Пътуващ проблем на продавача, използващ клон и обвързан
Като се има предвид набор от градове и разстояние между всяка двойка градове, проблемът е да се намери най -кратката възможна обиколка, която посещава всеки град точно веднъж и се връща в началната точка.

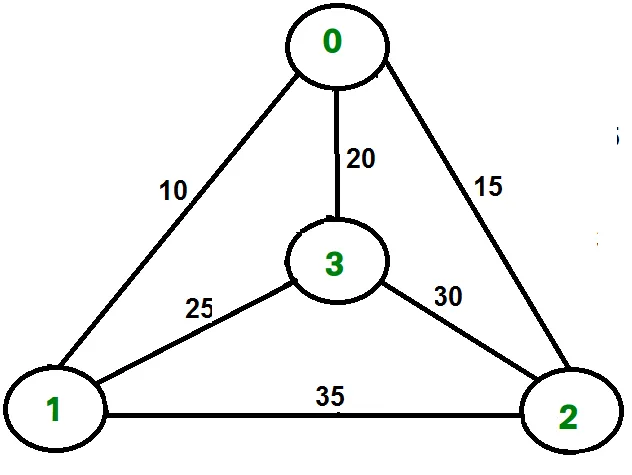
Например помислете за графиката, показана на фигура от дясната страна. TSP турне в графиката е 0-1-3-2-0. Цената на обиколката е 10+25+30+15, което е 80.
Обсъждахме следните решения
1) Наивно и динамично програмиране
2) Приблизително решение с помощта на MST
Разклонение и обвързано решение
Както се вижда от предишните статии в клон и обвързан метод за текущия възел в дърво, ние изчисляваме обвързано с най -доброто възможно решение, което можем да получим, ако спускаме този възел. Ако самият обвързан с най -доброто възможно решение е по -лошо от най -доброто (най -доброто изчислено досега), тогава игнорираме подпредрата, вкоренена с възела.
Обърнете внимание, че цената чрез възел включва две разходи.
1) Разходи за достигане на възела от корена (когато достигнем възел, ние имаме изчислени тези разходи)
2) Разходи за достигане на отговор от текущия възел към листо (изчисляваме обвързана с тази цена, за да решим дали да игнорираме подпред с този възел или не).
- В случаи на a Проблем за максимизиране Горната граница ни казва максималното възможно решение, ако следваме дадения възел. Например в 0/1 раница използвахме алчен подход, за да намерим горна граница .
- В случаи на a проблем с минимизирането Долната граница ни казва минималното възможно решение, ако следваме дадения възел. Например в Проблем за заданието на работата Получаваме по -ниска граница, като назначаваме работа с най -малко разходи на работник.
В клон и обвързана предизвикателната част е да разберем начин да се изчисли обвързване на най -доброто възможно решение. По -долу е идея, използвана за изчисляване на границите за проблем на пътуващия продавач.
Цената на всяка обиколка може да бъде написана по -долу.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Например помислете за показаната по -горе графика. По -долу са минимални разходи два ръба, съседни на всеки възел.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Сега имаме идея за изчисляването на долната граница. Нека да видим как да го приложим на държавното дърво за търсене на пространство. Започваме да изброяваме всички възможни възли (за предпочитане в лексикографски ред)
1. Коренният възел: Без загуба на общност предполагаме, че започваме от върха '0', за която долната граница е изчислена по -горе.
Справяне с ниво 2: Следващото ниво изброява всички възможни върхове, към които можем да отидем (като се има предвид, че във всеки път трябва да се появи върх само веднъж), които са 1 2 3 ... N (обърнете внимание, че графиката е завършена). Помислете, че изчисляваме за Vertex 1, тъй като се преместихме от 0 на 1 Нашата обиколка вече включва ръба 0-1. Това ни позволява да направим необходимите промени в долната граница на корена.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Как работи? За да включим Edge 0-1, добавяме цената на ръба от 0-1 и изваждаме тегло на ръба, така че долната граница да остане възможно най-стегната, което би било сумата от минималните ръбове от 0 и 1, разделена на 2. Ясно е, че ръбът не може да бъде по-малък от този.
Справяне с други нива: Докато преминаваме към следващото ниво, отново изброяваме всички възможни върхове. За горния случай, който върви по -нататък след 1, проверяваме за 2 3 4 ... n.
Помислете за долната граница за 2, когато се преместихме от 1 на 1, ние включваме ръба 1-2 в обиколката и променяме новата долна граница за този възел.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
Забележка: Единствената промяна във формулата е, че този път включихме втора минимална цена на ръба за 1, тъй като минималната цена на ръба вече е извадена на предишно ниво.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include using namespace std ; const int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. int final_path [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path bool visited [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. int final_res = INT_MAX ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution void copyToFinal ( int curr_path []) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int firstMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int min = INT_MAX ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i int secondMin ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int i ) { int first = INT_MAX second = INT_MAX ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] void TSPRec ( int adj [ N ][ N ] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path []) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level -1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level -1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array memset ( visited false sizeof ( visited )); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level -1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] void TSP ( int adj [ N ][ N ]) { int curr_path [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; memset ( curr_path -1 sizeof ( curr_path )); memset ( visited 0 sizeof ( curr_path )); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound & 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code int main () { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [ N ][ N ] = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); printf ( 'Minimum cost : %d n ' final_res ); printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ]); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.* ; class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited [] = new boolean [ N ] ; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int curr_path [] ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ] ; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] ; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int min = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i ][ k ] ; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int adj [][] int i ) { int first = Integer . MAX_VALUE second = Integer . MAX_VALUE ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] != first ) second = adj [ i ][ j ] ; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int adj [][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path [] ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] ; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ] ) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] ; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Arrays . fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int adj [][] ) { int curr_path [] = new int [ N + 1 ] ; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Arrays . fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Arrays . fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code public static void main ( String [] args ) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj [][] = {{ 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); System . out . printf ( 'Minimum cost : %dn' final_res ); System . out . printf ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { System . out . printf ( '%d ' final_path [ i ] ); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Python3 # Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float ( 'inf' ) # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal ( curr_path ): final_path [: N + 1 ] = curr_path [:] final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin ( adj i ): min = maxsize for k in range ( N ): if adj [ i ][ k ] < min and i != k : min = adj [ i ][ k ] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin ( adj i ): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range ( N ): if i == j : continue if adj [ i ][ j ] <= first : second = first first = adj [ i ][ j ] elif ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second and adj [ i ][ j ] != first ): second = adj [ i ][ j ] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited ): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N : # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 : # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]] [ curr_path [ 0 ]] if curr_res < final_res : copyToFinal ( curr_path ) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range ( N ): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] != 0 and visited [ i ] == False ): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1 : curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) else : curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res : curr_path [ level ] = i visited [ i ] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited ) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [ False ] * len ( visited ) for j in range ( level ): if curr_path [ j ] != - 1 : visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP ( adj ): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [ - 1 ] * ( N + 1 ) visited = [ False ] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range ( N ): curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math . ceil ( curr_bound / 2 ) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = True curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited ) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [ None ] * ( N + 1 ) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [ False ] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP ( adj ) print ( 'Minimum cost :' final_res ) print ( 'Path Taken : ' end = ' ' ) for i in range ( N + 1 ): print ( final_path [ i ] end = ' ' ) # This code is contributed by ng24_7
C# // C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System ; public class GFG { static int N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int [] final_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool [] visited = new bool [ N ]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32 . MaxValue ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal ( int [] curr_path ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int min = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ) if ( adj [ i k ] < min && i != k ) min = adj [ i k ]; return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin ( int [ ] adj int i ) { int first = Int32 . MaxValue second = Int32 . MaxValue ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ) { if ( i == j ) continue ; if ( adj [ i j ] <= first ) { second = first ; first = adj [ i j ]; } else if ( adj [ i j ] <= second && adj [ i j ] != first ) second = adj [ i j ]; } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec ( int [ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int [] curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]] != 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ] != 0 && visited [ i ] == false ) { int temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ) curr_bound -= (( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); else curr_bound -= (( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ) { curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ] i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array Array . Fill ( visited false ); for ( int j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP ( int [ ] adj ) { int [] curr_path = new int [ N + 1 ]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0 ; Array . Fill ( curr_path - 1 ); Array . Fill ( visited false ); // Compute initial bound for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ) curr_bound += ( firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i )); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = ( curr_bound == 1 ) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2 ; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } // Driver code static public void Main () { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int [ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP ( adj ); Console . WriteLine ( 'Minimum cost : ' + final_res ); Console . Write ( 'Path Taken : ' ); for ( int i = 0 ; i <= N ; i ++ ) { Console . Write ( final_path [ i ] + ' ' ); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
JavaScript const N = 4 ; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array ( N ). fill ( false ); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal ( curr_path ){ for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ final_path [ i ] = curr_path [ i ]; } final_path [ N ] = curr_path [ 0 ]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin ( adj i ){ let min = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let k = 0 ; k < N ; k ++ ){ if ( adj [ i ][ k ] < min && i !== k ){ min = adj [ i ][ k ]; } } return min ; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin ( adj i ){ let first = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; let second = Number . MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < N ; j ++ ){ if ( i == j ){ continue ; } if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= first ){ second = first ; first = adj [ i ][ j ]; } else if ( adj [ i ][ j ] <= second && adj [ i ][ j ] !== first ){ second = adj [ i ][ j ]; } } return second ; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path ) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if ( level == N ) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]] !== 0 ) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ curr_path [ 0 ]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if ( curr_res < final_res ) { copyToFinal ( curr_path ); final_res = curr_res ; } } return ; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if ( adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ] !== 0 && ! visited [ i ]){ let temp = curr_bound ; curr_weight += adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if ( level == 1 ){ curr_bound -= ( firstMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } else { curr_bound -= ( secondMin ( adj curr_path [ level - 1 ]) + firstMin ( adj i )) / 2 ; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if ( curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res ){ curr_path [ level ] = i ; visited [ i ] = true ; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec ( adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path ); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj [ curr_path [ level - 1 ]][ i ]; curr_bound = temp ; // Also reset the visited array visited . fill ( false ) for ( var j = 0 ; j <= level - 1 ; j ++ ) visited [ curr_path [ j ]] = true ; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP ( adj ) { let curr_path = Array ( N + 1 ). fill ( - 1 ); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0 ; visited . fill ( false ); // compute initial bound for ( let i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){ curr_bound += firstMin ( adj i ) + secondMin ( adj i ); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? ( curr_bound / 2 ) + 1 : ( curr_bound / 2 ); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited [ 0 ] = true ; curr_path [ 0 ] = 0 ; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec ( adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path ); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj = [[ 0 10 15 20 ] [ 10 0 35 25 ] [ 15 35 0 30 ] [ 20 25 30 0 ]]; TSP ( adj ); console . log ( `Minimum cost: ${ final_res } ` ); console . log ( `Path Taken: ${ final_path . join ( ' ' ) } ` ); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Резултат:
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
Закръгляването се извършва в този ред код:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
В алгоритъма на клона и обвързания TSP изчисляваме по -ниска граница на общата цена на оптималното решение, като добавяме минималните разходи за ръбове за всяка върха и след това се разделяме на две. Тази долна граница обаче може да не е цяло число. За да получим цяло число долна граница, можем да използваме закръгляне.
В горния код променливата Curr_Bound държи текущата долна граница на общата цена на оптималното решение. Когато посетим нов връх на ниво ниво, ние изчисляваме нова долна граница New_Bound, като вземем сумата от минималните разходи за ръбове за новия връх и нейните две най -близки съседи. След това актуализираме променливата Curr_bound, като закръгляме New_Bound до най -близкото цяло число.
Ако нивото е 1, закръгляме до най -близкото цяло число. Това е така, защото досега сме посетили само един връх и искаме да бъдем консервативни в нашата оценка за общите разходи на оптималното решение. Ако нивото е по -голямо от 1, ние използваме по -агресивна стратегия за закръгляне, която отчита факта, че вече сме посетили някои върхове и следователно можем да направим по -точна оценка на общата цена на оптималното решение.
Сложност на времето: Най -лошата сложност на клона и обвързания остава същата като тази на грубата сила ясно, защото в най -лошия случай никога не може да получим шанс да подредим възел. Като има предвид, че на практика той се представя много добре в зависимост от различния случай на TSP. Сложността също зависи от избора на ограничаващата функция, тъй като те са тези, които решават колко възли да бъдат подрязани.
Референции:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.ernet.in/dsa/node187.html