Програма Java для запису у файл
У цій статті ми побачимо різні способи запису у файл за допомогою мови програмування Java. Клас Java FileWriter у java використовується для запису символьно-орієнтованих даних у файл, оскільки цей клас є символьно-орієнтованим через те, що він використовується для обробки файлів у java.
Тут багато способи запису у файл на Java оскільки існує багато класів і методів, які можуть досягти такої мети:
- Використання writeString() метод
- Використання класу FileWriter
- Використання класу BufferedWriter
- Використання класу FileOutputStream
Спосіб 1: Використання методу writeString().
Цей метод підтримується Java версії 11. Цей метод може приймати чотири параметри. Це шлях до файлу, послідовність символів, кодування та параметри. Перші два параметри є обов’язковими для цього методу для запису у файл. Він записує символи як вміст файлу. Він повертає шлях до файлу та може створювати чотири типи винятків. Краще використовувати, коли вміст файлу короткий.
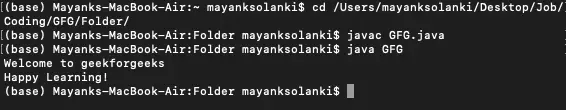
приклад: Це показує використання writeString() метод, який знаходиться в класі Files для запису даних у файл. Інший клас, Path, використовується для призначення назви файлу шляху, куди буде записаний вміст. Клас Files має іншу назву методу readString() щоб прочитати вміст будь-якого існуючого файлу, який використовується в коді, щоб перевірити, чи правильно записаний вміст у файлі.
Java
// Java Program to Write Into a File> // using writeString() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.IOException;> import> java.nio.file.Files;> import> java.nio.file.Path;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > throws> IOException> > {> > // Assigning the content of the file> > String text> > => 'Welcome to geekforgeeks
Happy Learning!'> ;> > // Defining the file name of the file> > Path fileName = Path.of(> > '/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'> );> > // Writing into the file> > Files.writeString(fileName, text);> > // Reading the content of the file> > String file_content = Files.readString(fileName);> > // Printing the content inside the file> > System.out.println(file_content);> > }> }> |
Вихід
Welcome to geekforgeeks Happy Learning!

Спосіб 2: Використання класу FileWriter
Якщо вміст файлу короткий, то краще використовувати клас FileWriter для запису у файл. Він також записує потік символів як вміст файлу, як метод writeString(). Конструктор цього класу визначає стандартне кодування символів і стандартний розмір буфера в байтах.
Наведений нижче приклад ілюструє використання класу FileWriter для запису вмісту у файл. Це вимагає створення об’єкта класу FileWriter з іменем файлу для запису у файл. Далі метод write() використовується для запису значення текстової змінної у файл. Якщо під час запису файлу станеться будь-яка помилка, буде створено виняток IOException, і повідомлення про помилку буде надруковано з блоку catch.
приклад:
Java
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileWriterClass> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Content to be assigned to a file> > // Custom input just for illustration purposes> > String text> > => 'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'> ;> > // Try block to check if exception occurs> > try> {> > // Create a FileWriter object> > // to write in the file> > FileWriter fWriter => new> FileWriter(> > '/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'> );> > // Writing into file> > // Note: The content taken above inside the> > // string> > fWriter.write(text);> > // Printing the contents of a file> > System.out.println(text);> > // Closing the file writing connection> > fWriter.close();> > // Display message for successful execution of> > // program on the console> > System.out.println(> > 'File is created successfully with the content.'> );> > }> > // Catch block to handle if exception occurs> > catch> (IOException e) {> > // Print the exception> > System.out.print(e.getMessage());> > }> > }> }> |
Вихід
File is created successfully with the content.

Спосіб 3: Використання класу BufferedWriter
Він використовується для запису тексту в потік виведення символів. Він має стандартний розмір буфера, але можна призначити великий розмір буфера. Це корисно для написання символів, рядків і масивів. Краще обернути цей клас будь-яким класом запису для запису даних у файл, якщо не потрібен швидкий вивід.
приклад:
Java
// Java Program to write into a File> // Using BufferedWriter Class> // Importing java input output libraries> import> java.io.BufferedWriter;> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Assigning the file content> > // Note: Custom contents taken as input to> > // illustrate> > String text> > => 'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'> ;> > // Try block to check for exceptions> > try> {> > // Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter> > BufferedWriter f_writer> > => new> BufferedWriter(> new> FileWriter(> > '/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'> ));> > // Step 2: Write text(content) to file> > f_writer.write(text);> > // Step 3: Printing the content inside the file> > // on the terminal/CMD> > System.out.print(text);> > // Step 4: Display message showcasing> > // successful execution of the program> > System.out.print(> > 'File is created successfully with the content.'> );> > // Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object> > f_writer.close();> > }> > // Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs> > catch> (IOException e) {> > // Print the exception on console> > // using getMessage() method> > System.out.print(e.getMessage());> > }> > }> }> |
Вихід
File is created successfully with the content.

У наступному прикладі показано використання класу BufferedWriter для запису у файл. Для запису вмісту у файл також потрібно створити об’єкт класу BufferedWriter, наприклад FileWriter. Але цей клас підтримує великий вміст для запису у файл за допомогою великого розміру буфера.
Спосіб 4: Використання класу FileOutputStream
Він використовується для запису необроблених потокових даних у файл. Класи FileWriter і BufferedWriter використовуються для запису лише тексту у файл, але двійкові дані можна записати за допомогою класу FileOutputStream.
У наступному прикладі показано запис даних у файл за допомогою класу FileOutputStream. Це також вимагає створення об’єкта класу з іменем файлу для запису даних у файл. Тут вміст рядка перетворюється на масив байтів, який записується у файл за допомогою написати() метод.
приклад:
Java
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileOutputStream Class> // Importing java input output classes> import> java.io.FileOutputStream;> import> java.io.IOException;> public> class> GFG {> > // Main driver method> > public> static> void> main(String[] args)> > {> > // Assign the file content> > String fileContent => 'Welcome to geeksforgeeks'> ;> > FileOutputStream outputStream => null> ;> > // Try block to check if exception occurs> > try> {> > // Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream> > outputStream => new> FileOutputStream(> 'file.txt'> );> > // Step 2: Store byte content from string> > byte> [] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();> > // Step 3: Write into the file> > outputStream.write(strToBytes);> > // Print the success message (Optional)> > System.out.print(> > 'File is created successfully with the content.'> );> > }> > // Catch block to handle the exception> > catch> (IOException e) {> > // Display the exception/s> > System.out.print(e.getMessage());> > }> > // finally keyword is used with in try catch block> > // and this code will always execute whether> > // exception occurred or not> > finally> {> > // Step 4: Close the object> > if> (outputStream !=> null> ) {> > // Note: Second try catch block ensures that> > // the file is closed even if an error> > // occurs> > try> {> > // Closing the file connections> > // if no exception has occurred> > outputStream.close();> > }> > catch> (IOException e) {> > // Display exceptions if occurred> > System.out.print(e.getMessage());> > }> > }> > }> > }> }> |
Вихід
File is created successfully with the content.