ابحث عن جميع التسلسلات الثنائية ذات الطول الزوجي بنفس مجموع بتات النصف الأول والثاني
بالنظر إلى الرقم n، ابحث عن جميع التسلسلات الثنائية ذات الطول 2n بحيث يكون مجموع البتات n الأولى هو نفس مجموع البتات n الأخيرة.
أمثلة:
Input: N = 2 Output: 0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010 Input: N = 3 Output: 011011 001001 011101 010001 101011 111111 110011 101101 100001 110101 001010 011110 010010 001100 000000 010100 101110 100010 110110 100100
تتمثل الفكرة في إصلاح البتات الأولى والأخيرة ثم التكرار للبتات المتبقية 2*(n-1). هناك أربعة احتمالات عندما نصلح البتات الأولى والأخيرة -
- البتات الأولى والأخيرة هي 1 متبقية n - 1 بت على كلا الجانبين يجب أن يكون لها نفس المبلغ أيضًا.
- البتات الأولى والأخيرة هي 0 متبقية n - 1 بتات على كلا الجانبين يجب أن يكون لها نفس المبلغ أيضًا.
- البت الأول هو 1 والبت الأخير هو 0 مجموع n - 1 بت على الجانب الأيسر يجب أن يكون 1 أقل من مجموع n-1 بت على الجانب الأيمن.
- البت الأول هو 0 والبت الأخير هو مجموع واحد من البتات n المتبقية على الجانب الأيسر يجب أن يكون 1 أكثر من مجموع البتات n-1 على الجانب الأيمن.
وفيما يلي تنفيذ الفكرة المذكورة أعلاه -
// C++ program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same #include using namespace std ; // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index void findAllSequences ( int diff char * out int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) cout < < out < < ' ' ; return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program int main () { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char out [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // null terminate output array out [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); return 0 ; }
Java // Java program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same import java.io.* ; import java.util.* ; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences ( int diff char out [] int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of more // than n with 2n bits if ( Math . abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { System . out . print ( out ); System . out . print ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' ; out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' ; out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program public static void main ( String [] args ) { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters char [] out = new char [ 2 * n + 1 ] ; // null terminate output array out [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); } } // This code is contributed by Pramod Kumar
Python3 # Python3 program to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # Function to print even length binary sequences # whose sum of first and second half bits is same # diff --> difference between sums of first n bits # and last n bits # out --> output array # start --> starting index # end --> ending index def findAllSequences ( diff out start end ): # We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) // 2 ): return ; # if all bits are filled if ( start > end ): # if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ): print ( '' . join ( list ( out )) end = ' ' ); return ; # fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 out [ start ] = '0' ; out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first and last bits as 1 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first and last bits as 0 out [ start ] = out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff out start + 1 end - 1 ); # fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 out [ start ] = '1' ; out [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 out start + 1 end - 1 ); # Driver program # input number n = 2 ; # allocate string containing 2*n characters out = [ '' ] * ( 2 * n ); findAllSequences ( 0 out 0 2 * n - 1 ); # This code is contributed by mits
C# // C# program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same using System ; class GFG { // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index static void findAllSequences ( int diff char [] outt int start int end ) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if ( Math . Abs ( diff ) > ( end - start + 1 ) / 2 ) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { Console . Write ( outt ); Console . Write ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt [ start ] = '0' ; outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt [ start ] = '1' ; outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); } // Driver program public static void Main () { // input number int n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters char [] outt = new char [ 2 * n + 1 ]; // null terminate output array outt [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 outt 0 2 * n - 1 ); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
PHP // PHP program to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // Function to print even length binary sequences // whose sum of first and second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start $end ) { // We can't cover difference of more than n with 2n bits if ( abs ( $diff ) > ( int )(( $end - $start + 1 ) / 2 )) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( $start > $end ) { // if sum of first n bits and last n bits are same if ( $diff == 0 ) print ( implode ( '' $out ) . ' ' ); return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit as 1 $out [ $start ] = '0' ; $out [ $end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( $diff + 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 $out [ $start ] = $out [ $end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 $out [ $start ] = $out [ $end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( $diff $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last bit as 0 $out [ $start ] = '1' ; $out [ $end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( $diff - 1 $out $start + 1 $end - 1 ); } // Driver program // input number $n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n characters $out = array_fill ( 0 2 * $n '' ); findAllSequences ( 0 $out 0 2 * $n - 1 ); // This code is contributed by chandan_jnu ?>
JavaScript < script > // JavaScript program to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and second // half bits is same // Function to print even length binary // sequences whose sum of first and // second half bits is same // diff --> difference between sums of // first n bits // and last n bits // out --> output array // start --> starting index // end --> ending index function findAllSequences ( diff outt start end ) { // We can't cover difference of // more than n with 2n bits if ( Math . abs ( diff ) > parseInt (( end - start + 1 ) / 2 10 )) return ; // if all bits are filled if ( start > end ) { // if sum of first n bits and // last n bits are same if ( diff == 0 ) { document . write ( outt . join ( '' )); document . write ( ' ' ); } return ; } // fill first bit as 0 and last bit // as 1 outt [ start ] = '0' ; outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff + 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 1 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '1' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first and last bits as 0 outt [ start ] = outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff outt start + 1 end - 1 ); // fill first bit as 1 and last // bit as 0 outt [ start ] = '1' ; outt [ end ] = '0' ; findAllSequences ( diff - 1 outt start + 1 end - 1 ); } // input number let n = 2 ; // allocate string containing 2*n // characters let outt = new Array ( 2 * n + 1 ); // null terminate output array outt [ 2 * n ] = '�' ; findAllSequences ( 0 outt 0 2 * n - 1 ); < /script>
الإخراج
0101 1111 1001 0110 0000 1010
تعقيد الوقت: O((4 ^ ن )* ن)
4^N بسبب 4 مكالمات متكررة وN (مبسطة من 2N) للوقت المستغرق في طباعة سلاسل بحجم 2N
المساحة المساعدة: على)
هناك طريقة أخرى نقوم من خلالها بإنشاء جميع السلاسل الممكنة ذات الطول n وتخزينها في قائمة في فهرس يمثل مجموعها. ثم نكرر كل قائمة وننشئ سلاسل بالحجم 2n عن طريق طباعة كل سلسلة مع إضافة جميع السلاسل الأخرى في القائمة إلى نفس القيمة.
C++ // C++ program to implement the approach #include using namespace std ; //function that generates the sequence void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n vector < vector < string > >& sumToString vector < string > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if ( n == 0 ) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index string seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . size (); i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence [ i ]; } vector < string > x = sumToString [ sumSoFar ]; x . push_back ( seq ); sumToString [ sumSoFar ] = x ; return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . push_back ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . erase ( sequence . begin ()); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . push_back ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . erase ( sequence . begin ()); } // function to form permutations of the sequences void permuteSequences ( vector < vector < string > > sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . size (); sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. size (); sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. size (); sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . size () - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] . size () - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] . size () - 1 ) { cout < < '1111 ' ; } else { cout < < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] [ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ] [ sequence2 ] < < ' ' ; } } } } } // function that finds all the subsequences void findAllSequences ( int n ) { vector < vector < string > > sumToString ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . push_back ( vector < string > ()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString vector < string > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } // Driver Code int main () { // Function Call findAllSequences ( 2 ); return 0 ; } // this code is contributed by phasing17
Java // Java program to implement the approach import java.util.* ; class GFG { // function that finds all the subsequences static void findAllSequences ( int n ) { ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString = new ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . add ( new ArrayList < String > ()); // list of strings // where index // represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString new ArrayList < String > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } static void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString ArrayList < String > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to // include if ( n == 0 ) { // add permutation to list of sequences with sum // corresponding to index String seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . size (); i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence . get ( i ); } ArrayList < String > x = sumToString . get ( sumSoFar ); x . add ( seq ); sumToString . set ( sumSoFar x ); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . add ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . remove ( 0 ); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . add ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . remove ( 0 ); } // function to form permutations of the sequences static void permuteSequences ( ArrayList < ArrayList < String > > sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . size (); sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ). size (); sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ). size (); sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . size () - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . size () - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . size () - 1 ) { System . out . print ( '1111' ); } else { System . out . println ( sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . get ( sequence1 ) + sumToString . get ( sumIndexArr ) . get ( sequence2 )); } } } } } // Driver Code public static void main ( String [] args ) { // Function Call findAllSequences ( 2 ); } // this code is contributed by phasing17 }
Python3 def findAllSequences ( n ): sumToString = [[] for x in range ( n + 1 )] # list of strings where index represents sum generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString [] 0 ) permuteSequences ( sumToString ) def generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString sequence sumSoFar ): #Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if n == 0 : sumToString [ sumSoFar ] . append ( '' . join ( sequence )) #add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index return #Generate sequence +0 sequence . append ( '0' ) generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ) sequence . pop () #Generate sequence +1 sequence . append ( '1' ) generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ) sequence . pop () def permuteSequences ( sumToString ): #There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for sumIndexArr in sumToString : # Append for sequence1 in sumIndexArr : for sequence2 in sumIndexArr : print ( sequence1 + sequence2 ) findAllSequences ( 2 ) #Contribution by Xavier Jean Baptiste
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class GFG { static void findAllSequences ( int n ) { List < List < string >> sumToString = new List < List < string >> (); for ( int i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . Add ( new List < string > ()); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString new List < string > () 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } static void generateSequencesWithSum ( int n List < List < string >> sumToString List < string > sequence int sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if ( n == 0 ) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index string seq = '' ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < sequence . Count ; i ++ ) { seq = seq + sequence [ i ]; } sumToString [ sumSoFar ]. Add ( seq ); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . Add ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . RemoveAt ( 0 ); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . Add ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . RemoveAt ( 0 ); } static void permuteSequences ( List < List < string >> sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( int sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . Count ; sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( int sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count ; sequence1 ++ ) { for ( int sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count ; sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . Count - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. Count - 1 ) { Console . Write ( '1111' ); } else { Console . WriteLine ( sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence2 ]); } } } } } static void Main () { findAllSequences ( 2 ); } } // This code is contributed by divyesh072019.
JavaScript < script > function findAllSequences ( n ) { let sumToString = []; for ( let i = 0 ; i < n + 1 ; i ++ ) { sumToString . push ([]); // list of strings where index represents sum } generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString [] 0 ); permuteSequences ( sumToString ); } function generateSequencesWithSum ( n sumToString sequence sumSoFar ) { // Base case if there are no more binary digits to include if ( n == 0 ) { //add permutation to list of sequences with sum corresponding to index sumToString [ sumSoFar ]. push ( sequence . join ( '' )); return ; } // Generate sequence +0 sequence . push ( '0' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar ); sequence . shift (); // Generate sequence +1 sequence . push ( '1' ); generateSequencesWithSum ( n - 1 sumToString sequence sumSoFar + 1 ); sequence . shift (); } function permuteSequences ( sumToString ) { // There are 2^n substring in this list of lists for ( let sumIndexArr = 0 ; sumIndexArr < sumToString . length ; sumIndexArr ++ ) { // Append for ( let sequence1 = 0 ; sequence1 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length ; sequence1 ++ ) { for ( let sequence2 = 0 ; sequence2 < sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length ; sequence2 ++ ) { if ( sumIndexArr == sumToString . length - 1 && sequence1 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length - 1 && sequence2 == sumToString [ sumIndexArr ]. length - 1 ) { document . write ( '1111' ); } else { document . write ( sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence1 ] + sumToString [ sumIndexArr ][ sequence2 ] + ' ' ); } } } } } findAllSequences ( 2 ); // This code is contributed by decode2207. < /script>
الإخراج
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
تحليل التعقيد الزمني:
createSequencesWithSum = يا((2 ن )*ن)
- 2 ن : نقوم بإنشاء جميع التقليب للسلاسل الثنائية بالحجم N
- N: تحويل قائمة الأحرف إلى سلسلة وتخزينها في صفيف. يتم ذلك في الحالة الأساسية.
permuteSequences = يا((2 ن ) * ن!/(ن/2)! 2 * ن)
- 2 ن : نقوم بالتكرار خلال كل السلسلة التي تم إنشاؤها بالحجم n
- ن!/(ن/2)! 2 : هذا أمر صعب بعض الشيء في الشرح
لنأخذ N = 2 كمثال. مجموعتنا من التسلسل المحتمل للحجم n ستكون:
| مؤشر المصفوفة | 1 | 2 | |
| قائمة السلاسل | 00 | 0110 | 11 |
في قائمة السلاسل التي يمثل الفهرس المجموع، نحصل على عدد السلاسل ذات الحجم 2n باستخدام صيغة 'n Choose k'. في حالتنا ستكون nCk *nCk حيث يمثل k عدد 1s في كل نصف السلسلة ذات الحجم 2n:
ك = 0 لدينا (2C0)^2 = سلسلة واحدة (0000)
ك = 1 لدينا (2C1)^2 سلسلة = 4 سلاسل (0101 0110 1001 1010)
ك = 2 لدينا (2c2)^2 = سلسلة واحدة (1111)
نحصل على أطول قائمة من السلاسل عندما يكون k = N/2 ومن ثم ن ج ن/2 = ن!/[(ن/2)! * (N - N/2)!] وهو ما يُبسط إلى ن ج ن/2 = ن!/(ن/2)! 2
ومن ثم يجب علينا تكرار كل عنصر على الأكثر ن ج ن/2 لتشكيل سلاسل بطول 2N
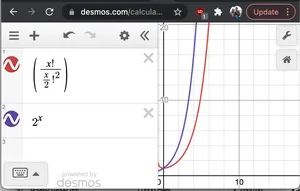
بدون دليل رسمي إذا قمنا بالرسم البياني 2^N و N!/(N/2)! 2 نرى ذلك 2 ن لديه معدل نمو أسرع من الأخير. لذلك يا (2 ن * ن!/(ن/2) 2 ) < O(2 ن *2 ن ) = يا(2 2n ) = يا(4 ن )
 رسم بياني لـ 2^x وnC(n/2)
رسم بياني لـ 2^x وnC(n/2) - N: يجب علينا طباعة كل سلسلة بحجم 2N
أخيرًا يمكننا تجاهل التعقيد الزمني لـ generatorSequencesWithSum لأن permuteSequence هو المصطلح الرئيسي
تعقيد الوقت: يا (2 ن * ن!/(ن/2)! 2 * N) (أفضل من الحل الأول لـ O((4^N) * N انظر الشرح أعلاه لمزيد من التفاصيل)
مساحة مساعدة : يا (2 ن ) لأننا نقوم بتخزين جميع تبديلات السلسلة الثنائية بالحجم N
#include using namespace std ; class FirstHalf { public : string data ; int sum ; FirstHalf ( string data int sum ) { this -> data = data ; this -> sum = sum ; } }; // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map < int vector < string >> mp ; // first N-half bits vector < FirstHalf > firstHalf ; // function to find sum of the bits from a String int sumOfString ( string s ) { int sum = 0 ; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( auto c : s ) { sum += ( c - '0' ); } return sum ; } void perm ( string p char * bin int level int n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . push_back ( FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value mp [ sum ]. push_back ( p ); return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { char c = bin [ i ]; perm ( p + c bin level -1 n ); } } void result () { int i = 0 ; for ( auto first : firstHalf ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key vector < string > secondHalf = mp [ sum ]; for ( auto second : secondHalf ) { // append first and second half and print cout < < first . data + second < < ' ' ; // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) cout < < endl ; } } } int main (){ char up [ 2 ] = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; string x = '' ; perm ( x up n n ); result (); return 0 ; } // This code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
Java import java.util.* ; class GFG { static class FirstHalf { String data ; int sum ; FirstHalf ( String data int sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } //MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Map < Integer ArrayList < String >> map = new HashMap <> (); //first N-half bits static List < FirstHalf > firstHalf = new ArrayList <> (); //function to find sum of the bits from a String public static int sumOfString ( String s ) { int sum = 0 ; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( char c : s . toCharArray ()) { sum += c - '0' ; } return sum ; } public static void perm ( String p char [] bin int level int n ) { //p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) //bin: {'0' '1'} //l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) //n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { //at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); //store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . add ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); //put current permutation to its respective sum value map . putIfAbsent ( sum new ArrayList < String > ()); map . get ( sum ). add ( p ); return ; } //generate calls for permutation //working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( char c : bin ) { perm ( p + c bin level - 1 n ); } } public static void result () { int i = 0 ; for ( FirstHalf first : firstHalf ) { //for each firstHalf string //find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; //retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key ArrayList < String > secondHalf = map . get ( sum ); for ( String second : secondHalf ) { //append first and second half and print System . out . print ( first . data + second + ' ' ); //after every 6 solution line is changed in output //only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) System . out . println (); } } } public static void main ( String [] args ) { char [] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; perm ( '' up n n ); result (); } } //Code contributed by Animesh Singh
Python3 # Python code implementation class FirstHalf : def __init__ ( self data sum ): self . data = data self . sum = sum # MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum map = {} # first N-half bits firstHalf = [] # function to find sum of the bits from a String def sumOfString ( s ): sum = 0 # ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for i in range ( len ( s )): sum += ord ( s [ i ]) - ord ( '0' ) return sum def perm ( p bin level n ): # p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) # bin: ['0' '1'] # l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) # n: total levels if level == 0 : # at solution level find sum of the current permutation sum = sumOfString ( p ) # store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . append ( FirstHalf ( p sum )) # put current permutation to its respective sum value if sum not in map : map [ sum ] = [] map [ sum ] . append ( p ) return # generate calls for permutation # working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for i in range ( len ( bin )): perm ( p + bin [ i ] bin level - 1 n ) def result (): i = 0 for j in range ( len ( firstHalf )): # for each firstHalf string # find sum of the bits of current string sum = firstHalf [ j ] . sum # retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key secondHalf = map [ sum ] for k in range ( len ( secondHalf )): # append first and second half and print print ( firstHalf [ j ] . data + secondHalf [ k ] + ' ' end = '' ) # after every 6 solution line is changed in output # only for formatting below lines could be removed i = i + 1 if ( i % 6 == 0 ): print ( ' n ' ) up = [ '0' '1' ] n = 2 perm ( '' up n n ) result () # The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
C# using System ; using System.Collections.Generic ; class FirstHalf { public string data ; public int sum ; public FirstHalf ( string data int sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } class Gfg { // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum static Dictionary < int List < string >> mp = new Dictionary < int List < string >> (); // first N-half bits static List < FirstHalf > firstHalf = new List < FirstHalf > (); // function to find sum of the bits from a String static int sumOfString ( string s ) { int sum = 0 ; // ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) foreach ( char c in s ) { sum += ( c - '0' ); } return sum ; } static void perm ( string p char [] bin int level int n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: {'0' '1'} // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation int sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . Add ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if ( mp . ContainsKey ( sum )) { mp [ sum ]. Add ( p ); } else { mp . Add ( sum new List < string > { p }); } return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s // then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { char c = bin [ i ]; perm ( p + c bin level - 1 n ); } } static void result () { int i = 0 ; foreach ( FirstHalf first in firstHalf ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string int sum = first . sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key List < string > secondHalf = mp [ sum ]; foreach ( string second in secondHalf ) { // append first and second half and print Console . Write ( first . data + second + ' ' ); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) Console . WriteLine (); } } } static void Main ( string [] args ) { char [] up = { '0' '1' }; int n = 2 ; string x = '' ; perm ( x up n n ); result (); } }
JavaScript class FirstHalf { constructor ( data sum ) { this . data = data ; this . sum = sum ; } } // MAP: Key -> sum of bits; Value -> All possible permutation with respective sum const map = new Map (); // first N-half bits const firstHalf = []; // function to find sum of the bits from a String function sumOfString ( s ) { let sum = 0 ; //ex: converts '1' to 1 -> (ASCII('1') - ASCII('0') = 1) for ( let i = 0 ; i < s . length ; i ++ ) { sum += s . charCodeAt ( i ) - '0' . charCodeAt ( 0 ); } return sum ; } function perm ( p bin level n ) { // p: processed string(processed permutation at current level) // bin: ['0' '1'] // l: current level of recursion tree (leaf/solution level = 0) // n: total levels if ( level == 0 ) { // at solution level find sum of the current permutation let sum = sumOfString ( p ); // store current permutation to firstHalf list firstHalf . push ( new FirstHalf ( p sum )); // put current permutation to its respective sum value if ( ! map . has ( sum )) map . set ( sum []); map . get ( sum ). push ( p ); return ; } // generate calls for permutation // working: first solution with all 0s then replacing last 0 with 1 and so on... for ( let i = 0 ; i < bin . length ; i ++ ) { perm ( p + bin [ i ] bin level - 1 n ); } } function result () { let i = 0 ; for ( let j = 0 ; j < firstHalf . length ; j ++ ) { // for each firstHalf string // find sum of the bits of current string let sum = firstHalf [ j ]. sum ; // retrieve respective secondHalf from map based on sum key let secondHalf = map . get ( sum ); for ( let k = 0 ; k < secondHalf . length ; k ++ ) { // append first and second half and print process . stdout . write ( firstHalf [ j ]. data + secondHalf [ k ] + ' ' ); // after every 6 solution line is changed in output // only for formatting below lines could be removed i ++ ; if ( i % 6 == 0 ) process . stdout . write ( 'n' ); } } } const up = [ '0' '1' ]; const n = 2 ; perm ( '' up n n ); result ();
الإخراج
0000 0101 0110 1001 1010 1111
الخوارزمية:
1. قم بإنشاء كافة التباديل الثنائية بالحجم n
2. احسب مجموع بتات كل تبديل وتذكره للنصف الثاني
[على سبيل المثال: بالنسبة لـ n=2 تذكر أن هناك سلسلتين بمجموع = 1، أي '01' '10' ]
3. كرر جميع التباديلات المولدة وألحق لكل منها النصف الثاني حسب مجموع البتات
تحليل التعقيد الزمني:
مجموع السلسلة () = O(N) : اجتياز كل بت وإضافته إلى المجموع
موج الشعر بإستمرار() = يا(2 ن * ن)
2N * N : نقوم بإنشاء جميع التباديل للبتات الثنائية بالحجم N ونجد مجموع البتات لكل تبديل
نتيجة() = يا((2 ن ) * (ن!/(ن/2)!)2)
2 ن : نقوم بالتكرار من خلال جميع التباديل الممكنة للحجم N (النصف الأول)
NCN/2 = ن!/(ن/2)! 2 : (الحجم الأقصى للنصف الثاني): الشرح أدناه:
لنأخذ N = 4 كمثال.:
// تبدو خريطة التجزئة
0 -> [0000] ................................ (حجم القائمة: 4C0 = 1)
1 -> [0001 0010 0100 1000] ................................ (حجم القائمة: 4C1 = 4)
2 -> [0011 0101 0110 1001 1010 1100] ................................ (حجم القائمة: 4C2 = 6)
3 -> [0111 1011 1101 1110] ................................ (حجم القائمة: 4C3 = 4)
4 -> [1111] ................................ (حجم القائمة: 4C4 = 1)
نلاحظ هنا أن كل قائمة لها حجم N اختر مفتاح والذي سيكون الحد الأقصى عند N اختر N/2
نظرًا لأننا نكرر كل 2 ن التباديل وإلحاق النصف الثاني من الخريطة. تحتوي الخريطة على الحد الأقصى لحجم القائمة عند الموضع N/2.
أسوأ حالة تحدث في الموضع N/2 حيث يتعين علينا اجتياز NCN/2 = N!/(N/2)! 2 التباديل.
التعقيد الزمني: O(2 ن * ن!/(ن/2)! 2 )
المساحة المساعدة: O(2 ن ) لأننا نقوم بتخزين جميع تبديلات السلسلة الثنائية بالحجم N