait for the threads to end. Pthread_join ( p1 NULL ); Pthread_join ( p2 NULL ); printf ( 'Actual Count: %d | Expected Count:' ' %d n ' ans MAX * 2 ); return 0 ; }
Java import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger ; public class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static AtomicInteger [] flag = new AtomicInteger [ 2 ] ; static AtomicInteger turn = new AtomicInteger (); static final int MAX = 1000000000 ; static int ans = 0 ; static void lockInit () { flag [ 0 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 1 ] = new AtomicInteger (); flag [ 0 ] . set ( 0 ); flag [ 1 ] . set ( 0 ); turn . set ( 0 ); } static void lock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 1 ); turn . set ( 1 - self ); // Memory fence to prevent the reordering of instructions beyond this barrier. // In Java volatile variables provide this guarantee implicitly. // No direct equivalent to atomic_thread_fence is needed. while ( flag [ 1 - self ] . get () == 1 && turn . get () == 1 - self ) Thread . yield (); } static void unlock ( int self ) { flag [ self ] . set ( 0 ); } static void func ( int s ) { int i = 0 ; int self = s ; System . out . println ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); lock ( self ); // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i ++ ) ans ++ ; unlock ( self ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Initialize the lock lockInit (); // Create two threads (both run func) Thread t1 = new Thread (() -> func ( 0 )); Thread t2 = new Thread (() -> func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); try { // Wait for the threads to end. t1 . join (); t2 . join (); } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { e . printStackTrace (); } System . out . println ( 'Actual Count: ' + ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + MAX * 2 ); } }
Python import threading flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 MAX = 10 ** 9 ans = 0 def lock_init (): # This function initializes the lock by resetting the flags and turn. global flag turn flag = [ 0 0 ] turn = 0 def lock ( self ): # This function is executed before entering the critical section. It sets the flag for the current thread and gives the turn to the other thread. global flag turn flag [ self ] = 1 turn = 1 - self while flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 and turn == 1 - self : pass def unlock ( self ): # This function is executed after leaving the critical section. It resets the flag for the current thread. global flag flag [ self ] = 0 def func ( s ): # This function is executed by each thread. It locks the critical section increments the shared variable and then unlocks the critical section. global ans self = s print ( f 'Thread Entered: { self } ' ) lock ( self ) for _ in range ( MAX ): ans += 1 unlock ( self ) def main (): # This is the main function where the threads are created and started. lock_init () t1 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 0 )) t2 = threading . Thread ( target = func args = ( 1 )) t1 . start () t2 . start () t1 . join () t2 . join () print ( f 'Actual Count: { ans } | Expected Count: { MAX * 2 } ' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : main ()
JavaScript class PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence { static flag = [ 0 0 ]; static turn = 0 ; static MAX = 1000000000 ; static ans = 0 ; // Function to acquire the lock static async lock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 1 ; PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn = 1 - self ; // Asynchronous loop with a small delay to yield while ( PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ 1 - self ] == 1 && PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . turn == 1 - self ) { await new Promise ( resolve => setTimeout ( resolve 0 )); } } // Function to release the lock static unlock ( self ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . flag [ self ] = 0 ; } // Function representing the critical section static func ( s ) { let i = 0 ; let self = s ; console . log ( 'Thread Entered: ' + self ); // Lock the critical section PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . lock ( self ). then (() => { // Critical section (Only one thread can enter here at a time) for ( i = 0 ; i < PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX ; i ++ ) { PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans ++ ; } // Release the lock PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . unlock ( self ); }); } // Main function static main () { // Create two threads (both run func) const t1 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 0 )); const t2 = new Thread (() => PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . func ( 1 )); // Start the threads t1 . start (); t2 . start (); // Wait for the threads to end. setTimeout (() => { console . log ( 'Actual Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . ans + ' | Expected Count: ' + PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . MAX * 2 ); } 1000 ); // Delay for a while to ensure threads finish } } // Define a simple Thread class for simulation class Thread { constructor ( func ) { this . func = func ; } start () { this . func (); } } // Run the main function PetersonYieldLockMemoryFence . main ();
C++ // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include // Function to lock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was locked successfully } // Function to unlock a pthread mutex void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the mutex was unlocked successfully } // Function to create a pthread void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was created successfully } // Function to join a pthread void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); // Assert that the thread was joined successfully } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
C // mythread.h (A wrapper header file with assert // statements) #ifndef __MYTHREADS_h__ #define __MYTHREADS_h__ #include #include #include void Pthread_mutex_lock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_lock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_mutex_unlock ( pthread_mutex_t * m ) { int rc = pthread_mutex_unlock ( m ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_create ( pthread_t * thread const pthread_attr_t * attr void * ( * start_routine )( void * ) void * arg ) { int rc = pthread_create ( thread attr start_routine arg ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } void Pthread_join ( pthread_t thread void ** value_ptr ) { int rc = pthread_join ( thread value_ptr ); assert ( rc == 0 ); } #endif // __MYTHREADS_h__
Python import threading import ctypes # Function to lock a thread lock def Thread_lock ( lock ): lock . acquire () # Acquire the lock # No need for assert in Python acquire will raise an exception if it fails # Function to unlock a thread lock def Thread_unlock ( lock ): lock . release () # Release the lock # No need for assert in Python release will raise an exception if it fails # Function to create a thread def Thread_create ( target args = ()): thread = threading . Thread ( target = target args = args ) thread . start () # Start the thread # No need for assert in Python thread.start() will raise an exception if it fails # Function to join a thread def Thread_join ( thread ): thread . join () # Wait for the thread to finish # No need for assert in Python thread.join() will raise an exception if it fails
Výstup:
Thread Entered: 1
Thread Entered: 0
Actual Count: 2000000000 | Expected Count: 2000000000