Největší číslo v BST, které je menší nebo rovno k
Vzhledem ke kořeni a Binární vyhledávací strom a celé číslo k . Úkolem je najít největší počet v binárním vyhledávacím stromu méně než nebo rovný až k, pokud žádný takový prvek neexistuje, tisk -1.
Příklady:
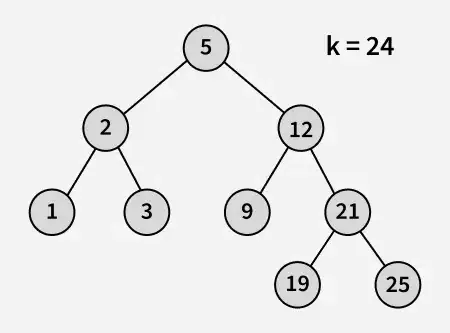
Vstup:

výstup: 21
Vysvětlení: 19 a 25 jsou dvě čísla nejbližší 21 a 19 je největší číslo, které má hodnotu menší nebo rovnou 21.
Vstup: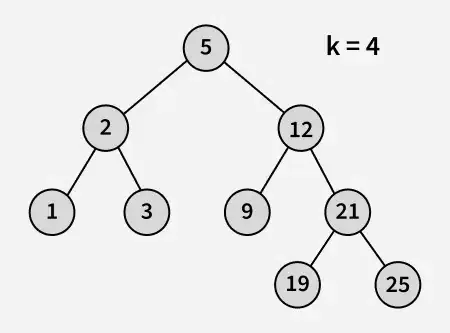
výstup: 3
Vysvětlení: 3 a 5 jsou dvě čísla nejbližší 4 a 3 je největší číslo, které má hodnotu menší nebo rovnou 4.
Obsah
- [Naivní přístup] Použití rekurze - O(h) čas a O(h) prostor
- [Očekávaný přístup] Použití iterace - O(h) čas a O(1) prostor
[Naivní přístup] Použití rekurze - O(h) čas a O(h) prostor
C++Myšlenka je začít na vykořenit a porovnejte jeho hodnotu s k. Pokud je hodnota uzlu větší než k, přejděte do levého podstromu. Jinak najděte hodnotu největšího čísla menší než rovnou k v pravý podstrom . Pokud pravý podstrom vrátí hodnotu -1 (to znamená, že žádná taková hodnota neexistuje), vrátí hodnotu aktuálního uzlu. Jinak vrátí hodnotu vrácenou pravým podstromem (protože bude větší než hodnota aktuálního uzlu, ale menší než k).
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * left * right ; Node ( int val ){ data = val ; left = nullptr ; right = nullptr ; } }; // function to find max value less than k int findMaxFork ( Node * root int k ) { // Base cases if ( root == nullptr ) return -1 ; if ( root -> data == k ) return k ; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if ( root -> data < k ) { int x = findMaxFork ( root -> right k ); if ( x == -1 ) return root -> data ; else return x ; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork ( root -> left k ); } int main () { int k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node * root = new Node ( 5 ); root -> left = new Node ( 2 ); root -> left -> left = new Node ( 1 ); root -> left -> right = new Node ( 3 ); root -> right = new Node ( 12 ); root -> right -> left = new Node ( 9 ); root -> right -> right = new Node ( 21 ); root -> right -> right -> left = new Node ( 19 ); root -> right -> right -> right = new Node ( 25 ); cout < < findMaxFork ( root k ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data ; Node left right ; Node ( int val ) { data = val ; left = null ; right = null ; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork ( Node root int k ) { // Base cases if ( root == null ) return - 1 ; if ( root . data == k ) return k ; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if ( root . data < k ) { int x = findMaxFork ( root . right k ); if ( x == - 1 ) return root . data ; else return x ; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork ( root . left k ); } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node ( 5 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 1 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right = new Node ( 12 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 9 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 21 ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( 19 ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( 25 ); System . out . println ( findMaxFork ( root k )); } }
Python # Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node : def __init__ ( self val ): self . data = val self . left = None self . right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork ( root k ): # Base cases if root is None : return - 1 if root . data == k : return k # If root's value is smaller # try in right subtree elif root . data < k : x = findMaxFork ( root . right k ) if x == - 1 : return root . data else : return x # If root's data is greater # return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork ( root . left k ) if __name__ == '__main__' : k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node ( 5 ) root . left = Node ( 2 ) root . left . left = Node ( 1 ) root . left . right = Node ( 3 ) root . right = Node ( 12 ) root . right . left = Node ( 9 ) root . right . right = Node ( 21 ) root . right . right . left = Node ( 19 ) root . right . right . right = Node ( 25 ) print ( findMaxFork ( root k ))
C# // C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node left right ; public Node ( int val ) { data = val ; left = null ; right = null ; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork ( Node root int k ) { // Base cases if ( root == null ) return - 1 ; if ( root . data == k ) return k ; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if ( root . data < k ) { int x = FindMaxFork ( root . right k ); if ( x == - 1 ) return root . data ; else return x ; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return FindMaxFork ( root . left k ); } static void Main () { int k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node ( 5 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 1 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right = new Node ( 12 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 9 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 21 ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( 19 ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( 25 ); Console . WriteLine ( FindMaxFork ( root k )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor ( val ) { this . data = val ; this . left = null ; this . right = null ; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork ( root k ) { // Base cases if ( root === null ) return - 1 ; if ( root . data === k ) return k ; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if ( root . data < k ) { let x = findMaxFork ( root . right k ); if ( x === - 1 ) return root . data ; else return x ; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork ( root . left k ); } let k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node ( 5 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 1 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right = new Node ( 12 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 9 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 21 ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( 19 ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( 25 ); console . log ( findMaxFork ( root k ));
Výstup
21
[Očekávaný přístup] Použití iterace - O(h) čas a O(1) prostor
C++Myšlenka je začít na vykořenit a porovnat jeho hodnotu s k . Pokud je hodnota uzlu <= k aktualizujte výslednou hodnotu na hodnotu root a přesuňte se na právo podstrom jinak přesunout do vlevo podstrom. Podle iterativně použitím této operace napříč všemi uzly můžeme minimalizovat prostor potřebný pro rekurze stoh.
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include using namespace std ; class Node { public : int data ; Node * left * right ; Node ( int val ){ data = val ; left = nullptr ; right = nullptr ; } }; // function to find max value less than k int findMaxFork ( Node * root int k ) { int result = -1 ; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while ( root != nullptr ) { // If root is smaller go to right side if ( root -> data <= k ){ result = root -> data ; root = root -> right ; } // If root is greater go to left side else root = root -> left ; } return result ; } int main () { int k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node * root = new Node ( 5 ); root -> left = new Node ( 2 ); root -> left -> left = new Node ( 1 ); root -> left -> right = new Node ( 3 ); root -> right = new Node ( 12 ); root -> right -> left = new Node ( 9 ); root -> right -> right = new Node ( 21 ); root -> right -> right -> left = new Node ( 19 ); root -> right -> right -> right = new Node ( 25 ); cout < < findMaxFork ( root k ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data ; Node left right ; Node ( int val ) { data = val ; left = null ; right = null ; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork ( Node root int k ) { int result = - 1 ; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while ( root != null ) { // If root is smaller go to right side if ( root . data <= k ) { result = root . data ; root = root . right ; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root . left ; } } return result ; } public static void main ( String [] args ) { int k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node ( 5 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 1 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right = new Node ( 12 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 9 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 21 ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( 19 ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( 25 ); System . out . println ( findMaxFork ( root k )); } }
Python # Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node : def __init__ ( self val ): self . data = val self . left = None self . right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork ( root k ): result = - 1 # Start from root and keep looking for larger while root is not None : # If root is smaller go to right side if root . data <= k : result = root . data root = root . right # If root is greater go to left side else : root = root . left return result if __name__ == '__main__' : k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node ( 5 ) root . left = Node ( 2 ) root . left . left = Node ( 1 ) root . left . right = Node ( 3 ) root . right = Node ( 12 ) root . right . left = Node ( 9 ) root . right . right = Node ( 21 ) root . right . right . left = Node ( 19 ) root . right . right . right = Node ( 25 ) print ( findMaxFork ( root k ))
C# // C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System ; class Node { public int data ; public Node left right ; public Node ( int val ) { data = val ; left = null ; right = null ; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork ( Node root int k ) { int result = - 1 ; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while ( root != null ) { // If root is smaller go to right side if ( root . data <= k ) { result = root . data ; root = root . right ; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root . left ; } } return result ; } static void Main () { int k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node ( 5 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 1 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right = new Node ( 12 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 9 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 21 ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( 19 ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( 25 ); Console . WriteLine ( FindMaxFork ( root k )); } }
JavaScript // JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor ( val ) { this . data = val ; this . left = null ; this . right = null ; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork ( root k ) { let result = - 1 ; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while ( root !== null ) { // If root is smaller go to right side if ( root . data <= k ) { result = root . data ; root = root . right ; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root . left ; } } return result ; } let k = 24 ; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node ( 5 ); root . left = new Node ( 2 ); root . left . left = new Node ( 1 ); root . left . right = new Node ( 3 ); root . right = new Node ( 12 ); root . right . left = new Node ( 9 ); root . right . right = new Node ( 21 ); root . right . right . left = new Node ( 19 ); root . right . right . right = new Node ( 25 ); console . log ( findMaxFork ( root k ));
Výstup
21Vytvořit kvíz