Мінімаксний алгоритм в теорії ігор | Набір 1 (введення)
Мінімакс — це свого роду алгоритм відстеження, який використовується в процесі прийняття рішень і теорії ігор, щоб знайти оптимальний хід для гравця, припускаючи, що ваш опонент також грає оптимально. Він широко використовується в покрокових іграх для двох гравців, таких як Tic-Tac-Toe, Backgammon, Mancala, Chess тощо.
У Minimax два гравці називаються максимайзером і мінімізатором. The максимайзер намагається отримати якомога вищий бал, поки мінімізатор намагається зробити навпаки й отримати найменший бал.
Кожен стан дошки має значення, пов’язане з ним. У даному стані, якщо максимайзер має перевагу, тоді рахунок на дошці матиме деяке позитивне значення. Якщо мінімізатор має перевагу в такому стані дошки, тоді воно матиме деяке від’ємне значення. Значення дошки розраховуються за допомогою деяких евристик, які є унікальними для кожного типу гри.
приклад:
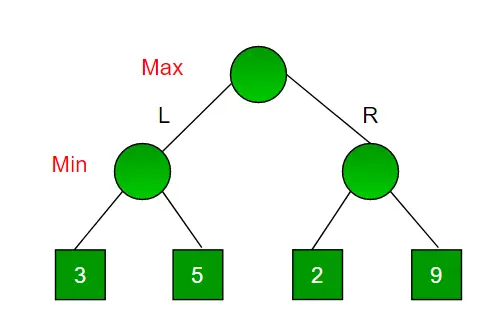
Розглянемо гру, яка має 4 кінцевих стани та шляхи досягнення кінцевого стану від кореня до 4 листків ідеального бінарного дерева, як показано нижче. Припустімо, що ви максимізуючий гравець і отримуєте перший шанс перейти, тобто ви на корені, а ваш опонент на наступному рівні. Який хід ви б зробили як максимізуючий гравець, враховуючи, що ваш суперник також грає оптимально?

Оскільки це алгоритм на основі відстеження, він пробує всі можливі рухи, потім повертається назад і приймає рішення.
- Максимізатор йде ЛІВОРУЧ: тепер черга мінімайзерів. Мінімізатор тепер має вибір між 3 і 5. Будучи мінімізатором, він точно вибере найменше з обох, тобто 3
- Максимізатор йде ВПРАВО: тепер черга мінімайзерів. Мінімізатор тепер має вибір між 2 і 9. Він вибере 2, оскільки це найменше серед двох значень.
Будучи максимізатором, ви вибрали б більше значення, яке дорівнює 3. Отже, оптимальним рухом для максимізатора є піти ВЛІВОРУЧ, а оптимальним значенням є 3.
Тепер дерево гри виглядає так:

Наведене вище дерево показує два можливі бали, коли максимайзер робить ліворуч і праворуч.
Примітка. Незважаючи на те, що в правому піддереві є значення 9, мінімізатор ніколи не вибере його. Треба завжди виходити з того, що суперник грає оптимально.
Нижче наведено реалізацію того самого.
C++
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(> int> depth,> int> nodeIndex,> bool> isMax,> > int> scores[],> int> h)> {> > // Terminating condition. i.e> > // leaf node is reached> > if> (depth == h)> > return> scores[nodeIndex];> > // If current move is maximizer,> > // find the maximum attainable> > // value> > if> (isMax)> > return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,> false> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,> false> , scores, h));> > // Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> > // attainable value> > else> > return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,> true> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,> true> , scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(> int> n)> {> > return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> > // The number of elements in scores must be> > // a power of 2.> > int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> > int> n => sizeof> (scores)/> sizeof> (scores[0]);> > int> h = log2(n);> > int> res = minimax(0, 0,> true> , scores, h);> > cout < <> 'The optimal value is : '> < < res < < endl;> > return> 0;> }> |
Java
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> > static> int> minimax(> int> depth,> int> nodeIndex,> boolean> isMax,> > int> scores[],> int> h)> {> > // Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> > if> (depth == h)> > return> scores[nodeIndex];> > // If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> > // value> > if> (isMax)> > return> Math.max(minimax(depth+> 1> , nodeIndex*> 2> ,> false> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+> 1> , nodeIndex*> 2> +> 1> ,> false> , scores, h));> > // Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> > // attainable value> > else> > return> Math.min(minimax(depth+> 1> , nodeIndex*> 2> ,> true> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+> 1> , nodeIndex*> 2> +> 1> ,> true> , scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> > static> int> log2(> int> n)> {> return> (n==> 1> )?> 0> :> 1> + log2(n/> 2> );> }> // Driver code> > public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> > // The number of elements in scores must be> > // a power of 2.> > int> scores[] = {> 3> ,> 5> ,> 2> ,> 9> ,> 12> ,> 5> ,> 23> ,> 23> };> > int> n = scores.length;> > int> h = log2(n);> > int> res = minimax(> 0> ,> 0> ,> true> , scores, h);> > System.out.println(> 'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > }> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
C#
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(> int> depth,> int> nodeIndex,> bool> isMax,> > int> []scores,> int> h)> {> > // Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> > if> (depth == h)> > return> scores[nodeIndex];> > // If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> > // value> > if> (isMax)> > return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,> false> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,> false> , scores, h));> > // Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> > // attainable value> > else> > return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,> true> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,> true> , scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(> int> n)> {> > return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> > // The number of elements in scores must be> > // a power of 2.> > int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> > int> n = scores.Length;> > int> h = log2(n);> > int> res = minimax(0, 0,> true> , scores, h);> > Console.WriteLine(> 'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
Python3
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> > maxTurn, scores,> > targetDepth):> > # base case : targetDepth reached> > if> (curDepth> => => targetDepth):> > return> scores[nodeIndex]> > > if> (maxTurn):> > return> max> (minimax(curDepth> +> 1> , nodeIndex> *> 2> ,> > False> , scores, targetDepth),> > minimax(curDepth> +> 1> , nodeIndex> *> 2> +> 1> ,> > False> , scores, targetDepth))> > > else> :> > return> min> (minimax(curDepth> +> 1> , nodeIndex> *> 2> ,> > True> , scores, targetDepth),> > minimax(curDepth> +> 1> , nodeIndex> *> 2> +> 1> ,> > True> , scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores> => [> 3> ,> 5> ,> 2> ,> 9> ,> 12> ,> 5> ,> 23> ,> 23> ]> treeDepth> => math.log(> len> (scores),> 2> )> print> (> 'The optimal value is : '> , end> => '')> print> (minimax(> 0> ,> 0> ,> True> , scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
Javascript
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> > function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> > scores, h)> {> > // Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> > if> (depth == h)> > return> scores[nodeIndex];> > > // If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> > // value> > if> (isMax)> > return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,> false> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,> false> , scores, h));> > > // Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> > // attainable value> > else> > return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,> true> , scores, h),> > minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,> true> , scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> > function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> > // The number of elements in scores must be> > // a power of 2.> > let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> > let n = scores.length;> > let h = log2(n);> > let res = minimax(0, 0,> true> , scores, h);> > document.write(> 'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
Вихід:
The optimal value is: 12
Часова складність: O(b^d) b — коефіцієнт розгалуження, а d — кількість глибини або шару графа чи дерева.
Космічна складність: O(bd), де b — коефіцієнт розгалуження на d — максимальна глибина дерева, подібного до DFS.
Ідея цієї статті полягає в тому, щоб представити Minimax на простому прикладі.
- У наведеному вище прикладі для гравця є лише два варіанти. Загалом, варіантів може бути більше. У цьому випадку нам потрібно повторити для всіх можливих ходів і знайти максимум/мінімум. Наприклад, в Tic-Tac-Toe перший гравець може зробити 9 можливих ходів.
- У наведеному вище прикладі бали (листя дерева гри) надано нам. Для типової гри нам потрібно отримати ці значення
Незабаром ми розглянемо Tic Tac Toe з алгоритмом Minimax.
Цю статтю надав Акшай Л. Арадх'я.